Abstract
Background
The ratio of C-reactive protein to albumin (CRP/Alb) is a biochemical marker of systemic inflammatory response and has been associated with poor survival in cancer. This study retrospectively investigated the relationship between the CRP/Alb ratio and prognosis in gastric cancer patients.
Methods
This study enrolled 453 patients with a histopathological diagnosis of gastric adenocarcinoma who underwent curative surgery.
Results
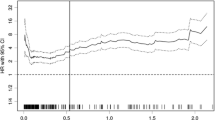
A statistically significant weak correlation was observed between CRP/Alb ratio and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (NLR) (r = 0.19; P < 0.0001). There were statistically significant correlations between high CRP/Alb ratio and age (P = 0.0004), tumor size (P = 0.02), depth of invasion (P = 0.012), and lymph node metastasis (P = 0.022). A high NLR was significantly correlated with age (P = 0.0027), tumor size (P = 0.0006), depth of invasion (P < 0.0001), lymphatic involvement (P = 0.0031), venous involvement (P = 0.0022), and stage of disease (P = 0.0024). Based on results by receiver operating characteristic analysis, patients were divided as follows: CRP/Alb ratio ≥ 0.0232 (CARHigh), CRP/Alb ratio < 0.0232 (CARLow), NLR ≥ 2.43 (NLRHigh), and NLR < 2.43 (NLRLow). Five-year survival rates of patients with both CARHigh and NLRHigh, either CARHigh or NLRHigh, and both CARLow and NLRLow were 59.6, 75.8, and 87.5%, respectively, with statistically significant differences (P < 0.0001). Multivariate analysis revealed that the combination of CRP/Alb ratio and NLR was an independent prognostic indicator.
Conclusions
The combination of CRP/Alb ratio and NLR may be useful in predicting prognosis in gastric cancer patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM et al (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61:69–90
Park HJ, Ahn JY, Jung HY et al (2014) Clinical characteristics and outcomes for gastric cancer patients aged 18–30 years. Gastric Cancer 17:649–660
Nam DH, Lee YK, Park JC et al (2013) Prognostic value of early postoperative tumor marker response in gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 20:3905–3911
Coussens LM, Werb Z (2002) Inflammation and cancer. Nature 420:860–867
Kinoshita A, Onoda H, Imai N et al (2012) Comparison of the prognostic value of inflammation-based prognostic scores in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer 107:988–993
Inoue D, Ozaka M, Matsuyama M et al (2015) Prognostic value of neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and level of C-reactive protein in a large cohort of pancreatic cancer patients: a retrospective study in a single institute in Japan. Jpn J Clin Oncol 45:61–66
Fairclough E, Cairns E, Hamilton J et al (2009) Evaluation of a modified early warning system for acute medical admissions and comparison with C-reactive protein/albumin ratio as a predictor of patient outcome. Clin Med (Lond, Engl) 9:30–33
Ranzani OT, Zampieri FG, Forte DN et al (2013) C-reactive protein/albumin ratio predicts 90-day mortality of septic patients. PLoS ONE 8:e59321
Kinoshita A, Onoda H, Imai N et al (2015) The C-reactive protein/albumin ratio, a novel inflammation-based prognostic score, predicts outcomes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 22:803–810
Xu XL, Yu HQ, Hu W et al (2015) A novel inflammation-based prognostic score, the C-reactive protein/albumin ratio predicts the prognosis of patients with operable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 10:e0138657
Choi Y, Kim JW, Nam KH et al (2017) Systemic inflammation is associated with the density of immune cells in the tumor microenvironment of gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 20:602–611
Japanese Gastric Cancer Association (2011) Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma: 3rd English edition. Gastric Cancer 14:101–112
Bozzetti F, Bonfanti G, Morabito A et al (1986) A multifactorial approach for the prognosis of patients with carcinoma of the stomach after curative resection. Surg Gynecol Obstet 162:229–234
Maruyama K (1987) The most important prognostic factors for gastric cancer patients. Scand J Gastroenterol 22:63–68
Morris-Stiff G, Gomez D, Prasad KR (2008) C-reactive protein in liver cancer surgery. Eur J Surg Oncol 34:727–729
Yu Q, Yu XF, Zhang SD et al (2013) Prognostic role of C-reactive protein in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev APJCP 14:5735–5740
Detsky AS, McLaughlin JR, Baker JP et al (1987) What is subjective global assessment of nutritional status? JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 11:8–13
Vellas B, Villars H, Abellan G et al (2006) Overview of the MNA—its history and challenges. J Nutr Health Aging 10:456–463 (Discussion 463–455)
Kondrup J, Rasmussen HH, Hamberg O et al (2003) Nutritional risk screening (NRS 2002): a new method based on an analysis of controlled clinical trials. Clin Nutr 22:321–336
Onodera T, Goseki N, Kosaki G (1984) Prognostic nutritional index in gastrointestinal surgery of malnourished cancer patients. Nihon Geka Gakkai Zasshi 85:1001–1005
Nozoe T, Iguchi T, Egashira A et al (2011) Significance of modified Glasgow prognostic score as a useful indicator for prognosis of patients with gastric carcinoma. Am J Surg 201:186–191
Imaoka H, Mizuno N, Hara K et al (2016) Evaluation of modified glasgow prognostic score for pancreatic cancer: a retrospective cohort study. Pancreas 45:211–217
Nozoe T, Matono R, Ijichi H et al (2014) Glasgow prognostic score (GPS) can be a useful indicator to determine prognosis of patients with colorectal carcinoma. Int Surg 99:512–517
Hirashima K, Watanabe M, Shigaki H et al (2014) Prognostic significance of the modified Glasgow prognostic score in elderly patients with gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol 49:1040–1046
Liu Z, Jin K, Guo M et al (2017) Prognostic value of the CRP/Alb ratio, a novel inflammation-based score in pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 24:561–568
Kim JH, Han DS, Bang HY et al (2015) Preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is a prognostic factor for overall survival in patients with gastric cancer. Ann Surg Treat Res 89:81–86
Stotz M, Gerger A, Eisner F et al (2013) Increased neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio is a poor prognostic factor in patients with primary operable and inoperable pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer 109:416–421
Kumar R, Geuna E, Michalarea V et al (2015) The neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and its utilisation for the management of cancer patients in early clinical trials. Br J Cancer 112:1157–1165
Haruki K, Shiba H, Shirai Y et al (2016) The C-reactive protein to albumin ratio predicts long-term outcomes in patients with pancreatic cancer after pancreatic resection. World J Surg 40:2254–2260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-016-3491-4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saito, H., Kono, Y., Murakami, Y. et al. Prognostic Significance of the Preoperative Ratio of C-Reactive Protein to Albumin and Neutrophil–Lymphocyte Ratio in Gastric Cancer Patients. World J Surg 42, 1819–1825 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-017-4400-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-017-4400-1