Abstract
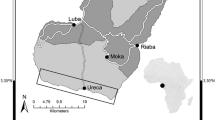
A risk assessment process was used to trial the impact of potential new operating rules on the frequency of nest inundation for the White-throated snapping turtle, Elseya albagula, in the impounded waters of the Burnett River, Queensland, Australia. The proposed operating rules would increase the barrage storage level during the turtle nesting season (May–July) and then would be allowed to reduce to a lower level for incubation for the rest of the year. These proposed operating rules reduce rates of nest inundation by altering water levels in the Ben Anderson Barrage impoundment of the Burnett River. The rules operate throughout the turtle reproductive period and concomitantly improve stability of littoral habitat and fishway operation. Additionally, the proposed rules are expected to have positive socio-economic benefits within the region. While regulated water resources will inherently have a number of negative environmental implications, these potential new operating rules have the capacity to benefit the environment while managing resources in a more sustainable manner. The operating rules have now been enacted in subordinate legislation and require the operator to maintain water levels to minimize turtle nest inundation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradbury SP, Feijtel TCJ, Leeuwen CJV (2004) Peer reviewed: meeting the scientific needs of ecological risk assessment in a regulatory context. Environ Sci Technol 38:463A–470A. doi:10.1021/es040675s
Brizga S, Arthington A, Choy S, Duivenvoorden LJ, Kennard M, Maynard R, Poplawski W (2000) Burnett basin WAMP: current environmental conditions and impacts of existing water resource development. Department of Natural Resources Report, Queensland
Bucak T, Saraoğlu E, Levi EE, Nihan Tavşanoğlu Ü, Idil Çakiroğlu A, Jeppesen E, Beklioğlu M (2012) The influence of water level on macrophyte growth and trophic interactions in eutrophic Mediterranean shallow lakes: a mesocosm experiment with and without fish. Fresh Biol 57(8):1631–1642. doi:10.111/j.1365-2427.2012.02825.x
Bunn SE, Arthington AH (2002) Basic principles and ecological consequences of altered flow regimes for aquatic biodiversity. Environ Manag 30:492–507. doi:10.1007/s00267-002-2737-0
Coops H, Beklioglu M, Crisman TL (2003) The role of water–level fluctuations in shallow lake ecosystems—workshop conclusions. Hydrobiologia 506–509:23–27. doi:10.1023/B:HYDR.0000008595.14393.77
Department of Environment (DoE) (2014a) Finalised priority assessment lists—items currently under assessment. http://www.environment.gov.au/system/files/pages/e0a90020-a411-4508-adac-53758c304de1/files/fpal-current_3.pdf. Accessed 22 Sep 2014
Department of Environment (DoE) (2014b) Species profile—Elseya irwini (Irwin’s turtle). http://www.environment.gov.au/cgi-bin/sprat/public/publicspecies.pl?taxon_id=78961#threat_class_summary. Accessed 21 Sep 2014
Department of Environment (DoE) (2014c) Species profile—Rheodytes leukops (Fitzroy River turtle). http://www.environment.gov.au/cgi-bin/sprat/public/publicspecies.pl?taxon_id=1761#threat_class_summary. Accessed 21 Sep 2014
Department of Environment (DoE) (2014d) Threatened ecological communities. http://www.environment.gov.au/biodiversity/threatened/communities. Accessed 21 Sep 2014
Department of Environment and Resource Management (DERM) (2010) Burnett Basin Resource Operations Plan May 2003, Revision 11th edn. State of Queensland. http://www.dnrm.qld.gov.au/water/catchments-planning/catchments/burnett-basin. Accessed 29 Sep 2014
Department of Information, Science, Technology, Innovation and the Arts (DSITIA) (2013a) Review of Water Resource (Burnett Basin) Plan 2000 and Resource Operations Plan: Appendix A—Assessment of critical water requirements for selected ecological assets. http://www.dnrm.qld.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0015/105531/wrp-environmental-assessment-appendixa.pdf
Department of Information, Science, Technology, Innovation and the Arts (DSITIA) (2013b) Review of Water Resource (Burnett Basin) Plan 2000 and Resource Operations Plan: Appendix E—Assessment of alternative environmental management rules (surface water). http://www.dnrm.qld.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0003/105519/wrp-environmental-assessment-appendixe.pdf
