Abstract
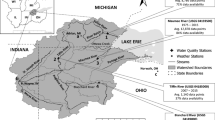
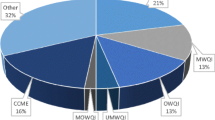
A water quality index expressed as a single number is developed to describe overall water quality conditions using multiple water quality variables. The index consists of water quality variables: dissolved oxygen, specific conductivity, turbidity, total phosphorus, and fecal coliform. The objectives of this study were to describe the preexisting indices and to define a new water quality index that has advantages over these indices. The new index was applied to the Big Lost River Watershed in Idaho, and the results gave a quantitative picture for the water quality situation. If the new water quality index for the impaired water is less than a certain number, remediation—likely in the form of total maximum daily loads or changing the management practices—may be needed. The index can be used to assess water quality for general beneficial uses. Nevertheless, the index cannot be used in making regulatory decisions, indicate water quality for specific beneficial uses, or indicate contamination from trace metals, organic contaminants, and toxic substances.



Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Ali, M. Z. 2003. The application of the neural network technique for river water quality classification with emphasis on the impact of land use activities: A case study from several catchments in Malaysia, School of Geography, University of Nottingham, U.K., available at: http://www.geog.nottingham.ac.uk/newgeog/profiles/researchstudents/ali-mohdzahit.htm
APHA. 1998. American Public Health Association, Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th ed. L.S. Clesceri, A.E. Greenberg, and A.D. Eaton (eds.), Washington D.C., 1220 pp.
BASIN. 2001. Water quality information references, National Sanitation Foundation, water quality index, available at: http://bcn.boulder.co.us/basin/data/info/references.html.
Copeland, C. 2002. Water quality: Implementing the Clean Water Act, available at: http://www.policyalmanac.org/environment/archive/crs_water_quality.shtml
C. Cude (2001) ArticleTitleOregon water quality index: A tool for evaluating water quality management effectiveness Journal of American Water Resources Association 37 125–137 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXislyku74%3D
M. K. Mitchell W. B. Stapp (1996) Field manual for water quality monitoring: An environmental education program for schools Thomson-Shore, Inc Dexter, Michigan 277
Ott, D. S. 1998. Water quality assessment of the Upper Snake River Basin, Idaho and western Wyoming, quality control data, water years 1992–1996, open file report 98–179. U.S. Geological Survey, Boise, Idaho, 176 pp.
SAFE. 1995. Strategic assessment of Florida’s environment, Florida stream water quality index, statewide summary, available at: http://www.pepps.fsu.edu/safe/environ/swq1.html
WEP. 1996. Lower Great Miami watershed enhancement program (WEP), Miami valley river index, available at: http://www.mvrpc.org/wq/wep.htm
P. A. Zandbergen K. J. Hall (1998) ArticleTitleAnalysis of the British Columbia water quality index for watershed managers: A case study of two small watersheds Water Quality Research Journal of Canada 33 519–549 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXnvF2gsrc%3D
Acknowledgments
Individuals in the IRC of Idaho National Engineering and Environmental Laboratory (INEEL), especially Bob Breckenridge and Ron Rope, have provided very important encouragement. In addition, Curtis Cude of the Oregon Department of Water Quality and Dr. Ken Hall, professor, Institute for Resources, Environment and Sustainability, B.C., Canada added very useful comments that improved the quality of this study. We would like to express our appreciation to all of them. Support for this study from the Inland Northwest Research Alliance (INRA) was greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Said, A., Stevens, D. & Sehlke, G. An Innovative Index for Evaluating Water Quality in Streams. Environmental Management 34, 406–414 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-004-0210-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-004-0210-y