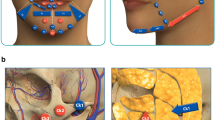
Abstract
Introduction
A harmonious face is defined in terms of a balanced relationship among all facial tissues. This balance among skin, fat, muscle, and bone is lost with aging as progressive changes occur in their volume, shape, position, and consistency. Aging of the human face generally starts in the third decade of life, mainly in the midface and periorbital areas. Traditional face-lifting surgeries result in minimal improvements in the midface area. Various techniques have been developed using different dissection planes and vectors with different forms of incision, including endoscopic techniques.
Methods
We attempted to combine endoscopic subperiosteal dissection techniques with the percutaneous needle technique, especially in young- to middle-aged patients. We aim to share technical details of our preferred suspension and fixation method for an endoscopic midface lift with the aid of a percutaneous needle and to present the outcomes of this particular technique in 75 patients.
Results
Significant rejuvenation of the nasojugal groove was achieved, and patient satisfaction was high. All cases exhibited satisfactory, symmetrical, and stable elevation of the midface. None of the patients required a second surgery.
Conclusion
Trinity lift allowed for stronger, easier, and faster application of sutures during endoscopic facial surgery without any other mucosal or transcutaneous incisions.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Psillakis JM, Rumley TO, Camargos A (1988) Subperiosteal approach as an improved concept for correction of the aging face. Plast Reconstr Surg 82:383–394. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-198809000-00001
Mendelson BC, Muzaffar AR, Adams WP (2002) Surgical anatomy of the midcheek and malar mounds. Plast Reconstr Surg 110:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-200209010-00026
Owsley JQ, Zweifler M (2002) Midface lift of the malar fat pad: technical advances. Plast Reconstr Surg 110:674–685. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-200208000-00048
Owsley JQ, Roberts CL (2008) Some anatomical observations on midface aging and long-term results of surgical treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg 121:258–268. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000293872.14916.bb
Sasaki GH, Cohen AT (2002) Meloplication of the malar fat pads by percutaneous cable-suture technique for midface rejuvenation: outcome study (392 cases, 6 years’ experience). Plast Reconstr Surg 110:635–654. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-200208000-00042
DeFatta R, Williams E (2011) Midface lifting: current standards. Facial Plast Surg 27:077–085. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1270417
Stuzin JM (2007) Restoring facial shape in face lifting: the role of skeletal support in facial analysis and midface soft-tissue repositioning. Plast Reconstr Surg 119:362–376. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000251092.82860.25
Stuzin JM, Rohrich RJ, Dayan E (2019) The facial fat compartments revisited: clinical relevance to subcutaneous dissection and facial deflation in face lifting. Plast Reconstr Surg 144:1070–1078. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000006181
Paul MD, Calvert JW, Evans GRD (2006) The evolution of the midface lift in aesthetic plastic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:1809–1827. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000218839.55122.c0
De Cordier BC, de la Torre JI, Al-Hakeem MS et al (2002) Rejuvenation of the midface by elevating the malar fat pad: review of technique, cases, and complications. Plast Reconstr Surg 110:1526–1536. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.PRS.0000029816.67278.1B
Ramirez OM (1994) Endoscopic full facelift. Aesthet Plast Surg 18:363–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00451341
Boxrud C, Rose JG, Chang L (2007) Closed meloplication percutaneous cable suture technique. Facial Plast Surg Clin N Am 15(191–199):vi. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsc.2007.02.001
Quatela V, Azzi J-P, Antunes M (2014) Endoscopic-assisted facelifting. Facial Plast Surg 30:413–421. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1383559
Marotta JC, Quatela VC (2008) Lower eyelid aesthetics after endoscopic forehead midface-lift. Arch Facial Plast Surg. https://doi.org/10.1001/archfaci.10.4.267
Askeroglu U, Pilanci O (2019) A new perspective to the periorbital aesthetics: bella eyes. Aesthet Plast Surg 43:1564–1569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-019-01497-0
de la Fuente A, Franz Hönig J (2005) Transtemporal endoscopic multiplanar upper midface lift (MUM lift). Aesthet Surg J 25:471–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asj.2005.06.003
