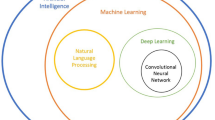
Abstract
Notoriously characterized by subjectivity and lack of solid scientific validation, reporting aesthetic outcome in plastic surgery is usually based on ill-defined end points and subjective measures very often from the patients’ and/or providers’ perspective. With the tremendous increase in demand for all types of aesthetic procedures, there is an urgent need for better understanding of aesthetics and beauty in addition to reliable and objective outcome measures to quantitate what is perceived as beautiful and attractive. In an era of evidence-based medicine, recognition of the importance of science with evidence-based approach to aesthetic surgery is long overdue. View the many limitations of conventional outcome evaluation tools of aesthetic interventions, objective outcome analysis provided by tools described to be reliable is being investigated such as advanced artificial intelligence (AI). The current review is intended to analyze available evidence regarding advantages as well as limitations of this technology in objectively documenting outcome of aesthetic interventions. It has shown that some AI applications such as facial emotions recognition systems are capable of objectively measuring and quantitating patients' reported outcomes and defining aesthetic interventions success from the patients’ perspective. Though not reported yet, observers’ satisfaction with the results and their appreciation of aesthetic attributes may also be measured in the same manner.
Level of Evidence III This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atiyeh BS, Chahine F (2021) Outcome measurement of beauty and attractiveness of facial aesthetic rejuvenation surgery. J Craniofac Surg 32(6):2091–2096. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000007821
Zhang C, Wang J (2022) Additional thoughts on artificial intelligence evaluation of facelift surgery. Aesthet Surg J 42(3):NP188–NP189. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjab374
Khetpal S, Peck C, Parsaei Y, Duan K, Gowda AU, Pourtaheri N, Lopez J, Steinbacher D (2022) Perceived age and attractiveness using facial recognition software in rhinoplasty patients: a proof-of-concept study. J Craniofac Surg 33(5):1540–1544. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000008625
Sharma K, Steele K, Birks M, Jones G, Miller G (2019) Patient-reported outcome measures in plastic surgery: an introduction and review of clinical applications. Ann Plast Surg 83(3):247–252. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0000000000001894
Boyaci O, Serpedin E, Stotland MA (2020) Personalized quantification of facial normality: a machine learning approach. Sci Rep 10(1):21375. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-78180-x
Rajesh A, Asaad M (2022) Artificial intelligence in surgery: a revolution in progress. Am Surg 6:31348221117024. https://doi.org/10.1177/00031348221117024
Jarvis T, Thornburg D, Rebecca AM, Teven CM (2020) Artificial intelligence in plastic surgery: current applications, future directions, and ethical implications. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 8(10):e3200. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000003200
Kanevsky J, Corban J, Gaster R, Kanevsky A, Lin S, Gilardino M (2016) Big data and machine learning in plastic surgery: a new frontier in surgical innovation. Plast Reconstr Surg 137(5):890e–897e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000002088
Prado AS (2018) The fourth industrial revolution tackles plastic surgeons. Plast Reconstr Surg 142(5):821e–822e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000004914
Cardoso JS, Silva W, Cardoso MJ (2020) Evolution, current challenges, and future possibilities in the objective assessment of aesthetic outcome of breast cancer locoregional treatment. Breast 49:123–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.breast.2019.11.006
Dagli MM, Rajesh A, Asaad M, Butler CE (2021) The use of artificial intelligence and machine learning in surgery: a comprehensive literature review. Am Surg 6:31348211065101. https://doi.org/10.1177/00031348211065101
Mantelakis A, Assael Y, Sorooshian P, Khajuria A (2021) Machine learning demonstrates high accuracy for disease diagnosis and prognosis in plastic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 9(6):e3638. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000003638
Kim YJ, Kelley BP, Nasser JS, Chung KC (2019) Implementing precision medicine and artificial intelligence in plastic surgery: concepts and future prospects. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 7(3):e2113. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000002113
Boonipat T, Asaad M, Lin J, Glass GE, Mardini S, Stotland M (2020) Using artificial intelligence to measure facial expression following facial reanimation surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 146(5):1147–1150. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000007251
Boonipat T, Asaad M, Lin J, Sakkal N, Stotland M, Mardini S (2020) Using artificial intelligence to analyze facial action units following facial reanimation surgery. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 57(4):26
Li CW, Wang CC, Chou CY, Lin CS (2020) Customized precision facial assessment: an AI-assisted analysis of facial microexpressions for advanced aesthetic treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 8(3):e2688. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000002688
