Abstract
Backgrounds
Double-eyelid blepharoplasty remains popular in east Asia. To avoid rigid eyelids and sinking scar after double-eyelid blepharoplasty, a new surgical approach with selective neurovascular preservation (SNVP) method is proposed to crease more physiological and dynamic double-eyelid crease.
Methods
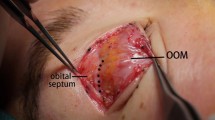
During the full-incision double-eyelid surgery, a strip of preseptal orbicularis oculi muscle was resected. The longitudinally spreading upper eyelid nerves and vessels were preserved carefully. Four to five anchoring points between these neurovascular branches were made to reach the pretarsal fascia. Skin- orbicularis oculi muscle–pretarsal fascia sutures were placed on the anchoring points.
Results
From May 2018 to April 2020, 385 patients received double-eyelid surgery with SNVP method. Eyelid edema resolved quickly within a week and generally disappeared in 4 weeks. In total, 259 (67.27%) patients scored very satisfied, and 109 (28.31%) patients scored satisfied on six-month follow-up.
Conclusions
The SNVP approach can produce reliable and dynamic palpebral crease with inconspicuous scar. Vital neurovascular branches of upper eyelid could be saved, thus reducing postoperative complications and recovery period.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
McCurdy JA Jr (2005) Upper blepharoplasty in the Asian patient: the double eyelid operation. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am 13(1):47–64
Kiranantawat K, Suhk JH, Nguyen AH (2015) The Asian eyelid: relevant anatomy. Semin Plast Surg 29(3):158–164
Sayoc BT (1956) Absence of superior palpebral fold in slit eyes; an anatomic and physiologic explanation. Am J Ophthalmol 42:298–300
Hirohiko K, Raman M, Dinesh S (2009) Upper eyelid anatomy: an update. Ann Plast Surg 63(3):336–343
Kakizaki H, Takahashi Y, Nakano T, Asamoto K, Ikeda H, Iwaki M, Selva D, Leibovitch I (2012) The causative factors or characteristics of the Asian double eyelid: an anatomic study. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 28:376–381
Saonanon P, Thongtong P, Wongwuticomjon T (2016) Differences between single and double eyelid anatomy in Asians using ultrasound biomicroscopy. Observational Study Asia Pac J Ophthalmol Phila 5(5):335–338
Saonanon P (2014) Update on Asian eyelid anatomy and clinical relevance. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 25(5):436–442
Park JI (1999) Orbicularis-levator fixation in double-eyelid operation. Arch Facial Plast Surg Apr-Jun 1(2):90–95
Kim HS, Hwang K, Kim CK, Kim KK (2013) Double-eyelid surgery using septoaponeurosis junctional thickening results in dynamic fold in Asians. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 1(2):1–9
Pan L, Sun Y, Yan S, Shi H, Jin T, Li J, Zhang L, Wu SF (2019) A flexible suspension technique of blepharoplasty: clinical application and comparison with traditional technique. Aesthetic Plast Surg 43(2):404–411
Li GF, Ding W, Tan J, Zhang B, Chen X, He B (2018) A new method for double-eyelid blepharoplasty using orbital septum. Ann Plast Surg 81(6):633–636
Vestal KP, Rathbun JE, Seiff SR (1994) Anatomy of the terminal nerves in the upper eyelid. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 10(1):1–5
Higashino T, Okazaki M, Mori H, Yamaguchi K, Akita K (2018) Microanatomy of sensory nerves in the upper eyelid: a cadaveric anatomical study. Plast Reconstr Surg 142(2):345–353
Lopez R, Lauwers F, Paoli JR, Boutault F, Guitard J (2008) The vascular system of the upper eyelid. Anatomical study and clinical interest. Surg Radiol Anat 30(3):265–269
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Human and animal rights
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the standards of the institutional ethical committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, X. Full-Incision Double-Eyelid Blepharoplasty with Selective Neurovascular Preservation Method. Aesth Plast Surg 46, 241–247 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02418-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02418-w