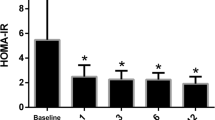
Abstract
Background
Bariatric surgery has gained reputation for its metabolic effect and is increasingly being performed to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, there is still a gray area regarding the choice of surgical procedure according to patient characteristics due to inadequate evidences, so far. We aim to compare the efficacy of two most commonly performed bariatric/metabolic surgeries, sleeve gastrectomy (SG) and gastric bypass (GB) with regard to remission of T2DM after surgery.
Methods
Outcomes of 579 (349 female and 230 male) patients who had undergone SG (109) or GB (470) for the treatment of T2DM with 1-year follow-up were assessed. The remission of T2DM after SG or GB surgery was evaluated in matched groups using the ABCD scoring system. The ABCD score is composed of the age, BMI, C-peptide levels and duration of T2DM (years).
Results
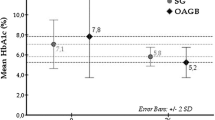
The weight loss of the SG patient at 1 year after surgery was similar to the GB patients [26.3 (1.1) vs. 32.6 (1.2) %; p = 0.258]. The mean BMI decreased from 35.7 (7.2) to 28.3 (3.7) Kg/m2 in SG patients at 1 year after surgery and decreased from 36.9 (7.2) to 26.7 (4.5) Kg/m2 in the GB patients. The mean HbA1c decreased from 8.8 to 6.1 % of the SG group and from 8.6 to 5.9 % of the GB group. Sixty-one (56.0 %) patients of the SG group and 300 (63.8 %) of the GB group achieved complete remission of T2DM (HbA1c < 6.0 %) at 1 year after surgery without statistical difference. However, GB exhibited significantly better glycemic control than the SG surgery in groups stratified by different ABCD score. At 5 year after surgery, GB had a better remission of T2DM than SG (53.1 vs. 35.3 %; p = 0.055).
Conclusions
In conclusion, although both SG and GB are effective metabolic surgery, GB carries a higher power on T2DM remission than SG. ABCD score is useful in T2DM patient classification and selection for different procedures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Whiting DR, Guariguata L, Weil C, Shaw J (2011) IDF diabetes atlas: global estimated of the prevalence of diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 94:311–312
Zimmer P, Alberti KG, Shaw J (2013) Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. JAMA 414:782–787
American Diabetes Association (2008) Economic costs of diabetes in the U.S. in 2007. Diabetes Care 13:596–615
Gerstein HC, Miller ME, Byington RP et al (2008) Action to control cardiovascular risk in diabetes study group. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 358:2545–2559
Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E et al (2004) Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 292:1724–1737
Sjostrom L, Narbro K, Sjostrom D et al (2007) Effect of bariatric surgery on mortality in Swedish obese subjects. NEJM 357:741–752
Lee WJ, Chong K, Ser KH et al (2011) Gastric bypass vs sleeve gastrectomy for type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Surg 146:143–148
Cohen RV, Pinheiro JC, Schiavon C et al (2012) Effective of gastric bypass surgery in patients with type 2 diabetes and only mild obesity. Diabetes Care 35:1420–1428
Schauer PR, Kashyap SR, Wolski K et al (2012) Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy in obese patients with diabetes. N Engl J Med 366:1567–1576
Ikramuddin S, Korner J, Lee WJ et al (2013) Roux-en-Y gastric bypass vs intensive medical management for the control of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia: The diabetes surgery study randomized clinical trial. JAMA 309:2240–2249
Liang Z, Wu Q, Chen B, Yu P, Zhao H, Quyang X (2013) Effect of laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for type 2 diabetes mellitus with hypertension: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 101:50–56
Schauer PR, Bhatt DL, Kirwan JP et al (2014) Bariatric surgery versus intensive medical therapy for diabetes. N Engl J Med 370:2002–2013
Buchwald H, Oien DM (2013) Metabolic/bariatric surgery worldwide 2011. Obes Surg 23:427–436
Peterli R, Borbely Y, Ker B et al (2013) Early results of the Swiss multicentre bypass or sleeve study (SM-BOSS): a prospective randomized trial comparing laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Ann Surg 258:690–695
