Abstract
Background
The implementation of intraoperative navigation in liver surgery is handicapped by intraoperative organ shift, tissue deformation, the absence of external landmarks, and anatomical differences in the vascular tree. To investigate the impact of surgical manipulation on the liver surface and intrahepatic structures, we conducted a prospective clinical trial.
Methods
Eleven consecutive patients [4 female and 7 male, median age = 67 years (range = 54–80)] with malignant liver disease [colorectal metastasis (n = 9) and hepatocellular cancer (n = 2)] underwent hepatic resection. Pre- and intraoperatively, all patients were studied by CT-based 3D imaging and assessed for the potential value of computer-assisted planning. The degree of liver deformation was demonstrated by comparing pre- and intraoperative imaging.
Results
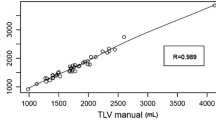
Intraoperative CT imaging was successful in all patients. We found significant deformation of the liver. The deformation of the segmental structures is reflected by the observed variation of the displacements. There is no rigid alignment of the pre- and intraoperative organ positions due to overall deflection of the liver. Locally, a rigid alignment of the anatomical structure can be achieved with less than 0.5 cm discrepancy relative to a segmental unit of the liver. Changes in total liver volume range from −13 to +24%, with an average absolute difference of 7%.
Conclusions
These findings are fundamental for further development and optimization of intraoperative navigation in liver surgery. In particular, these data will play an important role in developing automation of intraoperative continuous registration. This automation compensates for liver shift during surgery and permits real-time 3D visualization of navigation imaging.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auer LM, Auer DP (1998) Virtual endoscopy for planning and simulation of minimally invasive neurosurgery. Neurosurgery 43:529–537
Kockro RA, Serra L, Tseng-Tsai Y et al (2000) Planning and simulation of neurosurgery in a virtual reality environment. Neurosurgery 46:118–135
Chao EY, Barrance P, Genda E et al (1997) Virtual reality (VR) techniques in orthopaedic research and practice. Stud Health Technol Inform 39:107–114
Sutherland CJ (1986) Practical application of computer-generated three-dimensional reconstructions in orthopedic surgery. Orthop Clin North Am 17:651–656
Fischer L, Cardenas C, Thorn M et al (2002) Limits of Couinaud’s liver segment classification: a quantitative computer-based three-dimensional analysis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 26:962–967
Lamade W, Glombitza G, Fischer L et al (2000) The impact of 3-dimensional reconstructions on operation planning in liver surgery. Arch Surg 135:1256–1261
Marescaux J, Clement JM, Tassetti V et al (1998) Virtual reality applied to hepatic surgery simulation: the next revolution. Ann Surg 228:627–634
Oldhafer KJ, Hogemann D, Stamm G (1999) 3-dimensional (3-D) visualization of the liver for planning extensive liver resections. Chirurg 70:233–238
Heizmann O, Loehe F, Volk A (2008) Ischemic preconditioning improves postoperative outcome after liver resections: a randomized controlled study. Eur J Med Res 13:79–86
Rau HG, Schauer R, Helmberger T et al (2000) Impact of virtual reality imaging on hepatic liver tumor resection: calculation of risk. Langenbecks Arch Surg 385:162–170
Schmidbauer S, Hallfeldt KK, Sitzmann G (2002) Experience with ultrasound scissors and blades (UltraCision) in open and laparoscopic liver resection. Ann Surg 235:27–30
Vauthey JN, Chaoui A, Do KA et al (2000) Standardized measurement of the future liver remnant prior to extended liver resection: methodology and clinical associations. Surgery 127:512–519
Yigitler C, Farges O, Kianmanesh R et al (2003) The small remnant liver after major liver resection: how common and how relevant? Liver Transpl 9:S18–S25
Bismuth H (1982) Surgical anatomy and anatomical surgery of the liver. World J Surg 6:3–9
Couinaud C (1954) Lobes et Segments Hepatiques - Notes Sur Larchitecture Anatomique et Chirurgicale du Foie. Presse Med 62:709–712
Strasberg SM (2005) Nomenclature of hepatic anatomy and resections: a review of the Brisbane 2000 system. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 12:351–355
Lang H, Junge A, Sitter H et al (1995) Liver segmentectomy as anatomically precise resections. An experimental study in sheep. Eur J Surg 161:677–682
Wigmore SJ, Redhead DN, Yan XJ et al (2001) Virtual hepatic resection using three-dimensional reconstruction of helical computed tomography angioportograms. Ann Surg 233:221–226
