ABSTRACT
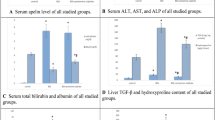
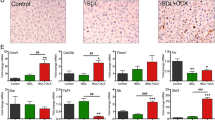
Apoptosis is an important process in a wide variety of biologic systems. Cholestasis, or impaired bile formation, occurs in a wide variety of human liver diseases. Retention and accumulation of toxic hydrophobic bile salts in hepatocytes may cause hepatocyte toxicity by inducing apoptosis. In addition, the translocation of bacteria and endotoxin, well documented in patients with obstructive jaundice, contribute to the induction of hepatocyte apoptosis. We hypothesized that oral bile acid replacement, glutamine administration, or both can attenuate or abolish hepatocyte apoptosis. Male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 250 to 300 g were randomized to four groups (10 in each group). Group 1 underwent a sham operation and was simultaneously treated with normal saline. Group 2 underwent common bile duct (CBD) ligation and was simultaneously treated with normal saline. Group 3 underwent CBD ligation and was simultaneously treated with oral glutamine. Group 4 underwent CBD ligation and was simultaneously treated with oral bile acid replacement. After 3 days (n = 5) and 7 days (n = 5), liver tissues were harvested for histopathologic analysis and apoptosis measurements. When compared with the sham operation group, significantly increased hepatocyte apoptosis and ductular proliferation occurred after CBD ligation for either 3 or 7 days. After administration of either glutamine or bile acid, the increased hepatocyte apoptosis and ductular proliferation after CBD ligation for 3 days were significantly diminished. However, both failed to diminish the changes after CBD ligation for 7 days. Significantly increased hepatocyte apoptosis and ductular proliferation occurred after CBD ligation. The administration of either glutamine or bile acid effectively diminished the hepatocyte apoptosis and ductular proliferation after CBD ligation for 3 days, whereas both failed to show the same effect after CBD ligation for 7 days.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
JFR Kerr AH Wyllie AR Currie (1972) ArticleTitleApoptosis: a basic biology phenomenon with wide-ranging implication in tissue kinetics Br. J. Cancer 26 239–257 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSyD3crgslU%3D Occurrence Handle4561027
RT Allen WJ Hunter SuffixIII DK Agrawae (1997) ArticleTitleMorphological and biochemical characterization and analysis of apoptosis J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 37 215–228 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1056-8719(97)00033-6 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXls12lsLk%3D Occurrence Handle9279777
CP Seiger (1992) ArticleTitleAnthranoid laxative and colorectal cancer Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 13 229–231
M Trauner PJ Meier JL Boyer (1998) ArticleTitleMolecular pathogenesis of cholestasis N. Engl. J. Med. 339 1217–1227 Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM199810223391707 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXntFGiur4%3D Occurrence Handle9780343
H Miyoshi C Rust PJ Roberts et al. (1999) ArticleTitleHepatocyte apoptosis after bile duct ligation in the mouse involves Fas Gastroenterology 117 669–677 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXmtFSht74%3D Occurrence Handle10464144
T Patel SF Bronk GJ Gotes (1994) ArticleTitleIncreases of intracellular magnesium promote glycodeoxycholate-induced apoptosis in rat hepatocytes J. Clin. Invest. 94 2183–2192 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXisFWhtLg%3D Occurrence Handle7989573
CMP Rodrigues G Fan M Xiaoming et al. (1998) ArticleTitleA novel role for ursodeoxycholic acid in inhibiting apoptosis by modulating mitochondrial membrane perturbation J. Clin. Invest. 101 2790–2799 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXktVSiu74%3D Occurrence Handle9637713
M Leist F Gantner I Bohlinger et al. (1995) ArticleTitleTumor necrosis factor-induced hepatocyte apoptosis precedes liver failure in experimental murine shock model Am. J. Pathol. 146 1220–1234 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXmt1KktL0%3D Occurrence Handle7538266
J Grant (1988) ArticleTitleUse of l-glutamine in total parenteral nutrition J. Surg. Res. 44 506–513 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXktlOjtbo%3D
T Hwang S O’Dwyer R Smith (1986) ArticleTitlePreservation of small bowel using glutamine enriched parenteral nutrition Surg. Forum 37 56–58 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXms1aiuw%3D%3D
JW Shands PW Chun (1980) ArticleTitleThe dispersion of gram-negative lipopolysaccharide by deoxycholate J. Biol. Chem. 255 1221–1226 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3cXht1eks78%3D Occurrence Handle6766138
JW Ding R Anderson V Soltesz et al. (1993) ArticleTitleThe role of bile and bile acids in bacterial translocation in obstructive jaundice in rats Eur. Surg. Res. 25 11–19 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXkt1Gku74%3D Occurrence Handle8482301
SM Sheen-Chen P Chau HW Harris (1998) ArticleTitleObstructive jaundice alters Kupffer cell function independent of bacterial translocation J. Surg. Res. 80 205–209 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M%2Fpsleqsw%3D%3D
SM Sheen-Chen HS Chen HT Ho et al. (2002) ArticleTitleEffect of bile acid replacement on endotoxin-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in obstructive jaundice World J. Surg. 26 448–450 Occurrence Handle11910478
SM Sheen-Chen HT Ho WJ Chen et al. (2002) ArticleTitleObstructive jaundice alters CD44 expression in rat small intestine Digestion 65 112–117 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xjsl2rtLc%3D
Sheen-Chen SM, Ho HT, Chen WJ, et al. Obstructive jaundice alters proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression in rat small intestine. World J. Surg.
SM Sheen-Chen HS Chen HT Ho et al. (2003) ArticleTitleObstructive jaundice alters LFA-1à expression in rat small intestine Dig. Dis. Sci. 48 1165–1170 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1023737317477 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXjslyiurw%3D Occurrence Handle12822880
SD Heys F Ashkanani (1999) ArticleTitleGlutamine with worud Br. J. Surg. 86 289–290 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3hsF2nuw%3D%3D
SD Heys DB Gough L Khan et al. (1996) ArticleTitleNutritional pharmacology and malignant disease: a therapeutic modality in patients with cancer? Br. J. Surg. 83 608–619
JM Holman LF Rikkers (1982) ArticleTitleBiliary obstruction and host defense failure J. Surg. Res. 32 208–213 Occurrence Handle7070073
CEH Scott-Conner JB Grogan (1994) ArticleTitleThe pathophysiology of biliary obstruction and its effect on phagocytic and immune function J. Surg. Res. 57 316–336 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuA3c%2FpslI%3D
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by grant CMRP 1145 from the Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Chang Gung University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheen-Chen, SM., Hung, KS., Ho, HT. et al. Effect of Glutamine and Bile Acid on Hepatocyte Apoptosis after Bile Duct Ligation in the Rat. World J. Surg. 28, 457–460 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-004-7189-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-004-7189-7