Alexandrou A, Arment E, Kouskouni E, Tsoka E, Diamantis T, Lambrinoudaki I (2014) Cross-sectional long-term micronutrient deficiencies after sleeve gastrectomy versus Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: a pilot study. Surg Obes Relat Dis 10:262–268
Vix M, Liu KH, Diana M, D’Urso A, Mutter D, Marescaux J (2014) Impact of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass versus sleeve gastrectomy on vitamin D metabolism: short-term results from a prospective randomized clinical trial. Surg Endoscoc 28:821–826
Angrisani L, Santonicola A, Iovino P et al (2015) Bariatric surgery worldwide 2013. Obes Surg 25:1822–1832
Transtulli S, Desiderio J, Guarino S et al (2013) Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy compared with other bariatric surgical procedures: a systematic review of randomized trials. Surg Obes Relat Dis 9:816–829
Buse JB, Laughlin S, Caprio S et al (2009) How do we define cure of diabetes? Diabetes Care 32:2133–2135
Lee WJ, Yu PJ, Wang W et al (2005) Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y versus mini-gastric bypass for the treatment of morbid obesity: a prospective randomized controlled clinical trial. Ann Surg 242:20–28
Ser KH, Lee WJ, Lee YC et al (2010) Experience in laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for morbid obese Taiwanese: staple-line reinforcement is important for preventing leakage. Surg Endosc 16:2253–2259
Lee WJ, Hur KY, Lakadawala M, Kasama K, Wong SK, Chen SC et al (2013) Predicting success of metabolic surgery: age, body mass index, C-peptide, and duration score. Surg Obes Relat Dis 9:379–384
Lee WJ, Lee KT, Kasama K et al (2015) The effect and predictive score of gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy on type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with BMI < 30 Kg/m2. Obes Surg 25:1772–1778
Lakadawala M, Shaikh S, Bandukwala S et al (2013) Roux-en-Y gastric bypass stands the test of time: 5-year results in low body mass index (30-35) Indian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Surg Obes Relat Dis 9:370–378
Brethauer SA, Amino A, Ramero-Talamas H et al (2013) Can diabetes be surgically cured? Long-term metabolic effects of bariatric surgery in obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann Surg 258:628–637
Li J, Lai D, Wu D (2016) Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass versus laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy to treat morbid obesity-related comorbidities: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Surg 26:429–442
Yousseif A, Emmanuel J, Karra E, Millet Q, Elkalaawy M, Jenkinson AD et al (2014) Differential effects of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and laparoscopic gastric bypass on appetite, circulating acyl-ghrelin, peptide YY3-36 and active GLP-1 levels in non-diabetic humans. Obes Surg 24(2):241–252
Thaler JP, Cummings DE (2009) Minireview: hormonal and metabolic mechanisms of diabetes remission after gastrointestinal surgery. Endocrinology 150:2518–2525
Jullg M, Yip S, Xu A et al (2014) Lower Fetulin-A retinol binding protein 4 and several metabolites after gastric bypass compared to sleeve gastrectomy in patients with type 2 diabetes. PLoS One 9(5):e96489
Couupaye M, Riviere P, Breuil MC et al (2014) Comparison of nutritional status during the first year after sleeve gastrectomy an Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Obes Surg 24:276–283
Fang YL, Almulaifi AM, Lee WJ (2015) Letter to “predictive factors of type 2 diabetes mellitus remission following bariatric surgery: a meta-analysis”. Obes Surg 25:2424–2425
Lee WJ, Chong K, Chen SC et al (2016) Pre-operative prediction of type 2 diabetes remission after gastric bypass surgery: a comparison of DiaRem scores and ABCD scores. Obes Surg. doi:10.1007/s11695-016-2120-5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, WJ., Chong, K., Aung, L. et al. Metabolic Surgery for Diabetes Treatment: Sleeve Gastrectomy or Gastric Bypass?. World J Surg 41, 216–223 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-016-3690-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-016-3690-z