Endo I, Shimada H, Sugita M et al (2007) Role of three-dimensional imaging in operative planning for hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Surgery 142:666–675
Lang H, Radtke A, Hindennach M et al (2005) Impact of virtual tumor resection and computer-assisted risk analysis on operation planning and intraoperative strategy in major hepatic resection. Arch Surg 140:629–638
Saito S, Yamanaka J, Miura K et al (2005) A novel 3D hepatectomy simulation based on liver circulation: application to liver resection and transplantation. Hepatology 41:1297–1304
Cash DM, Miga MI, Glasgow SC et al (2007) Concepts and preliminary data toward the realization of image-guided liver surgery. J Gastrointest Surg 11:844–859
Hayashibe M, Suzuki N, Kobayashi S et al (2005) Development of a 3D visualization system for surgical field deformation with geometric pattern projection. Stud Health Technol Inform 111:172–177
Jacob AL, Regazzoni P, Steinbrich W et al (2000) The multifunctional therapy room of the future: image guidance, interdisciplinarity, integration and impact on patient pathways. Eur Radiol 10:1763–1769
Bourquain H, Schenk A, Link F et al (2002) HepaVision 2: a software assistant for preoperative planning in living-related liver transplantation and oncologic liver surgery. In: Lemke HU, Vannier MW, Inamura K, Farman AG, Doi K, Reiber JHC (eds) CARS 2002: Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery: Proceedings of the 16th International Congress and Exhibition, Paris, June 26-29, 2002. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 341-346
Preim B, Bourquain H, Selle D et al (2002) Resection proposals for oncologic liver surgery based on vascular territories. In: Lemke HU, Vannier MW, Inamura K, Farman AG, Doi K, Reiber JHC (eds), CARS 2002: Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery: Proceedings of the 16th international congress and exhibition, Paris, June 26-29, 2002, Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 353–358
Schenk A, Prause G, Peitgen HO (2000) Efficient semiautomatic segmentation of 3D objects. In: Delp SL, DiGioia AM, Jaramaz B (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention: MICCAI 2000, Proceedings of the third international conference, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, October 11–14, 2000. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 1935, pp 186–195
Selle D, Preim B, Schenk A et al (2002) Analysis of vasculature for liver surgical planning. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 21:1344–1357
Van Ooijen PMA, Wolf R, Schenk A et al (2003) Recent developments in organ-selective reconstruction and analysis of multiphase liver CT. Imaging Decis 7:37–43
Herline AJ, Herring JL, Stefansic JD et al (2000) Surface registration for use in interactive, image-guided liver surgery. Comput Aided Surg 5:11–17
Voirin D, Payan Y, Amavizca M et al (2002) Computer-aided hepatic tumour ablation: requirements and preliminary results. C R Biol 325:309–319
Aylward SR, Cleary KR, Hawkes DJ (2005) Intraoperative image processing for surgical guidance. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 24:1401–1404
Porter BC, Rubens DJ, Strang JG et al (2001) Three-dimensional registration and fusion of ultrasound and MRI using major vessels as fiducial markers. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 20:354–359
Hassenpflug P, Schobinger M, Vetter M et al (2008) Generation of attributed relational vessel graphs from threedimensional freehand ultrasound for intraoperative registration in image-guided liver surgery. In: Galloway RL (ed) Medical Imaging 2003-Visualization, Image-Guided Procedures, and Display. Proceedings of SPIE 5029, pp 222–230
Carrillo A, Duerk JL, Lewin JS et al (2000) Semiautomatic 3-D image registration as applied to interventional MRI liver cancer treatment. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 19:175–185
Penney GP, Blackall JM, Hamady MS et al (2004) Registration of freehand 3D ultrasound and magnetic resonance liver images. Med Image Anal 8:81–91
Wilson DL, Carrillo A, Zheng L et al (1998) Evaluation of 3D image registration as applied to MR-guided thermal treatment of liver cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging 8:77–84
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heizmann, O., Zidowitz, S., Bourquain, H. et al. Assessment of Intraoperative Liver Deformation During Hepatic Resection: Prospective Clinical Study. World J Surg 34, 1887–1893 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-010-0561-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-010-0561-x