Friedman O (2005) Changes associated with the aging face. Facial Plast Surg Clin N Am 13:371–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsc.2005.04.004
Lambros V (2007) Observations on periorbital and midface aging. Plast Reconstr Surg 120:1367–1376. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000279348.09156.c3
Mendelson B, Wong C-H (2012) Changes in the facial skeleton with aging: implications and clinical applications in facial rejuvenation. Aesthet Plast Surg 36:753–760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-012-9904-3
Little JW (2000) Volumetric perceptions in midfacial aging with altered priorities for rejuvenation. Plast Reconstr Surg 105:252–266. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-200001000-00043
Sclafani AP, Dibelius G (2015) Transpalpebral midface lift. Facial Plast Surg Clin N Am 23:209–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsc.2015.01.007
Patrocinio L, Patrocinio T, Patrocinio J (2013) Subperiosteal Midface-Lift. Facial Plast Surg 29:206–213. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1347000
Moelleken B (1999) The superficial subciliary cheek lift, a technique for rejuvenating the infraorbital region and nasojugal groove: a clinical series of 71 patients. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:1863–1874. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199911000-00043
Saltz R, Ohana B (2012) Thirteen years of experience with the endoscopic midface lift. Aesthet Surg J 32:927–936. https://doi.org/10.1177/1090820X12462714
Hamra ST (2016) Building the composite face lift: a personal odyssey. Plast Reconstr Surg 138:85–96. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000002310
Hamra ST (1992) Composite rhytidectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg 90:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199207000-00001
Isse NG (1994) Endoscopic facial rejuvenation: endoforehead, the functional lift Case reports. Aesthet dPlast Surg 18:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00444243
Batniji RK, Williams EF (2005) Effects of subperiosteal midfacial elevation via an endoscopic brow-lift incision on lower facial rejuvenation. Facial Plast Surg 21:33–37. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2005-871761
LaFerriere KA, Castellano RD (2005) Experience with percutaneous suspension of the malar fat pad for midface rejuvenation. Facial Plast Surg Clin N Am 13:393–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsc.2005.05.002
Keller GS, Namazie A, Blackwell K et al (2002) Elevation of the malar fat pad with a percutaneous technique. Arch Facial Plast Surg 4:20–25. https://doi.org/10.1001/archfaci.4.1.20
Ramirez OM (2001) Anchor subperiosteal forehead lift: from open to endoscopic. Plast Reconstr Surg 107:868–871. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-200103000-00035
Saltz R (2005) Endoscopic temporal-incision only midface lift is enhanced by endotine technique. Aesthet Surg J 25:80–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asj.2004.12.005
Byrd HS, Burt JD (2002) Achieving aesthetic balance in the brow, eyelids, and midface. Plast Reconstr Surg 110:926–933. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-200209010-00032
Fiala TG, Owsley JQ (1998) Use of the Mitek fixation device in endoscopic browlifting. Plast Reconstr Surg 101:1700–1703. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199805000-00045
Rohrich RJ, Beran SJ (1997) Evolving fixation methods in endoscopically assisted forehead rejuvenation: controversies and rationale. Plast Reconstr Surg 100:1575–1582. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199711000-00032
Hester TR, Codner MA, McCord CD et al (2000) Evolution of technique of the direct transblepharoplasty approach for the correction of lower lid and midfacial aging: maximizing results and minimizing complications in a 5-year experience. Plast Reconstr Surg 105:393–406. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-200001000-00063
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Human and Animal Rights
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
All patients signed an informed consent form.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
The endoscopic dissection starting from the temporal zone down to the midface. Anatomical landmarks and dissection planes were tagged in the presentation. Trinity Lift was also demonstrated in both external and endoscopic views (MP4 164130 kb)
Our preferred fixation suture was presented in the video (MP4 29682 kb)
Intraoperative view of Trinity Lift effect was demonstrated in the video (MP4 4097 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Askeroglu, U., Kayadibi, T. & Pilanci, O. Trinity Lift: A Unique Technique for Endoscopic Midface and Lower Periorbital Unit Lift. Aesth Plast Surg 45, 992–1001 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02126-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02126-5