Abstract
Background
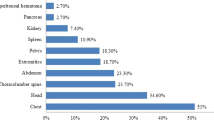
Blunt and penetrating liver trauma is common and often presents major diagnostic and management problems.
Methods
A literature review was undertaken to determine the current consensus on investigation and management strategies.
Results
The liver is the most frequently injured organ following abdominal trauma. Immediate assessment with ultrasound has replaced diagnostic peritoneal lavage in the resuscitation room, but computerised tomography remains the gold standard investigation. Nonoperative management is preferred in stable patients but laparotomy is indicated in unstable patients. Damage control techniques such as perihepatic packing, hepatotomy plus direct suture, and resectional debridement are recommended. Major complex surgical procedures such as anatomical resection or atriocaval shunting are now thought to be redundant in the emergency setting. Packing is also recommended for the inexperienced surgeon to allow control and stabilisation prior to transfer to a tertiary centre. Interventional radiological techniques are becoming more widely used, particularly in patients who are being managed nonoperatively or have been stabilised by perihepatic packing.
Conclusions
Management of liver injuries has evolved significantly throughout the last two decades. In the absence of other abdominal injuries, operative management can usually be avoided. Patients with more complex injuries or subsequent complications should be transferred to a specialist centre to optimise final outcome.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feliciano DV (1989) Surgery for liver trauma. Surg Clin North Am 69:273–284
Matthes G, Stengel D, Seifert J et al (2003) Blunt liver injuries in polytrauma: results from a cohort study with the regular use of whole-body helical computed tomography. World J Surg 27:1124–1130
Clancy TV, Maxwell GJ, Covington DL et al (2001) A statewide analysis of level I and II trauma centers for patients with major injuries. J Trauma 51:346–351
Miller PR, Croce MA, Bee TK et al (2002) Associated injuries in blunt solid organ trauma: the implications for missed injury in non-operative management. J Trauma 53:238–242
Shanmuganathan K, Mirvis SE, Chiu WC (2004) Penetrating torso trauma: triple-contrast helical CT in peritoneal violation and organ injury. A prospective study in 200 patients. Radiology 231:775–784
Lucas CE, Ledgerwood AM (2000) Changing times and the treatment of liver injury. Am Surg 66:337–341
Sikhondze WL, Madiba TE, Naidoo NM et al (2007) Predictors of outcome in patients requiring surgery for liver trauma. Injury 38:65–70
Feliciano DV, Mattox KL, Jordan GL et al (1986) Management of 1000 consecutive cases of hepatic trauma (1979–1984). Ann Surg 204:438–445
Cogbill TH, Moore EE, Jurkovich GJ et al (1988) Severe hepatic trauma: a multi-center experience with 1335 liver injuries. J Trauma 28:1433–1438
Schweizer W, Tanner S, Baer HU et al (1993) Management of traumatic liver injuries. Br J Surg 80:86–88
Krige JEJ, Bornman PC, Terblanche J (1997) Liver trauma in 446 patients. South Afr J Surg 1:10–15
Becker CD, Mentha G, Terrier F (1998) Blunt abdominal trauma in adults: role of CT in the diagnosis and management of visceral injuries. Eur Radiol 8:553–562
Becker CD, Gal I, Baer HU et al (1996) Blunt hepatic trauma in adults: correlation of CT injury grading with outcome. Radiology 201:215–222
Moore EE, Cogbill TH, Jurkovich GJ et al (1995) Organ injury scaling: spleen and liver (1994 revision). J Trauma 38:323–324
Gao JM, Du DY, Zhao XJ et al (2003) Liver trauma: Experience in 348 cases. World J Surg 27:703