Gibstein AR, Chen K, Nakfoor B, Lu SM, Cheng R, Thorne CH, Bradley JP (2021) Facelift surgery turns back the clock: artificial intelligence and patient satisfaction quantitate value of procedure type and specific techniques. Aesthet Surg J 41(9):987–999. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjaa238
Boonipat T, Hebel N, Zhu A, Lin J, Shapiro D (2022) Using artificial intelligence to analyze emotion and facial action units following facial rejuvenation surgery. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 6:S1748-6815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2022.08.007
Boonipat T, Lin J, Bite U (2021) Detection of baseline emotion in brow lift patients using artificial intelligence. Aesthet Plast Surg 45(6):2742–2748. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02430-0
Zhang BH, Chen K, Lu SM, Nakfoor B, Cheng R, Gibstein A, Tanna N, Thorne CH, Bradley JP (2021) Turning back the clock: artificial intelligence recognition of age reduction after face-lift surgery correlates with patient satisfaction. Plast Reconstr Surg 148(1):45–54. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000008020
Lou L, Cao J, Wang Y, Gao Z, Jin K, Xu Z, Zhang Q, Huang X, Ye J (2021) Deep learning-based image analysis for automated measurement of eyelid morphology before and after blepharoptosis surgery. Ann Med 53(1):2278–2285. https://doi.org/10.1080/07853890.2021.2009127
BahçeciŞimşek İ, Şirolu C (2021) Analysis of surgical outcome after upper eyelid surgery by computer vision algorithm using face and facial landmark detection. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 259(10):3119–3125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-021-05219-8
Hallac RR, Jackson SA, Grant J, Fisher K, Scheiwe S, Wetz E, Perez J, Lee J, Chitta K, Seaward JR, Kane AA (2021) Assessing outcomes of ear molding therapy by health care providers and convolutional neural network. Sci Rep 11(1):17875. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-97310-7
Dorfman R, Chang I, Saadat S, Roostaeian J (2020) Making the subjective objective: machine learning and rhinoplasty. Aesthet Surg J 40(5):493–498. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjz259
Qu Y, Lin B, Li S, Lin X, Mao Z, Li X, Chen R, Huang D (2022) Effect of multichannel convolutional neural network-based model on the repair and aesthetic effect of eye plastic surgery patients. Comput Math Methods Med 2022:5315146. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5315146
Lo LJ, Yang CT, Ho CT, Liao CH, Lin HH (2021) Automatic assessment of 3-dimensional facial soft tissue symmetry before and after orthognathic surgery using a machine learning model: a preliminary experience. Ann Plast Surg 86(3S):S224–S228. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0000000000002687
Tanikawa C, Yamashiro T (2021) Development of novel artificial intelligence systems to predict facial morphology after orthognathic surgery and orthodontic treatment in Japanese patients. Sci Rep 11(1):15853. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-95002-w
Choi JW, Park H, Kim BSIH, Kim N, Kwon SM, Lee JY (2022) Surgery-first orthognathic approach to correct facial asymmetry: artificial intelligence-based cephalometric analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 149(3):496e–499e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000008818
Montemurro P, Lehnhardt M, Behr B, Wallner C (2022) A machine learning approach to identify previously unconsidered causes for complications in aesthetic breast augmentation. Aesthetic Plast Surg 46:2669–2676. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-022-02997-2
Chen K, Lu SM, Cheng R, Fisher M, Zhang BH, Di Maggio M, Bradley JP (2020) Facial recognition neural networks confirm success of facial feminization surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 145(1):203–209. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000006342
Pfob A, Mehrara BJ, Nelson JA, Wilkins EG, Pusic AL, Sidey-Gibbons C (2021) Towards patient-centered decision-making in breast cancer surgery: machine learning to predict individual patient-reported outcomes at 1-year follow-up. Ann Surg 277(1):e144–e152. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000004862
Ter Horst R, van Weert H, Loonen T, Bergé S, Vinayahalingam S, Baan F, Maal T, de Jong G, Xi T (2021) Three-dimensional virtual planning in mandibular advancement surgery: soft tissue prediction based on deep learning. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 49(9):775–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2021.04.001
Kollar B, Schneider L, Horner VK, Zeller J, Fricke M, Brugger Z, Gentz M, Kiefer J, Eisenhardt SU (2022) Artificial intelligence-driven video analysis for novel outcome measures after smile reanimation surgery. Facial Plast Surg Aesthet Med. 24(2):117–123. https://doi.org/10.1089/fpsam.2020.0556
Knoedler L, Baecher H, Kauke-Navarro M, Prantl L, Machens HG, Scheuermann P, Palm C, Baumann R, Kehrer A, Panayi AC, Knoedler S (2022) Towards a reliable and rapid automated grading system in facial palsy patients: facial palsy surgery meets computer science. J Clin Med 11(17):4998. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11174998
Yoelin S, Green J, Hasan F, Mahbod B, Khan B, Dhawan SS, Dhawan AS (2022) The use of a novel artificial intelligence platform for the evaluation of rhytids. Aesthet Surg J 42(11):NP688–NP694. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjac200
