Abstract
Background
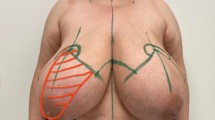
Reduction mammoplasty in patients with gigantic breast hypertrophy runs a high risk of complication. Traditionally, inferior pedicle reductions or free nipple grafting techniques have been recommended for gigantic breasts on the basis of measurements and expected resection weights. The superiomedial pedicle (SMP) technique has been less commonly used, due to concerns of vascular inadequacy. This study examines the outcomes of SMP in large reductions and outlines suggested modifications for enhanced safety.
Methods
This is a retrospective review of all patients who underwent SMP breast reduction in our institution between 2005 and 2016. Included are cases with resection weights greater than 800 g.
Results
A total of 173 patients with 341 breasts were included. Mean sternal notch to nipple (SNN) distance was mean 35.0 ± 6.6 cm (range 23–44.5) on the left and 34.9 ± 6.6 cm (range 18–46) on the right. Mean resection weight was 1152.2 ± 368.6 g (range 810–2926) on the left and 1159.4 ± 326.6 g (range 800–2528) on the right. The total complication rate was 22.7%. Minor complications occurred in 63 (18.6%) breasts. Major complications occurred in 12 (4.1%) breasts. NAC congestion and partial necrosis occurred in 1.8% and total NAC necrosis in 0.9%.
Conclusion
The SMP reduction technique is a safe option for gigantic breast reduction with comparable complication rates to other techniques. Preoperative measurements or resection weights are not reliable risk factors alone. High tissue density may be a significant risk factor. High-risk breasts mandate surgical planning and should be tailored to include technical modifications as described.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
02 June 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-022-02918-3
References
Hall-Findlay EJ, Shestak KC (2015) Breast reduction. Plast Reconstr Surg 136(4):531e–544e
Fino P, Di Taranto G, Toscani M, Scuderi N (2016) Surgical therapy of breast hypertrophy: a comparison of complications and satisfaction rate in large and small superior pedicle custom-made reduction mammaplasty. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 20(21):4411–4415
Sak MC, Akın S, Ersen B, Tunalı O, Ismail A (2017) Management of gigantomastia: outcomes of superomedial pedicle with vertical scar or wise pattern skin excision. World J Plast Surg 6(2):206–211
Karacaoglu E, Zienowicz RJ (2017) Septum-inferior-medial (SIM)-based pedicle: a safe pedicle with well-preserved nipple sensation for reduction in gigantomastia. Aesthet Plast Surg 41(1):1–9
Wettstein R, Christofides E, Pittet B, Psaras G, Harder Y (2011) Superior pedicle breast reduction for hypertrophy with massive ptosis. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 64(4):500–507
Dancey A, Khan M, Dawson J, Peart F (2008) Gigantomastia—a classification and review of the literature. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 61(5):493–502
Bauermeister AJ, Gill K, Zuriarrain A, Earle SA, Newman MI (2019) Reduction mammaplasty with superomedial pedicle technique: a literature review and retrospective analysis of 938 consecutive breast reductions. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 72(3):410–418
Lugo LM, Prada M, Kohanzadeh S, Mesa JM, Long JN, de la Torre J (2013) Surgical outcomes of gigantomastia breast reduction superomedial pedicle technique: a 12 year retrospective study. Ann Plast Surg 70(5):533–537
Davis GM, Ringler SL, Short K, Sherrick D, Bengtson BP (1995) Reduction mammaplasty: long-term efficacy, morbidity, and patient satisfaction. Plast Reconstr Surg 96(5):1106–1110
Dabbah A, Lehman JA Jr, Parker MG, Tantri D, Wagner DS (1995) Reduction mammaplasty: an outcome analysis. Ann Plast Surg 35(4):337–341
O'Grady KF, Thoma A, Dal Cin A (2005) A comparison of complication rates in large and small inferior pedicle reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 115(3):736–742
Ashour T, Khachaba Y, El Naggar A (2018) Supero-medial reduction mammaplasty: a safe and reliable technique in gigantomastia and severe breast ptosis. Electron Physician 10(8):7230–7234
Landau AG, Hudson DA (2008) Choosing the superomedial pedicle for reduction mammaplasty in gigantomastia. Plast Reconstr Surg 121(3):735–739
Nahabedian MY, McGibbon BM, Manson PN (2000) Medial pedicle reduction mammaplasty for severe mammary hypertrophy. Plast Reconstr Surg 105(3):896–904
Antony AK, Yegiyants SS, Danielson KK, Wisel S, Morris D, Dolezal RF, Cohen MN (2013) A matched cohort study of superomedial pedicle vertical scar breast reduction (100 breasts) and traditional inferior pedicle Wise-pattern reduction (100 breasts): an outcomes study over 3 years. Plast Reconstr Surg 132(5):1068–1076
Brown RH, Siy R, Khan K, Izaddoost S (2015) The superomedial pedicle wise-pattern breast reduction: reproducible, reliable, and resilient. Semin Plast Surg 29(2):94–101
Amini P, Stasch T, Theodorou P, Altintas AA, Phan V, Spilker G (2010) Vertical reduction mammaplasty combined with a superomedial pedicle in gigantomastia. Ann Plast Surg 64(3):279–285
