Abstract
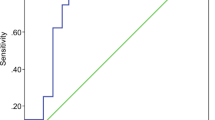
Well-known and suitable instruments for surgical audit are the POSSUM and P-POSSUM scoring systems. But these scores have not been well validated across the countries. The objective of the present study was to assess the predictive value of scores for colorectal surgery in France. Patients operated on for colorectal malignant or diverticular diseases, whether electively or on emergency basis, within a 4-month period were included in a prospective multicenter study conducted by the French Association for Surgery (Association Française de Chirurgie, AFC). The main outcome measure was postoperative in-hospital mortality. Independent factors leading to death were assessed by multivariate logistic regression analysis (AFC-index). The ratio of expected versus observed deaths was calculated, and the predictive value of the POSSUM and P-POSSUM scores were analyzed by the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. A total of 1426 patients were included. The in-hospital death rate was 3.4%. Four independent preoperative factors (AFC-index) have been found: emergency surgery, loss of more than 10% of weight, neurological disease history, and age > 70 years. POSSUM had a poor predictive value; it overestimated postoperative death in all cases. P-POSSUM had a good predictive value, except for elective surgery, where it overestimated postoperative death twofold. The predictive value of the AFC-index was also good. It had the same sensitivity and specificity as the P-POSSUM. POSSUM has not been validated in France in the field of colorectal surgery. P-POSSUM was as predictive as the AFC-index which is a simpler instrument based on four clinical parameters (without any mathematical formulas).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jones HJS, de Cossart L. Risk scoring in surgical patients. Br J Surg 1999;86:149–157
Copeland GP, Jones D, Walters M. POSSUM: a scoring system for surgical audit. Br J Surg 1991;78:356–360
Copeland GP. The POSSUM system of surgical audit. Arch Surg 2002;137:15–19
Whiteley MS, Prythech DR, Higgins B, et al. An evaluation of the POSSUM surgical scoring system. Br J Surg 1996;83:812–815
Prytherch D, Whiteley MS, Higgins B, et al. POSSUM and Portsmouth POSSUM for predicting mortality. Br J Surg 1998;85:1217–1220
Isbister WH, Al Sanea N. POSSUM: are-evaluation in patients undergoing surgery for rectal cancer. Aust NZ J Surg 2002;72:421–425
Yii MK, Ng KJ. Risk-adjusted surgical audit with the POSSUM scoring system in a developing country. Br J Surg 2002;89:110–113
Hosmer DW, Hosmer T, Le Cessie S, et al. A comparison of goodness-of-fit tests or logistic regression model. Stat Med 1997;16:965–980
Kwiatkowski F, Girard M, Hacene K, et al. SEM: a suitable statistical software adaptated for research in oncology. Bull. Cancer 2000;87:715–721 (in French)
Sagar PM, Hartley MN, Mancey-Jones B, et al. Comparative audit of colorectal resection with the POSSUM scoring system. Br J Surg 1994;81:1492–1494
Tekkis PP, Kocher HM, Bentley AJE, et al. Operative mortality rates among surgeons. Comparison of POSSUM and P-POSSUM scoring systems in gastrointestinal surgery. Dis Colon Rectum 2000;43:1528–1534
Tekkis PP, Kessaris N, Kocher HM, et al. Evaluation of POSSUM and P-POSSUM scoring systems in patients undergoing colorectal surgery. Br J Surg 2003;90:340–345
Tekkis PP, Prytherch DR, Kocher HM, et al. Development of a dedicated risk-adjustment scoring system for colorectal surgery (colorectal POSSUM). Br J Surg 2004;91:1174–1182
Senagore AJ, Delaney CP, Duepree HJ, et al. Evaluation of POSSUM and P-POSSUM scoring systems in assessing outcome after laparoscopic colectomy. Br J Surg 2003;90:1280–1284
Slim K, Panis Y, Mantion G, et al. Evaluation of POSSUM and P-POSSUM scoring systems in assessing outcome after laparoscopic colectomy. Br J Surg 2003;90:1611
Neary WD, Heather BP, Earnshaw JJ. The Physiological and Operative Severity Score for the enUmeration of Mortality and Morbidity (POSSUM). Br J Surg 2003;90:157–165
Longo WE, Virgo KS, Johnson FE, et al. Risk factors for morbidity and mortality after colectomy for colon cancer. Dis Colon Rectum 2000;43:83–91
Bozzetti F, Braga M, Gianotti L, et al. Postoperative enteral versus parenteral nutrition in malnourished patients with gastrointestinal cancer: a randomised multicentre trial. Lancet 2001;358:1487–1492
Bozzetti F, Gavazzi C, Miceli R, et al. Perioperative total parenteral nutrition in malnourished, gastrointestinal cancer patients: a randomized, clinical trial. J Parenter Enter Nutr 2000;24:7–14
Markus PM, Martell J, Leister I, et al. Predicting postoperative morbidity by clinical assessment. Br J Surg 2005;92:101–106
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all surgeon members of the Association Française de Chirurgie from the 81 centers who included patients in the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
K.S. designed the study, collected the data, and wrote the manuscript, Y.P. and G.M. designed the study and discussed the results and interpreted the data, A.A. and P.M. collected the data and participated in the discussion about the results, and F.K. performed the statistical analyses. All authors reviewed the manuscript
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Slim, K., Panis, Y., Alves, A. et al. Predicting Postoperative Mortality in Patients Undergoing Colorectal Surgery. World J. Surg. 30, 100–106 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-005-0081-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-005-0081-2