Abstract
Introduction
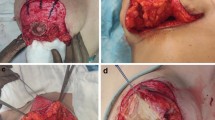
The aim of this work was to describe our technique, the “Bifidus pedicle”, which is a modification of the superomedial pedicle, for managing large breast cancers (BCs) in the upper outer quadrant (UOQ) in patients with medium/large breasts and associated ptosis. Observed complications, cosmetic outcome and oncologic safety were also reported.
Materials and Methods
Thirty patients underwent our modification of the superomedial pedicle combined with a Wise skin resection pattern for large BCs in the UOQ. All patients underwent contralateral Wise pattern breast reduction/mastopexy for symmetry.
Results
The average weight of the quadrantectomy specimen was 235 grams (range: 36–400 grams). Mean free tumour margin was 19.4 mm (range: 16–30). Mean operative time was 165 minutes (range: 150–220). Eight (13.2%) breasts had minor complications: two partial NAC necrosis, and six minimal wound dehiscences. Mean follow-up was 22 months (range: 12–30). Overall satisfaction rate was 91%; patients reported to be satisfied the most with the shape (92%) of the breasts, the achieved symmetry (94%), and the volume (85%), focusing on the fullness in the UOQ.
Conclusions
Our Bifidus pedicle allowed to fill even wide defects in the UOQ, because we selectively employed it in patients with medium to large ptotic breasts where the lower pole had enough tissue to be displaced. Satisfactory cosmetic and oncologic outcomes were achieved with low complication rate.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertozzi N, Pesce M, Santi PL, Raposio E (2017) Oncoplastic breast surgery: comprehensive review. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 21:2572–2585
Clough KB, Cuminet J, Fitoussi A et al (1998) Cosmetic sequelae after conservative treatment for breast cancer: classification and results of surgical correction. Ann Plast Surg 41:471–481
Clough KB, Ihrai T, Oden S et al (2012) Oncoplastic surgery for breast cancer based on tumour location and a quadrant-per-quadrant atlas. Br J Surg 99:1389–1395
Silverstein MJ, Savalia N, Khan S et al (2015) Extreme oncoplasty: breast conservation for patients who need mastectomy. Breast J 21:52–59
Dikmans REG, Nene LEH, Mb B et al (2017) The aesthetic items scale: a tool for the evaluation of aesthetic outcome after breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 5:e1254. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000001254
Hall-Findlay EJ (1999) A simplified vertical reduction mammaplasty: shortening the learning curve. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:748–763
Foustanos A, Panagiotopoulos K, Skouras G (2011) Intraoperative modification of pitanguy technique of reduction mammaplasty for elevation of the nipple-areola complex in case of severe breast ptosis. Aesth Plast Surg 35:55–60
Foustanos A (2009) Double flap technique: an alternative mastopexy approach. In: Shiffman MA (ed) Mastopexy and breast reduction. Springer, Berlin, pp 97–102
Wueringer E, Tschabitscher M (2003) New aspects of the topography of the mammary gland regarding its neurovascular supply along a regular ligamentous suspension. Eur J Morphol 40:181–189
LaTrenta GS, Hoffman LA (1994) Breast reduction. In: Rees TD, LaTrenta GS (eds) Aesthetic plastic surgery, 2nd edn. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 971–975
Crown A, Scovel LG, Rocha FG, Scott EJ, Wecheter DG, Grumley JW (2019) Oncoplastic breast conserving surgery is associated with a lower rate of surgical site complications compared to standard breast conserving surgery. Am J Surg 217:138–141
Crown A, Laskin R, Rocha FG, Grumley J (2019) Extreme oncoplasty: expanding indications for breast conserving surgery. Am J Surg 217:851–856
Clough KB, Kaufman GJ, Nos C, Buccimazza I, Sarfati M (2010) Improving breast cancer surgery: a classification and a quadrant per quadrant atlas for oncoplastic surgery. Ann Surg Oncol 17:1375–2139
Berry MG, Ballester M, Fitoussi A, Couturand B, Salmon R (2008) Lateral mammaplasty for oncoplastic breast surgery. Eur J Surg Oncol 34:1156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2008.06.021
Grieco MP, Bertozzi N, Grignaffini E, Raposio E (2018) A three-year experience with medial-pedicle-based breast reduction for different mammary hypertrophy. Acta Biomed 89:389–396
Clough KB, Baruch J (1992) Plastic surgery and conservative treatment of breast cancer. Indications and results. Ann Chir Plast Esthet 37:682–692
Masetti R, Pirullo PG, Mango S, Franceschini G, Chiesa F, Antinori A (2000) Oncoplastic techniques in the conservative treatment of breast cancer. Breast Cancer 7:276–280
Fitoussi AD, Curnier A, Couturaud B, Salmon RJ (2010) Oncoplastic breast surgery: a review and systematic approach. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 63:1233–1243
Regnault P (1974) Reduction mammaplasty by the “B” technique. Plast Reconstr Surg 53:19–25
Aquinati A, Tuttolomondo A, Ruocco G, Riccio M (2019) Improvement of superomedial breast reduction and mastopexy with a new “Hammock” Flap. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 7:e2309. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000002309
Schwartz JCD (2018) New approach to oncoplastic breast conservation: combining autologous volume replacement and the wise-pattern mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 6:e1987. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000001987
Chand ND, Browne V, Paramanathan N, Peiris LJ, Laws SA, Rainsbury RM (2017) Patient-reported outcomes are better after oncoplastic breast conservation than after mastectomy and autologous reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 5:e1419. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000001419
Hau E, Browne L, Capp A et al (2013) The impact of breast cosmetic and functional outcomes on quality of life: long-term results from the St. George and Wollongong randomized breast boost trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat 139:115–123
Funding
The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the author have financial interest to declare in relation to the content of this article.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Furthermore, for this type of study formal consent is not required.
Informed Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marongiu, F., Bertozzi, N., Sibilio, A. et al. “Bifidus pedicle”, The Use of Bilobed Superomedial Pedicle for Breast Reshaping Following Upper Outer Quadrantectomy: A New Oncoplastic Breast Surgery Technique. Aesth Plast Surg 45, 866–874 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01982-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01982-x