Abstract
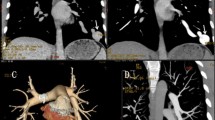
A pulmonary arteriovenous fistula (PAVF) is a rare vascular malformation commonly treated by embolization with coils or balloons to prevent the risk of several serious complications such as cerebral embolism and brain abscess. A 32-year-old female with two PAVFs and neurological ischemic manifestations has been successfully treated by transcatheter embolization of both fistulas using a new device (Amplatzer Vascular Plug). This self-expanding cylindrical nitinol mesh cage with high radial strength allows a chance of relocation until properly positioned. It is preferred to coils or balloons because a large caliber of feeding artery implied high risk of uncontrollable distal embolization. There appear to be no reports in the literature concerning use of this device, which could represent a useful innovative tool in embolotherapies, especially in large vascular areas.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pick A, Deschamps C, Stanson AW (1999) Pulmonary arteriovenous fistula: presentation, diagnosis, and treatment. World J Surg 23:1118–1122
White RI, Pollack JS, Wirth JA (1996) Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations: diagnosis and transcatheter embolotherapy. J Vase Interv Radiol 7:787–804
Swanson KL, Prakash UB, Stanson AW (1999) Pulmonary arteriovenous fistulas: Mayo Clinic experience, 1982–l997. Mayo Clin Proc 74:671–680
White RI Jr, Lynch-Nyhan A, Terry P, et al. (1988) Pulmonary arteriovenous malformations: techniques and long-term outcome of embolotherapy. Radiology 169:663–669
Lee DW, White RI Jr, Egglin TK, et al. (1997) Embolotherapy of large pulmonary arteriovenous malformations: long-term results. Ann Thorac Surg 64:930–993 discussion 939–940
Sagara K, Miyazono N, Inoue H, et al. (1998) Recanalization after coil embolotherapy of pulmonary arteriovenous malformations: study of long-term outcome and mechanism for recanalization. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1701:727–730
Apostolopoulou SC, Kelekis NL, Papagiannis J, et al. (2001) Transcatheter occlusion of a large pulmonary arteriovenous malformation with use of a Cardioseal device. J Vase Interv Radiol 12:767–769
Cil BE, Erdogan C, Akmangit I, et al. (2004) Use of the TriSpan coil to facilitate the transcatheter occlusion of pulmonary arteriovenous malformation. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 27:655–658
Lacombe P, Lagrange C, El Hajjam M, et al. (2005) Reperfusion of complex pulmonary arteriovenous malformations after embolization: report of three cases. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol., 28:30–35
Takahashi K, Tanimura K, Honda M, et al. (1999) Venous sac embolization of pulmonary arteriovenous malformation: preliminary experience using interlocking detachable coils. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 22:210–213
Saluja S, Sitko I, Lee DW, et al. (1999) Embolotherapy of pulmonary arteriovenous malformations with detachable balloons: long-term durability and efficacy. J Vase Interv Radiol 10:883–889
Wang JK, Tsai SK, Wu MH, et al. (2004) Short- and intermediate-term results of transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect with the Amplatzer Septal Occluder. Am Heart J 148:511–517
Santoro G, Bigazzi MC, Palladino MT, et al. (2004) Comparison of percutaneous closure of large patent ductus arteriosus bv multiple coils versus the Amplatzer duct occluder device. Am J Cardiol 94:252–255
De Giovanni JV (2001) The use of Amplatzer devices to occlude vascular fistulae. J Interventi Cardiol 14:45–48
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rossi, M., Rebonato, A., Greco, L. et al. A New Device for Vascular Embolization: Report on Case of Two Pulmonary Arteriovenous Fistulas Embolization Using the Amplatzer Vascular Plug. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 29, 902–906 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-005-0160-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-005-0160-7