Brammer RD, Bramhall SR, Mirza DF et al (2002) A 10-year experience of complex liver trauma. Br J Surg 89:1532–1537
Gur S, Orsel A, Atahan K et al (2003) Surgical treatment of liver trauma. Hepatogastroenterology 50:2109–2111
American College of Surgeons (1997) Advanced Trauma Life Support manual. American College of Surgeons, Chicago, IL
Peng RY, Bongard FS (1999) Hypothermia in trauma patients. J Am Coll Surg 188:688–696
Hoyt DB, Bulger EM, Knudson MM et al (1994) Death in the operating room: analysis of a multicenter experience. J Trauma 37:426–432
Nural MS, Yardan T, Guven H et al (2005) Diagnostic value of ultrasonography in the evaluation of blunt abdominal trauma. Diagn Interv Radiol 11:41–44
Kirby RM, Braithwaite M (2000) Management of liver trauma. Br J Surg 87:1732
Kimura A, Otsuka T (1991) Emergency center ultrasonography in the evaluation of hemoperitoneum: a prospective study. J Trauma 31:20–23
Scalea T, Rodriguez A, Chiu W et al (1999) Focused assessment with sonography for trauma (FAST): results from an international consensus conference. J Trauma 46:466–472
Royal College of Radiologists (2007) Making the best use of clinical radiology services: referral guidelines. RCR, London
Boulanger BR, Kearney PA, Brenneman FD et al (2000) Utilisation of FAST (focused assessment with sonography for trauma) in 1999: results of a survey of North American trauma centres. Am Surg 65:1049–1055
Richards JR, Schleper NH, Woo BD et al (2002) Sonographic assessment of blunt abdominal trauma: a 4-year prospective study. J Clin Ultrasound 30:59–67
Melanson SW, Heller M (1998) The emerging role of bedside ultrasonography in trauma care. Emerg Med Clin North Am 16:165–189
Bode PJ, Edwards MJ, Kruit MC et al (1999) Sonography in a clinical algorithm for early evaluation of 1671 patients with blunt abdominal trauma. AJR Am J Roentgenol 172:905–911
Jansen JO, Yule SR, Loudon MA (2008) Investigation of blunt abdominal trauma. BMJ 336:938–942
Pearl WS, Todd KH (1996) Ultrasonography for the initial evaluation of blunt abdominal trauma: A review of prospective trials. Ann Emerg Med 27:353–361
Rozycki GS, Shackford SR (1996) Ultrasound, what every trauma surgeon should know. J Trauma 40:1–4
McGahan JP, Richards JR (1999) Blunt abdominal trauma: the role of emergent sonography and a review of the literature. AJR Am J Roentgenol 172:897–903
Yoshii H, Sato M, Yamamoto S et al (1998) Usefulness and limitations of ultrasonography in the initial evaluation of blunt abdominal trauma. J Trauma 45:45–51
Hoffmann R, Nerlich M, Muggia-Sullan M et al (1992) Blunt abdominal trauma in cases of multiple trauma evaluated by ultrasonography: a prospective analysis of 291 patients. J Trauma 32:452–458
Rothlin MA, Naf R, Amgwerd M et al (1993) Ultrasound in blunt abdominal and thoracic trauma. J Trauma 34:488–495
McGahan JP, Rose J, Coates TL et al (1997) Use of ultrasonography in the patient with acute abdominal trauma. J Ultrasound Med 16:653–662
Rozycki GS, Ochsner MG, Schmidt JA et al (1995) A prospective study of surgeon performed ultrasound as the primary adjuvant modality for injured patient assessment. J Trauma 39:492–500
McKenney MG, Martim L, Lentz K et al (1996) 1000 consecutive ultrasounds for blunt abdominal trauma. J Trauma 40:607–612
Sirlin CB, Casola G, Brown MA et al (2001) US of blunt abdominal trauma: importance of free pelvic fluid in women of reproductive age. Radiology 219:229–235
Fernandez L, McKenney MG, McKenney KL et al (1998) Ultrasound in blunt abdominal trauma. J Trauma 45:841–848
McKenney M, Lentz K, Nunez D et al (1994) Can ultrasound replace diagnostic peritoneal lavage in the assessment of blunt trauma? J Trauma 37:439–441