Mistry RM, MacLennan SE, Hall-Findlay EJ (2017) Principles of breast re-reduction: a reappraisal. Plast Reconstr Surg 139(6):1313–1322
Cunningham BL, Gear AJ, Kerrigan CL, Collins ED (2005) Analysis of breast reduction complications derived from the BRAVO study. Plast Reconstr Surg 115(6):1597–1604
Davison SP, Mesbahi AN, Ducic I, Sarcia M, Dayan J, Spear SL (2007) The versatility of the superomedial pedicle with various skin reduction patterns. Plast Reconstr Surg 120(6):1466–1476
Lacerna M, Spears J, Mitra A, Medina C, McCampbell E, Kiran R, Mitra A (2005) Avoiding free nipple grafts during reduction mammaplasty in patients with gigantomastia. Ann Plast Surg 55(1):21–24
Gerzenshtein J, Oswald T, McCluskey P, Caplan J, Angel MF (2005) Avoiding free nipple grafting with the inferior pedicle technique. Ann Plast Surg 55(3):245–249
Mofid MM, Dellon AL, Elias JJ, Nahabedian MY (2002) Quantitation of breast sensibility following reduction mammaplasty: a comparison of inferior and medial pedicle techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg 109(7):2283–2288
Nahabedian MY, Mofid MM (2002) Viability and sensation of the nipple-areolar complex after reduction mammaplasty. Ann Plast Surg 49(1):24–32
Uslu A, Korkmaz MA, Surucu A, Karaveli A, Sahin C, Ataman MG (2019) Breast reduction using the superomedial pedicle- and septal perforator-based technique: our clinical experience. Aesthet Plast Surg 43(1):27–35
Greco R, Noone B (2017) Evidence-based medicine: reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 139(1):230e–239e
Hall-Findlay EJ (2002) Pedicles in vertical breast reduction and mastopexy. Clin Plast Surg 29(3):379–391
Hammond DC, Loffredo M (2012) Breast reduction. Plast Reconstr Surg 129(5):829e–e839
Gradinger GP (1988) Reduction mammoplasty utilizing nipple-areola transplantation. Clin Plast Surg 15(4):641–654
Colen SR (2001) Breast reduction with use of the free nipple graft technique. Aesthetic Surg J 21(3):261–271
Kerrigan CL, Comizio RC, Ho O (2010) Superomedial pedicle breast reduction using a vertical pattern. In: Hall-Findlay EJ, Evans GRD (eds) Aesthetic and reconstructive surgery of the breast, 1st edn. Saunders Ltd, London, pp 284–285
van Deventer PV, Graewe FR (2016) The blood supply of the breast revisited. Plast Reconstr Surg 137(5):1388–1397
van Deventer PV (2004) The blood supply to the nipple-areola complex of the human mammary gland. Aesthetic Plast Surg 28(6):393–398
Michelle le Roux C, Kiil BJ, Pan WR, Rozen WM, Ashton MW (2010) Preserving the neurovascular supply in the Hall-Findlay superomedial pedicle breast reduction: an anatomical study. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 63(4):655–662
Spear SL, Howard MA (2003) Evolution of the vertical reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 112(3):855–869
Roehl K, Craig ES, Gómez V, Phillips LG (2008) Breast reduction: safe in the morbidly obese? Plast Reconstr Surg 122(2):370–378
Fisher J, Kent K (2012) Reduction mammoplasty. In: Neligan P, Warren R (eds) Neligan’s plastic surgery, 3rd edn. W.B. Saunders Company Ltd, New York, pp 162–163
Hammond DC (1999) Short scar periareolar inferior pedicle reduction (SPAIR) mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 103(3):890–902
Hammond DC, O'Connor EA, Knoll GM (2015) The short-scar periareolar inferior pedicle reduction technique in severe mammary hypertrophy. Plast Reconstr Surg 135(1):34–40
Baslaim MM, Al-Amoudi SA, Hafiz M, Al-Hazmi WM, Salman BA, Al-Amoudi MK (2018) The safety, cosmetic outcome, and patient satisfaction after inferior pedicle reduction mammaplasty for significant macromastia. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 6(6):e1798
Kalliainen LK, ASPS Health Policy Committee (2012) ASPS clinical practice guideline summary on reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 130(4):785–789
Lista F, Ahmad J (2006) Vertical scar reduction mammaplasty: a 15-year experience including a review of 250 consecutive cases. Plast Reconstr Surg 117(7):2152–2169
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the members of our department for their support during this manuscript preparation. We also would like to thank the department of graphic design in our institution for the help of illustration preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Human or Animal Rights
The article does not obtain studies with human participants or animal performed by our authors.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, inform consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article was updated to correct the order of the authors’ family and given names.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singolda, R., Bracha, G., Zoabi, T. et al. Superiomedial Pedicle Breast Reduction for Gigantic Breast Hypertrophy: Experience in 341 Breasts and Suggested Safety Modifications. Aesth Plast Surg 45, 375–385 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01973-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01973-y