Abstract
Background
Botulinum toxin (BoNT) injection is the most commonly performed procedure in cosmetic surgery. However, blind injection is unable to take individual anatomical variations into consideration, which is the main contributing factor to complications. Ultrasound (US) imaging was introduced to reduce complications and improve effects. This article will review uses of US in aesthetic BoNT injection.
Method
A systematic electronic search was performed using the PubMed, MEDLINE, Web of science. Search terms were set to focus on aesthetic BoNT injection. Two independent reviewers subsequently reviewed the resultant articles based on strict inclusion and exclusion criteria. Selected manuscripts were analysed and grouped by procedure categories. Clinical cases were all performed by one plastic surgeon in our department.
Results
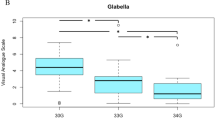
The search finally retained 24 articles. Five procedural categories were identified, including masseter (n = 16), frontalis (n = 2), glabella complex (n = 2), trapezius (n=1), and gastrocnemius (n = 3). US imaging is practical and instructive for pre-operative assessments as in needle-type selection, injection point localization and depth setting, as well as post-operative follow-ups regarding injection feedback (for instance, the extent of muscle volume decreases). What's more, ultrasound-guided injection makes needle trajectory visualized so as for the needle to reach the target muscle in avoidance of potential damage to neurovascular bundle, gland or adjacent muscle.
Conclusion
Muscles, such as masseter, frontalis, glabella complex, trapezius and gastrocnemius, and their adjacent structures can be well visualized using US, and as such, US can be a useful tool for a variety of pre-operative, intra-operative and post-operative procedures.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanna E, Pon K (2020) Updates on botulinum neurotoxins in dermatology. Am J Clin Dermatol 21(2):157–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-019-00482-2.
Quezada-Gaon N, Wortsman X, Peñaloza O, Carrasco J (2016) Comparison of clinical marking and ultrasound-guided injection of Botulinum type a toxin into the masseter muscles for treating bruxism and its cosmetic effects. J Cosmetic Dermatol 15(3):238–244. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.12208.
Lim E, Seet R (2010) Use of botulinum toxin in the neurology clinic. Nat Rev Neurol 6(11):624–636. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2010.149.
Walter U, Dressler D (2014) Ultrasound-guided botulinum toxin injections in neurology: technique, indications and future perspectives. Expert Rev Neurotherapeutics 14(8):923–936. https://doi.org/10.1586/14737175.2014.936387.
Chang CS, Lin S, Wallace CG et al (2019) Masseter muscle volume changes evaluated by 3-dimensional computed tomography after repeated botulinum toxin a injections in patients with square facial morphology. Ann Plastic Surg 82:S29–S32.
Xie Y, Zhou J, Li H, Cheng C, Herrler T, Li Q (2014) Classification of masseter hypertrophy for tailored botulinum toxin type a treatment. Plastic Reconstructive Surg 134(2):209e–218e. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000000371.
Choe S, Cho W, Lee C, Seo S (2005) Effects of botulinum toxin type a on contouring of the lower face. Dermatologic Surg 31(5):502–507. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4725.2005.31151.
Park M, Ahn K, Jung D (2003) Botulinum toxin type a treatment for contouring of the lower face. Dermatologic Surg 29(5):477–483. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1524-4725.2003.29116.x.
Bae H, Kim J, Seo K, Hu K, Kim S, Kim H (2020) Comparison between conventional blind injections and ultrasound-guided injections of botulinum toxin type a into the masseter: a clinical trial. Toxins 12(9):588. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12090588.
Cheng J, Hsu S, McGee J (2019) Botulinum toxin injections for masseter reduction in east Asians. Dermatologic Surg 45(4):566–572. https://doi.org/10.1097/dss.0000000000001859.
Lee H, Choi Y, Lee K, Hu K, Kim S, Kim H (2019) Ultrasonography of the internal architecture of the superficial part of the masseter muscle in vivo. Clin Anatomy (New York, NY) 32(3):446–452. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.23337.
Yeh Y, Peng J, Peng H (2018) Literature review of the adverse events associated with botulinum toxin injection for the masseter muscle hypertrophy. J Cosmetic Dermatol 17(5):675–687. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.12721. 2018
Bae J, Choi D, Lee J, Seo K, Tansatit T, Kim H (2014) The risorius muscle: anatomic considerations with reference to botulinum neurotoxin injection for masseteric hypertrophy. Dermatol Surg 40(12):1334–1339. https://doi.org/10.1097/dss.0000000000000223.