Brown MA, Casola G, Sirlin CB et al (2001) Blunt abdominal trauma: screening US in 2693 patients. Radiology 218:352–358
McKenney KL, Nunez DB, McKenney MG et al (1998) Sonography as the primary screening technique for blunt abdominal trauma: experience with 899 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 170:979–985
Nagy KK, Roberts RR, Joseph KT et al (2000) Experience with over 2500 diagnostic peritoneal lavage for suspected intra-abdominal injury following blunt trauma. Injury 31:479–482
Bain IM, Kirby RM, Tiwari P et al (1998) Survey of abdominal ultrasound and diagnostic peritoneal lavage for suspected intra-abdominal injury following blunt trauma. Injury 29:65–71
Sirlin CB, Brown MA, Andrade-Barreto OA et al (2004) Blunt abdominal trauma: clinical value of negative screening US scans. Radiology 230:661–668
Healey M, Simons RK, Winchell RJ et al (1996) A prospective evaluation of abdominal ultrasound in trauma: is it useful? J Trauma 40:875–885
Hoff WS, Holevar M, Nagy KK et al (2002) Practice management guidelines for the evaluation of blunt abdominal trauma: the EAST practice management guidelines work group. J Trauma 53:602–615
Rozycki GS, Ballard RB, Feliciano DV et al (1998) Surgeon-performed ultrasound for the assessment of truncal injuries: lessons learned from 1540 patients. Ann Surg 228:557–567
Boulanger BR, McLellan BA, Brenneman FD et al (1996) Emergent abdominal sonography as a screening test in a new diagnostic algorithm for blunt trauma. J Trauma 40:867–874
Rozycki GS, Ochsner MG, Jaffin JH et al (1993) Prospective evaluation of surgeons’ use of ultrasound in the evaluation of trauma patients. J Trauma 34:516–527
Shuman WP, Holtzman SR, Bree RL et al. (2005) American College of Radiology appropriateness criteria. Blunt abdominal trauma. Available at http://www.acr.org/SecondaryMainMenuCategories/quality_safety/app_criteria/pdf/ExpertPanelonGastrointestinalimaging.aspx
Stengel D, Bauwens K, Sehouli J et al (2001) Systematic review and meta-analysis of emergency ultrasonography for blunt abdominal trauma. Br J Surg 88:901–912
Stengel D, Bauwens K, Sehouli J et al. (2005) Emergency ultrasound based algorithms for diagnosing blunt abdominal trauma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (2):CD004446
Poletti PA, Mirvis SE, Shanmuganathan K et al (2000) CT criteria for management of blunt liver trauma: correlation with angiographic and surgical findings. Radiology 216:418–427
Delgado Millan MA, Deballon PO (2001) Computed tomography, angiography, and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in the nonoperative management of hepatic and spenic trauma. World J Surg 25:1397–1402
Shanmuganathan K, Mirvis SE (1998) CT scan evaluation of blunt hepatic trauma. Radiol Clin N Am 36:399–411
Yoon W, Jeong YY, Kim JK et al (2005) CT in blunt liver trauma. Radiographics 25:87–104
Taourel P, Vernhet H, Suau A et al (2007) Vascular emergencies in liver trauma. Eur J Radiol 64:73–82
Shanmuganathan K (2004) Multi-detector row CT imaging of blunt abdominal trauma. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 25:180–224
Shuman WP (1997) CT of blunt abdominal trauma in adults. Radiology 205:297–306
Lubner M, Menias C, Rucker C et al (2007) Blood in the belly: CT findings of hemoperitoneum. Radiographics 27:109–125
Fang JF, Chen RJ, Wong YC et al (1998) Pooling of contrast material on computed tomography mandates aggressive management of blunt hepatic injury. Am J Surg 176:315–319
Wong YC, Wang LJ, See LC et al (2003) Contrast material extravasation on contrast-enhanced helical computed tomographic scan of blunt abdominal trauma: its significance on the choice, time, and outcome of treatment. J Trauma 54:164–170