Department of Natural Resources and Mines (DNRM) (2014). Water Resource (Burnett Basin) Plan 2014. http://www.dnrm.qld.gov.au/water/catchments-planning/catchments/burnett-basin. Accessed 16 July 2014
Duivenvoorden LJ (2008) Effects of water level fluctuations on Vallisneria nana in the Burnett River in southeast Queensland, Australia. River Res Appl 24:1362–1376. doi:10.1002/rra.1157
Espinoza T, Marshall SM, McDougall AJ (2013) Spawning of the endangered Australian Lungfish (Neoceratodus forsteri) in a heavily regulated river: a pulse for life. River Res Appl 29:1215–1225. doi:10.1002/rra.2607
Ferreira PD Jr, de Tarso Amorim Castro P (2005) Nest placement of the giant amazon river turtle, Podocnemis expansa, in the Araguaia River, Goiäs State, Brazil. Ambio 34(3):212–217
Fordham DA, Georges A, Brooks BW (2008) Indigenous harvest, exotic pig predation and local persistence of a long-lived vertebrate: managing a tropical freshwater turtle for sustainability and conservation. J Appl Ecol 45:52–62. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2664.2007.01414x
Halliday I, Robins J (2007) Environmental flows for sub-tropical estuaries: understanding the freshwater needs of estuaries for sustainable fisheries production and assessing the impacts of water regulation. Final Report FRDC Project No. 2001/022; Coastal Zone Project FH3/AF, Queensland Department of Primary Industries & Fisheries
Hamann M, Schäuble CS, Limpus DJ, Emerick SP, Limpus CJ (2007) Management plan for the conservation of Elseya sp. (Burnett River) in the Burnett River Catchment. Environmental Protection Agency, Brisbane. ISBN 978-0-98036-0-8
Hamann M, Schäuble CS, Emerick SP, Limpus DJ, Limpus CJ (2009) Freshwater turtle populations in the Burnett River. Mem Qld Mus 52(2):221–232
Hollier C (2010) The effect of different water release volumes on the survival of incubating eggs of Elseya albagula, Central Queensland. Mini-thesis for Bachelor of Natural Resource Management. University of Melbourne, Australia
Hollier C (2012) Effects of experimental flooding on egg survival of Krefft’s River Turtle: Implications for freshwater turtle conservation. Thesis for Master of Environment, University of Melbourne
Kennett R, Georges A, Palmer-Allen M (1993) Early developmental arrest during immersion of eggs of a tropical freshwater turtle, Chelodina rugosa (Testudinata: Chelidae), from northern Australia. Aust J Zool 41(1):37–45
Kingsford RT (2000) Ecological impacts of dams, water diversions and river management on floodplain wetlands in Australia. Aust Ecol 25:109–127
Koehn JD (2013). Managing people, water, food and fish in the Murray–Darling Basin, south-eastern Australia. Fish Manag Ecol. doi:10.1111/fme.12035
Lackey R (1994) Ecological risk assessment. Fisheries 19:14–19
Leuven RSEW, Poudevigne I (2002) Riverine landscape dynamics and ecological risk assessment. Freshw Biol 47:845–865. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2427.2002.00918.x
Limpus C (2008). Freshwater Turtles in the Mary River: Review of biological data for turtles in the Mary River, with emphasis on Elusor macrurus and Elseya albagula. Queensland Government, Brisbane
Limpus DJ, Limpus CJ (2009) A management plan for the conservation of the White-throated Snapping Turtle, Elseya albagula, Burnett Catchment, Queensland. Presented at Australasian freshwater mini symposium/29th symposium on sea turtle biology and conservation, Brisbane, 9th February 2009
Limpus CJ, Limpus CJ, Parmenter CJ, Hodge J, Forrest MJ, McLachlan J (2011). The biology and management strategies for freshwater turtles in the Fitzroy River Catchment, with particular emphasis on Elseya albagula and Rheodytes leukops. A study initiated in response to the proposed construction of Rookwood Weir and the raising of Eden Bann Weir. Department of Environment and Heritage Protection, Brisbane
Magnusson WE (1982) Mortality of eggs of the crocodile Crocodylus porosus in northern Australia. J Herp 16(2):121–130
Marshall JC, McGregor G (2006) Ecological Risk Assessment of Water Resource Plans. Queensland Department of Natural Resources and Water, Brisbane
Marshall SM, Espinoza T, McDougall AJ (2014) Effects of water level fluctuations on spawning habitat of an endangered species, the Australian Lungfish (Neoceratodus forsteri). River Res Appl. doi:10.1002/rra.2754
Oxford University Press (2014) Definition of ‘depredation’. http://www.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/english/depredation. Accessed 27 Sep 2014