Lee H, Kim J, Youn K, Lee J, Kim H (2018) Ultrasound-guided botulinum neurotoxin type a injection for correcting asymmetrical smiles. Aesthetic Surg J 38(9):NP130–NP134. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjy128. 2018
Hu K, Kim S, Hur M et al (2010) Topography of the masseter muscle in relation to treatment with botulinum toxin type a. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endodontics 110(2):167–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.12.036.
Kim N, Chung J, Park R, Park J (2005) The use of botulinum toxin type a in aesthetic mandibular contouring. Plastic Reconstructive Surg 115(3):919–930. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000153236.79775.a0.
Kim N, Park R, Park J (2010) Botulinum toxin type a for the treatment of hypertrophy of the masseter muscle. Plastic Reconstructive Surg 125(6):1693–1705. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181d0ad03.
Huang J, Chen G, Chen X, Zhou B, Luo D (2014) A comparative study of the efficacy and safety of radiofrequency ablation and botulinum toxin a in treating masseteric hypertrophy. Exp Therapeutic Med 7(5):1203–1208. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2014.1552.
Wei J, Xu H, Dong J, Li Q, Dai C (2015) Prolonging the duration of masseter muscle reduction by adjusting the masticatory movements after the treatment of masseter muscle hypertrophy with botulinum toxin type a injection. Dermatologic Surg. https://doi.org/10.1097/dss.0000000000000162.
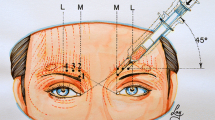
Cho Y, Lee H, Lee K, Lee K, Kang J, Kim H (2019) Ultrasonographic and three-dimensional analyses at the glabella and radix of the nose for botulinum neurotoxin injection procedures into the procerus muscle. Toxins 11(10):560. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11100560.
Lee H, Lee K, Tansatit T, Kim H (2020) Three-dimensional territory and depth of the corrugator supercilii: application to botulinum neurotoxin injection. Clin Anatomy 33(5):795–803. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.23507.
Bae J, Lee J, Choi D, Suhk J, Kim S (2018) Accessory nerve distribution for aesthetic botulinum toxin injections into the upper trapezius muscle: anatomical study and clinical trial: reproducible BoNT injection sites for upper trapezius. Surg Radiologic Anatomy SRA 40(11):1253–1259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-018-2059-4.
Kreisler A, Simonin C, Degardin A, Mutez E, Defebvre L (2020) Anatomy-guided injections of botulinum neurotoxin in neck muscles: How accurate is needle placement? Euro J Neurol 27(11):2142–2146. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.14415.
Wanitphakdeedecha R, Ungaksornpairote C, Kaewkes A, Sathaworawong A, Vanadurongwan B, Lektrakul N (2018) A pilot study comparing the efficacy of two formulations of botulinum toxin type a for muscular calves contouring. J Cosmetic Dermatol 17(6):984–990. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.12787.
Schnitzler A, Roche N, Denormandie P, Lautridou C, Parratte B, Genet F (2012) Manual needle placement: accuracy of botulinum toxin a injections. Muscle Nerve 46(4):531–534. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.23410.
Shi W, Zhu L, Wang T, Zhang G, Lian J (2019) Classification of hypertrophic gastrocnemius muscle and its treatment with botulinum toxin a. Aesthetic Plastic Surg 43(6):1588–1594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-019-01455-w.
Yu N, Liu Y, Chen C, Dong R, Yang E, Wang X (2020) Paradoxical bulging of mentalis after botulinum toxin type a injection. J Cosmetic Dermatol 19(6):1290–1293. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.13437.
Masuoka H (2017) The visualization of the functional role of the depressor Septi Nasi muscle by ultrasound. Plastic Reconstructive Surg Global Open 5(7):e1406. https://doi.org/10.1097/gox.0000000000001406.
Lee W, Moon H, Kim J, Yang E (2020) Safe glabellar wrinkle correction with soft tissue filler using doppler ultrasound. Aesthetic Surg J. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjaa197.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Human or Animals Participants
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Video.1. The video demonstrates the process of botox masseter injection under ultrasound guide (E-CUBE 7). Ultrasound can help visualize the masseter and navigate the needle to the targeted layer. The process of withdrawing needle can be showed clearly as well so as to make out-of-plane technique easy to carry out
Supplementary file1 (WMV 9400 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Yang, Y., Yu, N. et al. The “Visible” Muscles on Ultrasound Imaging Make Botulinum Toxin Injection More Precise: A Systematic Review. Aesth Plast Surg 46, 406–418 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02493-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02493-z