JL Isenhour, Marx J (2007) Advances in abdominal trauma. Emerg Med Clin North Am 25:713–733
Poletti PA, Wintermark M, Schmyer P et al (2002) Traumatic injuries: role of imaging in the management of the polytrauma victim. Eur Radiol 12:969–978
Sriussadaporn S (1993) CT scan in blunt abdominal trauma. Injury 24:541–544
Pachter HL, Hofstetter SR (1995) The current status of nonoperative management of adult blunt hepatic injuries. Am J Surg 169:442–454
Pachter HL, Knudson MM, Esrig B et al (1996) Status of non-operative management of blunt hepatic injuries in 1995: a multicenter experience in 404 patients. J Trauma 40:31–38
Carrillo EH, Spain DA, Wohltmann CD et al (2000) Interventional techniques are useful adjuncts in nonoperative management of hepatic injuries. J Trauma 46:619–624
Corr P, Beningfield SJ, Krige JEJ (1992) Selective hepatic artery embolization in complex liver trauma. Injury 23:347–349
Hagiwara A, Yukioka T, Ohta S et al (1997) Nonsurgical management of patients with blunt hepatic injury: efficacy of transcatheter arterial embolisation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 169:1151–1156
Ciraulo DL, Luk S, Palter M et al (1998) Selective hepatic arterial embolisation of Grade IV and V blunt hepatic injuries: An extension of resuscitation in the nonoperative management of traumatic hepatic injuries. J Trauma 45:353–358
Denton JR, Moore EE, Coldwell DM (1997) Multimodality treatment for grade 5 hepatic injuries: ‘perihepatic packing’, arterial embolisation and venous stenting. J Trauma 42:964–968
Burch JM (1997) New concepts in trauma. Am J Surg 173:44–46
Asensio JA, Demetriades D, Chahwan S et al (2000) Approach to the management of complex hepatic injuries. J Trauma 48:66–72
Richardson JD, Franklin GA, Lukan JK et al (2000) Evolution in the management of hepatic trauma: a 25-year perspective. Ann Surg 232:324–330
Johnson JW, Gracias VH, Schwab CW et al (2001) Evolution in damage control for exsanguinating penetrating abdominal injury. J Trauma 51:261–269
Bochicchio GV (2002) The management of complex liver injuries. Trauma Q 15:55–76
Hoffer EK, Borsa JJ, Bloch RD et al (1999) Endovascular techniques in the damage control setting. Imaging Symp 19:1340–1348
Johnston JW, Gracias VH, Reilly PM et al (2001) Hepatic angiography in the damage control population. J Trauma 50:176
Wagner WH, Lundell CJ, Donovan AJ (1985) Percutaneous angiographic embolisation for hepatic arterial haemorrhage. Arch Surg 120:1241–1249
Sclafani SJ, Shaftan GW, McAuley J et al (1984) Interventional radiology in the management of hepatic trauma. J Trauma 24:256
Wahl WL, Ahrns KS, Brandt MM et al (2002) The need for early angiographic embolisation in blunt liver injuries. J Trauma 52:1097–1101
Mohr AM, Lavery RF, Barone A et al (2003) Angiographic embolisation for liver injuries: low mortality, high morbidity. J Trauma 55:1077–1081
Pringle JH (1908) Notes on the arrest of hepatic hemorrhage due to trauma. Ann Surg 48:541–549
Ritchie JP, Fonkalsrud EW (1972) Subcapsular haematoma of the liver: nonoperative management. Arch Surg 104:781–784
Velmahos GC, Toutouzas KG, Radin R et al (2003) Nonoperative treatment of blunt injury to solid abdominal organs: a prospective study. Arch Surg 138:844–851
Haan JM, Bocchicchio GV, Kramer N et al (2005) Nonoperative management of blunt splenic injury: a 5-year experience. J Trauma 58:492–498
Stein DM, Scalea TM (2006) Nonoperative management of spleen and liver injuries. J Intensive Care Med 21:296–304
