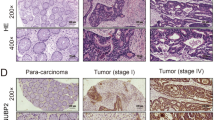
Abstract
Background
The functional loss of the tumor suppressor protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) occurs in a wide variety of human cancers including colorectal cancer (CRC), and SET overexpression has been reported as a key contributing mechanism to inhibit PP2A. Although SET binding protein 1 (SETBP1) overexpression and gain of function mutations have been described in several hematological malignancies as common events that increase the expression levels of the PP2A inhibitor SET, thereby leading to PP2A inactivation, the potential existence of SETBP1 alterations in CRC still remains unexplored.
Methods
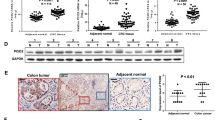
We studied the expression profile of SETBP1 by Western blot in a set of CRC cell lines and patient samples. Moreover, we performed co-immunoprecipitation assays to analyze the formation of the previously reported SETBP1–SET–PP2A inhibitory complex. Furthermore, we evaluated the mutational status of SETBP1 by pyrosequencing assays in a cohort of 55 CRC patients with metastatic disease after the immunohistochemical characterization of SET and p-PP2A expression in this cohort.
Results
We found high SETBP1 expression in several CRC lines but only in two of the patients analyzed. In addition, we demonstrated the formation of the SETBP1–SET–PP2A heterotrimeric complex in CRC cells. However, we failed to detect SETBP1 mutations in any of the CRC patient samples included in the study.
Conclusions
Our results suggest that SETBP1 expression is mainly similar o lower in colorectal cancer tissue compared to normal colonic mucosa. However, its overexpression is a low prevalent alteration which could contribute to inhibit PP2A in CRC through the formation of a SETBP1–SET–PP2A complex in some CRC patients. Moreover, SETBP1 mutations are, if exist, rare events in CRC patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brenner H, Kloor M, Pox CP (2014) Colorectal cancer. Lancet 383:1490–1502
Linnekamp JF, Wang X, Medema JP et al (2015) Colorectal cancer heterogeneity and targeted therapy: a case for molecular disease subtypes. Cancer Res 75:245–249
Cristóbal I, Blanco FJ, García-Orti L et al (2010) SETBP1 overexpression is a novel leukemogenic mechanism that predicts adverse outcome in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 115:615–625
Ruvolo PP (2016) The broken “Off” switch in cancer signaling: PP2A as a regulator of tumorigenesis, drug resistance, and immune surveillance. BBA Clin 6:87–99
Rincón R, Cristóbal I, Zazo S et al (2015) PP2A inhibition determines poor outcome and doxorubicin resistance in early breast cancer and its activation shows promising therapeutic effects. Oncotarget 6:4299–4314
Janssens V, Goris J (2001) Protein phosphatase 2A: a highly regulated family of serine/threonine phosphatases implicated in cell growth and signalling. Biochem J 353:417–439
Zolnierowicz S (2000) Type 2A protein phosphatase, the complex regulator of numerous signalling pathways. Biochem Pharmacol 60:1225–1235
Xie F, Bao X, Yu J et al (2015) Disruption and inactivation of the PP2A complex promotes the proliferation and angiogenesis of hemangioma endothelial cells through activating AKT and ERK. Oncotarget 6:25660–25676
Grech G, Baldacchino S, Saliba C et al (2016) Deregulation of the protein phosphatase 2A, PP2A in cancer: complexity and therapeutics options. Tumour Biol 37:11691–11700
Seo SB, McNamara P, Heo S et al (2001) Regulation of histone acetylation and transcription by INHAT, a human cellular complex containing the SET oncoprotein. Cell 104:119–130
ten Klooster JP, Iv Leeuwen, Scheres N et al (2009) Rac-1 induced cell migration requires membrane recruitment of the nuclear oncogene SET. EMBO J 26:336–345
Eichhorn PJ, Creyghton MP, Bernards R (2009) Protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunits and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1795:1–15
Piazza R, Valletta S, Winkelmann N et al (2013) Recurrent SETBP1 mutations in atypical chronic myeloid leukemia. Nat Genet 45:18–24
Makishima H, Yoshida K, Nguyen N et al (2013) Somatic SETBP1 mutations in myeloid malignancies. Nat Genet 45:942–946
Patnaik MM, Itzykson R, Lasho TL et al (2014) ASXL1 and SETBP1 mutations and their prognostic contribution in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: a two-center study of 466 patients. Leukemia 28:2206–2212
Kanagal-Shamanna R, Luthra R, Yin CC et al (2016) Myeloid neoplasms with isolated isochromosome 17q demonstrate a high frequency of mutations in SETBP1, SRSF2, ASXL1 and NRAS. Oncotarget 7:14251–14258
Bresolin S, De Filippi P, Vendemini F et al (2016) Mutations of SETBP1 and JAK3 in juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia: a report from the Italian AIEOP study group. Oncotarget 7:28914–28919
Cristóbal I, Manso R, Rincón R et al (2014) PP2A inhibition is a common event in colorectal cancer and its restoration using FTY720 shows promising therapeutic potential. Mol Cancer Ther 13:938–947
Cristóbal I, Rincón R, Manso R et al (2015) Deregulation of the PP2A inhibitor SET shows promising therapeutic implications and determines poor clinical outcome in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 21:347–356
Cristóbal I, Caramés C, Rincón R et al (2016) Downregulation of microRNA-199b predicts unfavorable prognosis and emerges as a novel therapeutic target which contributes to PP2A inhibition in metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 8:40169–40180
Nacional Center for Biotechnology Information. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/. Accessed 17 Nov 2016
Cristóbal I, Manso R, Rincón R et al (2014) Phosphorylated protein phosphatase 2A determines poor outcome in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 111:756–762
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B et al (2017) GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res 45(W1):W98–W102. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx247
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by PI15/00934 and PI16/01468 grants from “Instituto de Salud Carlos III FEDER”, Spain. B.T. is supported by “Fundación Conchita Rábago de Jiménez Díaz”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torrejón, B., Cristóbal, I., Caramés, C. et al. Analysis of Potential Alterations Affecting SETBP1 as a Novel Contributing Mechanism to Inhibit PP2A in Colorectal Cancer Patients. World J Surg 42, 3771–3778 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-018-4684-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-018-4684-9