Plummer MV (1976) Some aspects of nesting success in the turtle, Trionyx muticus. Herpetologica 32(4):353–359
Richter BD, Mathews R, Harrison DL, Wigington R (2003) Ecologically sustainable water management: managing river flows for ecological integrity. Ecol Appl 13(1):206–224
Rogers K, Biggs H (1999) Integrating indicators, endpoints and value systems in strategic management of the rivers of the Kruger National Park. Freshw Biol 41(2):439–451
Simons M, Podger G, Cooke R (1996) IQQM—a hydrologic modelling tool for water resource and salinity management. Environ Soft 11(1–3):185–192
Sutella T, Aroviita J, Keto A (2013) Assessing ecological status of regulated lakes with littoral macrophyte, macroinvertebrate and fish assemblages. Ecol Ind 24:185–192. doi:10.106/j.ecolind.2012.06.015
Thomson S, Georges A, Limpus CJ (2006) A new species of freshwater turtle in the genus Elseya (Testudines: Chelidae) from central coastal Queensland, Australia. Chelonian Conserv Biol 5(1):74–86. doi:10.2744/1071-8443(2006)5
Tucker AD (1999) Cumulative effects of dams and weirs on freshwater turtles: Fitzroy, Kolan, Burnett and Mary catchments. Report to Queensland Department of Natural Resources. Draft 2.0. Queensland Parks and Wildlife Service
Tucker AD, Guarino F, Priest TE (2012) Where lakes were once rivers: contrasts of freshwater turtle diets in dams and rivers of southeastern Queensland. Chelonian Conserv Biol 11(1):12–23
U.S. EPA (2004) Generic Ecological Assessment Endpoints (GEAEs) for Ecological Risk Assessments, EPA/630/P–02/004F October 2003, http://www.epa.gov/raf/publications/pdfs/GENERIC_ENDPOINTS_2004.PDF. Accessed 15 July 2014
Valdez RA, Hoffnagle TL, McIvor CC, McKinney T, Leibfried WC (2001) Effects of a test flood on fishes of the Colorado River in Grand Canyon, Arizona. Ecol Appl 11(3):686–700. doi:10.1890/1051-0761(2001)011
Van Houtan KS, Bass OL (2007) Stormy oceans are associated with declines in sea turtle hatching. Curr Biol 17(15):590–591. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2007.06.021
Vandewalle TJ, Christiansen JL (1996) A relationship between river modification and species richness of freshwater turtles in Iowa. J Iowa Acad Sci 103(1–2):1–8
Wallace JS, Acreman MC, Sullivan CA (2003) The sharing of water between society and ecosystems: from conflict to catchment-based co-management. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 358:2011–2026. doi:10.1098/rstb.2003.1383
Wantzen KM, Rothhaupt K, Mörtl M, Cantonati M, Tóth LG, Fischer P (2008) Ecological effects of water-level fluctuations in lakes: an urgent issue. Hydrobiologia 613:1–4. doi:10.1007/s10750-008-9466-1
Zar JH (1984) Biostatistical analysis. Prentice-Hall Inc, New Jersey, p 718
Acknowledgments
Funding for this turtle research was provided by the Queensland Department of Infrastructure and Planning as part of the Burnett Plan of Action, Phase 2. This funding was administered by the former Department of Environment and Resource Management. The continuation of the project since 2012 is managed by the Department of Environment and Heritage Protection. The authors were supported in the field studies by staff and volunteers, particularly William (Joel) Hodge and Claire Johnston. These studies were conducted for the Queensland Turtle Conservation Project DERM/2009/10/08–13 in accordance with the standard practices approved under the DERM Animal Experimentation Ethics Committee. Geoff Houghton, Director, Chaverim Outdoor Activities and Environment Centre gave access through their land and assisted with collection of data. SunWater Pty Ltd gave access through their lands to access nesting areas and provided river height data. Glenn McGregor (DSITIA) assisted in understanding the risk assessment process. Matthew Tuffield (DNRM) produced and edited figures used in the manuscript. Bob Mayer (Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries) assisted in interpreting statistical analyses. Bernie Cockayne and Dean Collins (DNRM) provided early reviews of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McDougall, A.J., Espinoza, T., Hollier, C. et al. A Risk Assessment Approach to Manage Inundation of Elseya albagula Nests in Impounded Waters: A Win–Win Situation?. Environmental Management 55, 715–724 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-014-0411-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-014-0411-y