Stylianos S (2000) Evidence-based guidelines for resource utilisation in children with isolated spleen or liver injury. The APSA Trauma Committee. J Pediatr Surg 35:164–167
Losty PD, Okoye BO, Walter DP et al (1997) Management of blunt liver trauma in children. Br J Surg 84:1006–1008
Kozar R, Moore JB, Niles SE et al (2005) Complications of nonoperative management of high-grade blunt hepatic injuries. J Trauma 59:1066–1071
Moore EE, Shackford SR, Pachter HL et al (1989) Organ injury scaling: spleen liver and kidney. J Trauma 29:1664–1666
Meredith JW, Young JS, Bowling J (1994) Nonoperative management of blunt hepatic trauma: the exception or the rule? J Trauma 36:529–535
Knudson MM, Lim RC Jr, Oakes DD et al (1990) Nonoperative management of blunt liver injuries in adults: the need for continued surveillance. J Trauma 30:1494–1500
Meyer AA, Crass RA, Lim RC Jr et al (1985) Selective nonoperative management of blunt liver injury using computed tomography. Arch Surg 120:550–554
Sherman HF, Savage BA, Jones LM et al (1994) Nonoperative management of blunt hepatic injuries: safe at any grade? J Trauma 37:616–621
Croce MA, Fabian TC, Menke PG et al (1995) Nonoperative management of blunt hepatic trauma is the treatment of choice for haemodynamically stable patients. Results of a prospective trial. Ann Surg 221:744–755
Pachter HL, Feliciano DV (1996) Complex hepatic injuries. Surg Clin N Am 76:763–782
Velmahos GC, Toutouzas K, Radin R et al (2003) High success with nonoperative management of blunt hepatic trauma: the liver is a sturdy organ. Arch Surg 138:475–485
Coughlin PA, Stringer MD, Lodge JP et al (2004) Management of blunt liver trauma in a tertiary referral centre. Br J Surg 91:317–321
Malhotra AK, Fabian TC, Croce MA et al (2000) Blunt hepatic injury: a paradigm shift from operative to nonoperative management in the 1990 s. Ann Surg 231:804–813
Hollands MJ, Little LM (1991) Non-operative management of blunt liver injuries. Br J Surg 78:968–972
Bynoe RP, Bell RM, Miles WS et al (1992) Complications of non-operative management of blunt hepatic injuries. J Trauma 32:308–315
Fang JF, Chen RJ, Lin BC et al (2000) Blunt hepatic injury: minimal intervention in the policy of treatment. J Trauma 49:722–728
Knudson MM, Maull KI (1999) Nonoperative management of solid organ injuries: past, present and future. Surg Clin North Am 79:1357–1371
Maull KI (2001) Current status of nonoperative management of liver injuries. World J Surg 25:1403–1404
Goan YG, Huang MS, Lin JM (1998) Nonoperative management for extensive hepatic and splenic injuries with significant hemoperitoneum in adults. J Trauma 45:360–364
Brasel KJ, DeLise CM, Oslen CJ et al (1997) Trends in the management of hepatic injury. Am J Surg 174:674–677
Ochsner MG (2001) Factors of failure for nonoperative management of blunt liver and splenic injuries. World J Surg 25:1393–1396
Nanace FC, Cohn I (1969) Surgical judgment in the management of stab injuries of the abdomen: a retrospective and prospective analysis based on a study of 600 stabbed patients. Ann Surg 170:569–580
Demetriades D, Rabinowitz C, Sofianos C (1986) Non-operative management of penetrating liver injuries: a prospective study. Br J Surg 73:736–737
Demetriades D, Charalambides D, Lakhoo M et al (1991) Gunshot wounds of the abdomen: role of selective conservative management. Br J Surg 78:220–222
Muckart DJJ, Abdool-Carrim ATO, King B (1990) Selective conservative management of abdominal gunshot wounds: a prospective study. Br J Surg 77:652–655
Farnell MB, Spencer QP, Thompson E et al (1988) Nonoperative management of blunt hepatic trauma in adults. Surgery 104:748–756
