Abstract
Background
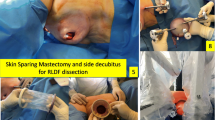
The introduction of skin-sparing mastectomy has revolutionized both breast cancer surgery and breast reconstruction. Latissimus dorsi myocutaneous flap is a versatile flap that is gaining renewed popularity with the development of flap modifications and the continued recognition of its reliability and safety. We report our results with a new modification of the extended latissimus dorsi flap after skin-sparing mastectomy for breast cancer.
Methods
From January 2002 to January 2006, 140 patients of breast carcinoma had unilateral skin-sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction. A total of 132 cases of invasive duct carcinoma and eight cases of invasive lobular carcinoma are included. Age ranged from 27 to 53 (median, 40.5) years. Tumor stage was stage I in 22 cases, stage II in 100 cases, and stage III in 18 cases. We performed a new modification to the standard extended latissimus dorsi flap, which allowed us to obtain enough autologous tissue to reconstruct the relatively large breast of the Egyptian women without implant. The postoperative aesthetic results and donor side morbidity, including contour deformity and scaring, were examined.
Results
We applied both an objective and subjective aesthetic result monitoring. Aesthetic grading results of breast reconstruction were excellent in 85, good in 42, fair in ten and poor in three cases. Both flap and donor site complications were minor. Patients were followed for a median of 32.4 (range, 12-48) months. During this period of follow-up, no episode of local or distant failure was observed.
Conclusions
Skin-sparing mastectomy with immediate breast reconstruction using our new modification of extended latissimus dorsi flap allows single-stage, totally autologous reconstruction with satisfactory aesthetic results and low morbidity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ibrahim A, Hussein H, Ismail K, Hablas A, Abdel-bar I, Ramadan M (2002) Garbia population-based cancer registry; Ministry of health and population, Egypt, December 2002
Toth BA, Lappert P (1991) Modified skin incision for mastectomy: the need for plastic surgical input in preoperative planning. Plast Reconstr Surg 87:1048–1053
Muhlbauer W, Olbrisch RR (1977) The latissimus dorsi myocutaneous flap for breast reconstruction. Chir Plast 4:27–34
Bostwick III J, Vasconez LO, Jurkiewicz MI (1978) Breast reconstruction after radical mastectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg 61:682–693
Hokin JAB (1983) Mastectomy reconstruction without prosthetic implant. Plast Recinstr Surg 72:810
McCrew JB, Papp CT (1991) Latissimus dorsi myocutaneous flap: “Fleur de lis” reconstruction. In: Hartrampf CR (ed) Breast reconstruction with living tissue. Hampton Press, Norfolk, p 221
Garbay JR, Rietjens M, Petit JY (1992) Esthetic results of breast reconstruction after amputation for cancer: 323 cases. J Gynecol Obst Biol Reprod 21:405–412
Lowery JC, Wilkins EG, Kuzon WM, Kuzon WM (1996) Evaluation of aesthetic results in breast reconstruction: an analysis of reliability. Ann Plast Surg 36:601–607
Slavin SA, Schnitt SJ, Duda RB (1997) Skin sparing mastectomy and immediate reconstruction: Oncologic risk and aesthetic results in patients with early stage breast cancer. Plast Reconstr Surg 102:49–62
Simmons RM, Fish KS, Gayle E, La Trenta GS, Swistel A, Christos P, et al. (1999) Local and distance recurrence rates in skin sparing mastectomies compared with non skin sparing mastectomies. Ann Surg Oncol 6:676–681
Newman LA, Kuerer HM, Hunt KK, Kroll SS, Ames FC, Ross MI, et al. (1998) Presentation, treatment and outcome of local recurrence after skin sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction. Ann Surg Oncol 5:620–626
Schaffer C, Gardner PM, Fix RJ (1999) Immediate breast reconstruction following skin sparing mastectomy: the UAB experience [abstract]. South Mede J 92:S78
Chang DW, Youssef A, Cha S (2002) Autologous breast reconstruction with the extended latissimus dorsi flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 1:751–759
Chang DW, Wang B, Robb GL, et al. (2000) Effect of obesity on flap and donor site complications in free TRAM flap breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 105:2374
McCrew JB, Papp C, Edwards A, McMellin A (1994) The autologous latissimus breast reconstruction. Clin Plast Surg 21:279
Delay E, Gounot N, Bouillot A (1998) Autologous latissimus breast reconstruction: a 3 years clinical experience with 100 patients. Plast Reconstr Surg 102:1461–1478
Menke H, Erkens M, Olbrisch RR (2001) Evolving concepts in breast reconstruction with latissimus dorsi flaps: results and follow up of 121 consecutive patients. Ann Plast Surg 47:107–114
Blondeel PN, Vanderstraeten GG, Monstrey SJ, et al. (1997) The donor site morbidity of free DIEP flaps and free TRAM flaps for breast reconstruction. BR J Plast Surg 50:322–330
Delay E, Jorquera F, Pasi PL (1999) Autologous latissimus breast reconstruction in association with the abdominal advancement flap. A new refinement in breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg 42:67–75
Gabka CJ, Mainwald G, Bohmert H (1998) Immediate breast reconstruction for breast carcinoma using the periareolar approach. Plast Reconst Surg 101:1228–1234
Carlson GW, Losken A, Moore B, Thornton J, Elliott M, Bolitho G (2001) Results of immediate breast reconstruction after skin sparing mastectomy. Ann Plast Surg46:222–228
de la Torre JI, Fix RJ, Gardner PM (2001) Reconstruction with the latissimus dorsi flap after skin sparing mastectomy. Ann Plast Surg 46:229–233
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Denewer, A., Setit, A., Hussein, O. et al. Skin-Sparing Mastectomy with Immediate Breast Reconstruction by a New Modification of Extended Latissimus Dorsi Myocutaneous Flap. World J Surg 32, 2586–2592 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-007-9401-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-007-9401-z