Atiyeh BS, Chahine F (2021) Evidence-based efficacy of high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) in aesthetic body contouring. Aesthetic Plast Surg 45(2):570–578. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01863-3
Cede J, Graf A, Zeitlinger J, Wagner F, Willinger K, Klug C (2021) Evaluation of facial aesthetics by laypersons in patients undergoing intraoral quadrangular Le Fort II osteotomy compared with conventional Le Fort I osteotomy. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 50(9):1210–1218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2021.01.013
Liang X, Yang X, Yin S, Malay S, Chung KC, Ma J, Wang K (2021) Artificial intelligence in plastic surgery: applications and challenges. Aesthetic Plast Surg 45(2):784–790. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-019-01592-2
Zuo KJ, Saun TJ, Forrest CR (2019) Facial recognition technology: a primer for plastic surgeons. Plast Reconstr Surg 143(6):1298e–1306e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000005673
Meng T, Guo X, Lian W, Deng K, Gao L, Wang Z, Huang J, Wang X, Long X, Xing B (2020) Identifying facial features and predicting patients of acromegaly using three-dimensional imaging techniques and machine learning. Front Endocrinol 29(11):492. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2020.00492
Ito H, Nakamura Y, Takanari K, Oishi M, Matsuo K, Kanbe M, Uchibori T, Ebisawa K, Kamei Y (2022) Development of a novel scar screening system with machine learning. Plast Reconstr Surg 150(2):465e–472e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000009312
Borsting E, DeSimone R, Ascha M, Ascha M (2020) Applied deep learning in plastic surgery: classifying rhinoplasty with a mobile app. J Craniofac Surg 31(1):102–106. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000005905
Chartier C, Watt A, Lin O, Chandawarkar A, Lee J, Hall-Findlay E (2021) BreastGAN: artificial intelligence-enabled breast augmentation simulation. Aesthet Surg J Open Forum. 4:ojab052. https://doi.org/10.1093/asjof/ojab052.
Hassan AM, Biaggi-Ondina A, Rajesh A, Asaad M, Nelson JA, Coert JH, Mehrara BJ, Butler CE (2022) Predicting patient-reported outcomes following surgery using machine learning. Am Surg 6:31348221109478. https://doi.org/10.1177/00031348221109478
Liu J (2020) Artificial intelligence is still far from truly revolutionizing plastic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 146(3):390e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000007101
Hammond JB (2020) Commentary on: eye-tracking technology in plastic and reconstructive surgery: a systematic review. Aesthet Surg J 40(9):1035–1036. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjz347
Crystal DT, Cuccolo NG, Ibrahim AMS, Furnas H, Lin SJ (2020) Photographic and video deepfakes have arrived: how machine learning may influence plastic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 145(4):1079–1086. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000006697
Morris MX, Song EY, Rajesh A, Asaad M, Phillips BT (2022) Ethical, legal, and financial considerations of artificial intelligence in surgery. Am Surg 6:31348221117042. https://doi.org/10.1177/00031348221117042
Dusseldorp JR, Guarin DL, van Veen MM, Jowett N, Hadlock TA (2019) In the eye of the beholder: changes in perceived emotion expression after smile reanimation. Plast Reconstr Surg 144(2):457–471. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000005865
Choi HI, Jung SK, Baek SH, Lim WH, Ahn SJ, Yang IH, Kim TW (2019) Artificial intelligent model with neural network machine learning for the diagnosis of orthognathic surgery. J Craniofac Surg 30(7):1986–1989. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000005650
Seo J, Yang IH, Choi JY, Lee JH, Baek SH (2021) Three-dimensional facial soft tissue changes after orthognathic surgery in cleft patients using artificial intelligence-assisted landmark autodigitization. J Craniofac Surg 32(8):2695–2700. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000007712
Lim J, Tanikawa C, Kogo M, Yamashiro T (2021) Determination of prognostic factors for orthognathic surgery in children with cleft lip and/or palate. Orthod Craniofac Res 24(Suppl 2):153–162. https://doi.org/10.1111/ocr.12477
Ye J, Lei C, Wei Z, Wang Y, Zheng H, Wang M, Wang B (2022) Evaluation of reconstructed auricles by convolutional neural networks. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 75(7):2293–2301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2022.01.037
Boczar D, Brydges H, Rodriguez Colon R, Onuh OC, Trilles J, Chaya BF, Gelb B, Ceradini DJ, Rodriguez ED (2022) Quantification of facial allograft edema during acute rejection: a software-based 3-dimensional analysis. Ann Plast Surg 89(3):326–330. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0000000000003274
Hidaka T, Tanaka K, Mori H (2022) An artificial intelligence-based cosmesis evaluation for temporomandibular joint reconstruction. Laryngoscope 133:841–848. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.30239
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Atiyeh, B., Emsieh, S., Hakim, C. et al. A Narrative Review of Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Objective Assessment of Aesthetic Endpoints in Plastic Surgery. Aesth Plast Surg 47, 2862–2873 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03328-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03328-9