Feliciano DV (1992) Continuing evolution in the approach to severe liver trauma. Ann Surg 216:521–523
Durham RM, Buckley J, Keegan M et al (1992) Management of blunt hepatic injuries. Am J Surg 164:477–481
Federico JA, Horner WR, Clark DE et al (1990) Blunt hepatic trauma. Nonoperative management in adults. Arch Surg 125:905–909
Carillo EH, Platz A, Miller FB et al (1998) Nonoperative management of blunt liver trauma. Br J Surg 85:461–468
Renz BM, Feliciano DV (1994) Gunshot wounds to the right thoracoabdomen: a prospective study of nonoperative management. J Trauma 37:737–744
Chmielewski GW, Nicholas JM, Dulchavsky SA et al (1995) Nonoperative management of gunshot of the abdomen. Am Surg 61:665–668
Demetriades D, Gomez H, Chahwan S et al (1999) Gunshot injuries to the liver: the role of selective nonoperative management. J Am Coll Surg 188:343–348
Beckingham IJ, Krige JE (2001) ABC of diseases of liver, pancreas and bilary system. Liver and pancreatic trauma. BMJ 322:783–785
Yaman I, Nazli O, Tugrul T et al (2007) Surgical treatment of hepatic injury: morbidity and mortality analysis of 109 cases. Hepatogastroenterology 54:1507–1511
Shapiro MB, Nance ML, Schiller HJ et al (2001) Nonoperative management of solid abdominal organ injuries from blunt trauma: impact of neurologic impairment. Am Surg 67:793–796
Schroeppel TJ, Croce MA (2007) Diagnosis and management of blunt abdominal solid organ injury. Curr Opin Crit Care 13:399–404
Davis KA, Brody JM, Cioffi WG (1996) Computed tomography in blunt hepatic trauma. Arch Surg 131:255–260
Allins A, Ho T, Nguyen TH et al (1996) Limited value of routine follow-up CT scans in nonoperative management of blunt liver and splenic injuries. Am Surg 62:883
Cuff RF, Cogbill TH, Lambert PJ (2000) Nonoperative management of blunt liver trauma: the value of follow-up abdominal computed tomography scans. Am Surg 66:332–336
Demetriades D, Hadkizacharia P, Constantinou C et al (2006) Selective nonoperative management of penetrating abdominal solid organ injuries. Ann Surg 244:620–628
Coimbra R, Hoyt DB, Engelhart S et al (2006) Nonoperative management reduces the overall mortality of grades 3 and 4 blunt liver injuries. Int Surg 91:251–257
Omoshoro-Jones JAO, Nicol AJ, Navsaria PH et al (2005) Selective non-operative management of liver gunshot injuries. Br J Surg 92:890–895
DuBose J, Inaba K, Teixeira PG et al (2007) Selective non-operative management of solid organ injury following abdominal gunshot wounds. Injury 38:1084–1090
Marr JDF, Krige JEJ, Terblanche J (2000) Analysis of 153 gunshot wounds of the liver. Br J Surg 87:1030–1034
Krige JEJ, Bornman PC, Terblance J (1992) Therapeutic perihepatic packing in complex liver trauma. Br J Surg 79:43–46
Nicol AJ, Hommes M, Primrose R et al (2007) Packing for control of hemorrhage in major liver trauma. World J Surg 31:569–574
Krige JEJ (2000) Liver fracture and bleeding. Br J Surg 87:1615–1616
Hoey BA, Schwab CW (2002) Damage control surgery. Scand J Surg 91:92–103
Neuhaus SJ, Bessell JR (2004) Damage control laparotomy in the Australian military. ANZ J Surg 74:18–22
Tugnoli G, Casali M, Villani S et al (2003) The “damage-control” in severe hepatic injuries: our experience. Ann Ital Chir 74:529–533
Rotondo MF, Schwab CW, McGonigal MD et al (1993) ‘Damage control’: An approach for improved survival in exsanguinating penetrating abdominal injury. J Trauma 35:375–383
Tilton BT (1905) Some considerations regarding wounds of the liver. Ann Surg 41:20–30
Madding GF, Peniston WH (1957) Liver haemostasis. Surg Gynaecol Obstet 104:417–424
Madding GF (1958) Wounds of the liver. Surg Clin North Am 38:1619–1629
Calne RY, Wells FC, Forty J (1982) Twenty-six cases of liver trauma. Br J Surg 69:365–368
