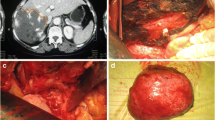
Abstract
Hemangioma is the most common primary tumor of the liver. The widespread use of ultrasonography (USG) and computed tomography (CT) has made the diagnosis more common. Although the vast majority of hemangiomas are diagnosed incidentally and are asymptomatic, treatment is still controversial. Surgery is the treatment of choice, especially in giant, symptomatic hemangiomas and uncertainty of diagnosis. Twenty-two patients (median age: 46 years) underwent resection (n = 12) or enucleation (n = 10) for liver hemangioma from 1989 to 2002. The primary indication for surgery was abdominal pain. Ten patients who were treated by enucleation were compared with twelve patients who were treated by liver resection. Mean tumor size was 90 mm with a range of 40–270 mm. There were no statistically significant differences in tumor size, preoperative liver function tests, hemoglobin levels, and platelet counts between the two groups. Operative time was longer in the resection group, and statistically significant the difference was (p = 0.048). Blood transfusion requirement and blood loss during intraoperative period were higher in the resection group (p = 0.025, p = 0.01, respectively). There were three postoperative complications, 1 in the enucleation group (plevral effusion), 2 in the resection group (liver abscess and wound infection). There was no surgery-related mortality in either group. Although most hemangiomas can be removed by enucleation or liver resection with low morbidity and mortality, if the location and number of hemangiomas are appropriate, enucleation is the choice of the therapy. Hospital stay, blood transfusion requirement, and blood loss can be kept minimal by the selection of enucleation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belli L, De Carlis L, Beati C, et al. Surgical treatment of symptomatic giant hemangiomas of the liver. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1992;174:474–478
Weimann A, Ringe B, Klempnauer J, et al. Benign liver tumors: differential diagnosis and indication for surgery. World J. Surg. 1997;21:983–991
Adam YG, Huvos AG, Forrter JG. Giant hemangiomas of the liver. Ann. Surg. 1970;172:239–245
Schwartz SI, Husser WC. Cavernous hemangioma of the liver: a single institution report of 16 resections. Ann. Surg. 1987;205:456–465
Kaneko H, Takagi S, Shiba T. Laparoscopic partial hepatectomy and left lateral segmentectomy: technique and results of a clinical series. Surgery 1996;120:468–475
Bengisun U, Ozbas S, Gurel M, et al. Laparoscopic hepatic wedge resection of hemangioma: report of two cases. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2000;385:363–365
Pringle JH. Notes on the arrest of hepatic hemorrhage due to trauma. Ann. Surg. 1908;58:541–549
Blumgart LH. Liver resection for benign disease and for liver and biliary tumors. In Blumgart LH, Fong Y, (eds,) Surgery of the Liver and Biliary Tract, 3rd edition, W.B. Saunders Philadelphia, company, 2000;1639–1713
Ishak KG, Rabin L. Benign tumors of the liver. Med. Clin. North Am. 1975;59:995–1013
Sinanan MN, Marchioro T. Management of cavernous hemangioma of the liver. Am. J. Surg. 1989;157:519–522
Conter RL, Longmire WP Jr. Recurrent hepatic hemangiomas. Possible association with estrogen therapy. Ann Surg. 1988;207:115–119
Nichols FC, van Heerden JA, Weiland LH. Benign liver tumors. Surg. Clin. North Am. 1989;69:297–314
Taavitsainen M, Airaksinen T, Kreula J, et al. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of liver hemangioma. Acta Radiol. 1990;31:69–71
Bruneton JN, Drouillard J, Fenart D, et al. Ultrasonography of hepatic cavernous hemangiomas. Br. J. Radiol. 1983;56:791–795
Johnson CM, Sheedy PF 2nd, Stanson AW, et al. Computed tomography and angiography of cavernous hemangiomas of the liver. Radiology 1981;138:115–121
Yamashita Y, Ogata I, Urata J, et al. Cavernous hemangioma of the liver: pathologic correlation with dynamic CT findings. Radiology 1997;203:121–125
Danet IM, Semelka RC, Braga L, et al. Giant hemangioma of the liver: MR imaging characteristics in 24 patients. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2003;21:95–101
Birnbaum BA, Weinreb JC, Megibow AJ, et al. Definitive diagnosis of hepatic hemangiomas: MR imaging versus Tc-99m-labeled red blood cell SPECT. Radiology 1990;176:95–101
Farges O, Daradkeh S, Bismuth H. Cavernous hemangiomas of the liver: are there any indications for resection? World J. Surg. 1995;19:19–24
Yamagata M, Kanematsu T, Matsumata T, et al. Management of haemangioma of the liver: comparison of results between surgery and observation. Br. J. Surg. 1991;78:1223–1225
Borgonovo G, Razzetta F, Arezzo A, et al. Giant hemangiomas of the liver: Surgical treatment by liver resection. Hepatogastroenterology 1997;44:231–244
Brouwers MA, Peeters PM, de Jong KP, et al. Surgical management of giant haemangioma of the liver. Br. J. Surg. 1997;84:314–316
Baer HU, Dennison AR, Mouton W, et al. Enucleation of giant hemangiomas of the liver. Technical and pathologic aspects of a neglected procedure. Ann. Surg. 1992;216:673–676
Alper A, Ariogul O, Emre A, et al. Treatment of liver hemangiomas by enucleation. Arch. Surg. 1988;123:660–661
Kuo PC, Lewis WD, Jenkins RL. Treatment of giant hemangiomas of the liver by enucleation. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 1994;178:49–53
Gedaly R, Pomposelli JJ, Pomfret EA, et al. Cavernous hemangioma of the liver: anatomic resection vs enucleation. Arch. Surg. 1999;134:407–411
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamaloglu, E., Altun, H., Ozdemir, A. et al. Giant Liver Hemangioma: Therapy by Enucleation or Liver Resection. World J. Surg. 29, 890–893 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-005-7661-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-005-7661-z