Abstract
Background
Brain-specific metastasis occurs frequently in lung cancer, and the mechanism is still unclear. The present study was designed to investigate the correlation between CXCR4 expression and brain-specific metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer.
Methods
The brain metastatic tumors and lung cancer tissues from 32 patients with solitary brain metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer (M1 group), who underwent combined surgical treatment from January 1998 to June 2008, and 32 paired patients without distant metastasis (M0 group) and 30 patients with primary brain tumor, were examined by immunohistochemistry to detect the expression of CXCR4 protein. The difference of CXCR4 expression was compared by the McNemar χ2 test or Fisher’s exact test. Estimation of survival was calculated with the Kaplan–Meier method, and the statistical differences were analyzed with the log-rank test.
Results
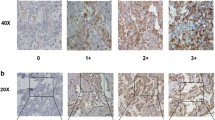
Overexpression of CXCR4 protein was observed in 29 (90.6%) M1 non-small cell lung cancers and in all (100%) brain metastatic tumors, which was significantly higher than that in the paired M0 non-small cell lung cancer and the primary brain tumors, respectively (p = 0.000). The 3- and 5-year cumulative survival rates of patients with solitary brain metastasis of lung cancer were 21.9 and 12.5%, significantly lower than the corresponding survival rates of M0 group patients (p = 0.005).
Conclusions
CXCR4 protein was highly overexpressed in M1 non-small cell lung cancer and brain metastatic tumors, which indicated that high-level CXCR4 expression correlates with brain-specific metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Muller A, Homey B, Soto H et al (2001) Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis. Nature 410:50–56
Chen Y, Stamatoyannopoulos G, Song CZ (2003) Down-regulation of CXCR4 by inducible small interfering RNA inhibits breast cancer cell invasion in vitro. Cancer Res 63:4801–4804
Kim SY, Lee CH, Midura BV et al (2008) Inhibition of the CXCR4/CXCL12 chemokine pathway reduces the development of murine pulmonary metastases. Clin Exp Metastasis 25:201–211
Spano JP, Andre F, Morat L et al (2004) Chemokine receptor CXCR4 and early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: pattern of expression and correlation with outcome. Ann Oncol 15:613–617
Kucia M, Jankowski K, Reca R et al (2004) CXCR4-SDF-1 signalling, locomotion, chemotaxis and adhesion. J Mol Histol 35:233–245
Li M, Ransohoff RM (2008) Multiple roles of chemokine CXCL12 in the central nervous system: a migration from immunology to neurobiology. Prog Neurobiol 84:116–131
Rossi D, Zlotnik A (2000) The biology of chemokines and their receptors. Annu Rev Immunol 18:217–242
Zlotnik A (2006) Involvement of chemokine receptors in organ-specific metastasis. Contrib Microbiol 13:191–199
Zlotnik A (2008) New insights on the role of CXCR4 in cancer metastasis. J Pathol 215:211–213
Banisadr G, Skrzydelski D, Kitabgi P et al (2003) Highly regionalized distribution of stromal cell-derived factor-1/CXCL12 in adult rat brain: constitutive expression in cholinergic, dopaminergic and vasopressinergic neurons. Eur J Neurosci 18:1593–1606
Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Walsh JW et al (1990) A randomized trial of surgery in the treatment of single metastases to the brain. N Engl J Med 322:494–500
Phillips RJ, Burdick MD, Lutz M et al (2003) The stromal derived factor-1/CXCL12-CXC chemokine receptor 4 biological axis in non-small cell lung cancer metastases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 167:1676–1686
Salmaggi A, Maderna E, Calatozzolo C et al (2009) CXCL12, CXCR4 and CXCR7 expression in brain metastases. Cancer Biol Ther 8:1608–1614
Gavrilovic IT, Posner JB (2005) Brain metastases: epidemiology and pathophysiology. J Neurooncol 75:5–14
Lee BC, Lee TH, Avraham S et al (2004) Involvement of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 and its ligand stromal cell-derived factor 1alpha in breast cancer cell migration through human brain microvascular endothelial cells. Mol Cancer Res 2:327–338
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G., Wang, Z., Liu, Xy. et al. High-Level CXCR4 Expression Correlates with Brain-Specific Metastasis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. World J Surg 35, 56–61 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-010-0784-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-010-0784-x