Lucas CE, Ledgerwood AM (1976) Prospective evaluation of hemostatic techniques for liver injuries. J Trauma 16:442–451
Baracco-Gandolfo VB, Vidarte O, Baracco-Miller V et al (1986) Prolonged closed liver packing in severe hepatic trauma: experience with 36 patients. J Trauma 26:754–756
Moore FA, Moore EE, Seagraves A (1985) Non-resectional management of major hepatic trauma. Am J Surg 150:725–729
Walt AJ (1986) Discussion: packing for control of hepatic haemorrhage. J Trauma 26:741–756
Little JM, Fernandes A, Tait N (1986) Liver trauma. Aust N Z J Surg 56:613–619
Pachter HL, Spencer FC, Hofstetter SR et al (1992) Significant trends in the treatment of hepatic injuries. Experience with 411 injuries. Ann Surg 215:492–500
Caruso DM, Battistella FD, Owings JT et al (1999) Perihepatic packing of major liver injuries: complications and mortality. Arch Surg 134:958–964
Sheridan R, Driscoll D, Felsen R (1997) Packing and temporary closure in liver injury. Injury 28:711–712
Cue JI, Cryer HG, Miller FB et al (1990) Packing and planned re-exploration for hepatic and retroperitoneal haemorrhage: critical refinements of a useful technique. J Trauma 30:1007–1013
Aydin U, Yazici P, Zeytunlu M et al (2008) Is it more dangerous to perform inadequate packing? World J Emerg Surg 3:1
Calne RY, McMaster P, Pentlow BD (1979) The treatment of major liver trauma by primary packing with transfer of the patients for definitive treatment. Br J Surg 66:338–339
Carmona RH, Peck DZ, Lim RC (1984) The role of packing and planned reoperation in severe hepatic trauma. J Trauma 24:779–784
Svoboda JA, Peter ET, Dang CV et al (1982) Severe liver trauma in the face of coagulopathy. A case for temporary packing and early exploration. Am J Surg 144:717–721
Feliciano DV, Mattox KL, Burch JM et al (1986) Packing for control of hepatic haemorrhage. J Trauma 26:738–743
Knudson MM, Lim RC, Olcott EW (1994) Morbidity and mortality following major penetrating liver injuries. Arch Surg 129:256–261
Sharp KW, Locicero RJ (1992) Abdominal packing for surgically uncontrollable haemorrhage. Ann Surg 215:467–475
Parks RW, Chrysos M, Diamond T (1999) Management of liver trauma. Br J Surg 86:1121–1135
Feliciano DV, Mattox KL, Jordan GL Jr (1981) Intra-abdominal packing for control of hepatic haemorrhage: a re-appraisal. J Trauma 21:285–290
Ivatury RR, Nallathambi M, Gunduz Y et al (1986) Liver packing for uncontrolled haemorrhage: a re-appraisal. J Trauma 26:744
Balogh Z, McKinley BA, Cox CS et al (2003) Abdominal compartment syndrome: the cause or the effect of multiple organ failure? Shock 20:483–492
Meldrum DR, Moore FA, Moore EE et al (1995) Cardiopulmonary hazards of perihepatic packing for major liver injuries. Am J Surg 170:537–542
Meldrum DR, Moore FA, Moore EE et al (1997) Prospective characterisation and selective management of the abdominal compartment syndrome. Am J Surg 174:667–673
Iuchtman M, Alfici R, Sternberg A et al (2004) Mesh wrap in severe pediatric liver trauma. J Pediatr Surg 39:1485–1489
Sitzmann JV, Spector SA, Jin X et al (2005) A technique for emergency liver packing. J Gastrointest Surg 9:284–287
Strong RW, Lynch SV, Wall DR et al (1998) Anatomic resection for severe liver trauma. Surgery 123:251–257
Beal SL (1990) Fatal hepatic haemorrhage: an unresolved problem in the management of complex liver injuries. J Trauma 30:163–169
Ochsner MG, Jaffin JH, Golocovosky M et al (1993) Major hepatic trauma. Surg Clin North Am 73:337–352
Watson CJE, Calne RY, Padhani AR, Dixon AK (1991) Surgical restraint in the management of liver trauma. Br J Surg 78:1071–1075
Mays ET, Conti S, Fallahzadeh H et al (1979) Hepatic artery ligation. Surgery 86:536–543
Flint LM, Polk HC Jr (1979) Selective hepatic artery ligation: limitations and failures. J Trauma 19:319–323
Wilson RH, Moorehead RJ (1991) Hepatic trauma and its management. Injury 22:439–445
Mays ET (1976) The hazards of suturing certain wounds of the liver. Surg Gynecol Obstet 143:201–204
Lim RC Jr, Guiliano AE, Trunkey DD (1997) Postoperative treatment of patients after liver resection for trauma: a follow-up study. Arch Surg 112:429–435
Ringe B, Pichlmayr R, Ziegler H et al (1991) Management of severe hepatic trauma by two-stage total hepatectomy and subsequent liver transplantation. Surgery 109:792–795
Duane TM, Como JJ, Bochichio GV et al (2004) Re-evaluating the management and outcomes of severe blunt liver injury. J Trauma 57:494–500
Pachter HL, Spencer FC, Hofstetter SR (1983) Experience with the finger fracture technique to achieve intra-hepatic hemostasis in 75 patients with severe injuries to the liver. Ann Surg 197:771–777
Menegaux F, Langlois P, Chigot JP (1993) Severe blunt trauma of the liver: a study of mortality factors. J Trauma 35:865–869
Khaneja SC, Pizzi WF, Barie PS et al (1997) Management of penetrating juxtahepatic inferior vena cava injuries under total vascular exclusion. J Am Coll Surg 184:469–474
Baumgartner F, Scudamore C, Nair C et al (1995) Venovenous bypass for major hepatic and caval trauma. J Trauma 39:671–673
Rogers FB, Reese J, Shackford SR et al (1997) The use of venovenous bypass and total vascular isolation of the liver in the surgical management of juxtahepatic venous injuries in blunt hepatic trauma. J Trauma 43:530–533
McAnena OJ, Moore EE, Moore FA (1989) Insertion of a retrohepatic vena cava balloon shunt through the saphenofemoral junction. Am J Surg 158:463–466
Buechter KJ, Sereda D, Gomez G et al (1989) Retrohepatic vein injuries: experience with 20 cases. J Trauma 29:1698–1704
Elerding SC, Moore EE Jr (1980) Recent experience with trauma of the liver. Surg Gynecol Obstet 150:853–855
Rovito PF (1987) Atrial caval shunting in blunt hepatic vascular injury. Ann Surg 205:318–321
Beal SL, Ward RE (1989) Successful atrial caval shunting in the management of retrohepatic venous injuries. Am J Surg 158:409–413
Hollands MJ, Little JM (1990) Hepatic venous injury after blunt abdominal trauma. Surgery 197:149–152
Burch JM, Feliciano DV, Mattox KL (1988) The atriocaval shunt. Facts and fiction. Ann Surg 207:555–568
Pachter HL, Spencer FC, Hofstetter SR (1986) The management of juxtaheptatic venous injuries without an atrial-caval shunt: preliminary clinical observations. Surgery 99:569
Coln D, Creighton J, Schorn L (1980) Successful management of hepatic vein injury from blunt trauma in children. Am J Surg 140:858
Jeng LB, Hsu CH, Wang CS et al (1993) Emergent liver transplantation to salvage a hepatic avulsion injury with a disrupted suprahepatic vena cava. Arch Surg 128:1075–1077
Ginzburg E, Shatz D, Lynn M et al (1998) The role of liver transplantation in subacute trauma patients. Am Surg 64:363–364
Ringe B, Pichlmayr R (1995) Total hepatectomy and liver transplantation: a life saving procedure in patients with severe hepatic trauma. Br J Surg 82:837–839
Demirbas A, Fragulidis GP, Karatzas T et al (1997) Role of liver transplantation in the management of liver trauma. Transplant Proc 29:2848
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badger, S.A., Barclay, R., Campbell, P. et al. Management of Liver Trauma. World J Surg 33, 2522–2537 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-009-0215-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-009-0215-z