Abstract
Background
Nasal filling has gained popularity in plastic surgery practice and strengthened the surgeon's hand. Mild deformities of the nose can be treated with nasal filling instead of rhinoplasty, or small contour irregularities following surgical rhinoplasty can be corrected by dermal filler injections. It is a significant advantage of hyaluronic acid (HA) fillers that they can be dissolved with hyaluronidase in case of the patient dislikes the appearance and desires a surgical rhinoplasty. However, there is no publication about when rhinoplasty surgery can be performed safely after hyaluronidase injection.
Objectives
In this case series, we shared our experiences with nasal filling in plastic surgery practice under three headings: primary nasal filling, nasal filling for post-rhinoplasty defects and rhinoplasty after hyaluronidase injection in dissatisfied filling patients. We presented our nasal filling technique, indications, result analysis and also our rhinoplasty experiences we performed at different times after hyaluronidase injection.
Methods
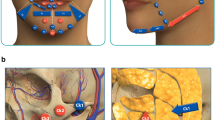
Nasal filling patients from July 2015 to March 2020 were divided and analyzed in three groups: (a) Primary nasal filling was provided to 62 patients, (b) nasal filling for post-rhinoplasty defect was provided to 18 patients, and (c) rhinoplasty after hyaluronidase injection was performed in five patients who are not satisfied with results. The duration between hyaluronidase and rhinoplasty operation was, respectively, 6 months, 3 months, 3 months, 2 months and 1 week.
Results
(a) In primary nasal filling, 57 patients were fully satisfied, two patients were satisfied, and three patients were dissatisfied with results. Results were stable up to at least 6 months (Range 6–14 months). (b) In nasal filling for post-rhinoplasty defects, all patients were fully satisfied with results. Results were stable for at least 12 months (Range 12–36 months). (c) In rhinoplasty after hyaluronidase injection, any filling residue was not observed, and there were no complications. The postoperative results were satisfactory.
Conclusion
Nasal filling with hyaluronic acid represents an excellent alternative for patients who do not wish to undergo a rhinoplasty or a revision rhinoplasty procedure. HA filler can be dissolved easily with hyaluronidase if the patient does not like the result, and we think that rhinoplasty can be performed safely at least one week later from hyaluronidase treatment.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASAPS: Cosmetic (aesthetic) surgery national data bank statistics (2018) https://www.surgery.org/sites/default/files/ASAPS-Stats2018_0.pdf
Rauso R, Tartaro G, Chirico F, Zerbinati N, Albani G, Rugge L (2020 Mar) Rhinofilling with hyaluronic acid thought as a cartilage graft. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 48(3):223–228
Kontis TC (2018) The art of camouflage: when can a revision rhinoplasty be nonsurgical. Facial Plast Surg 34(3):270–277
Stupak HD, Moulthrop TH, Wheatley P, Tauman AV, Johnson CM Jr (2007) Calcium hydroxylapatite gel (Radiesse) injection for the correction of postrhinoplasty contour deficiencies and asymmetries. Arch Facial Plast Surg 9(02):130–136
De Lorenzi C (2014) Complications of injectable fillers, part 2: vascular complications. Aesthet Surg J 34(4):584–600
Jasin ME (2013 May) Nonsurgical rhinoplasty using dermal fillers. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am 21(2):241–252
Soparkar C, Patrinely J (2007) Hyaluronidase and restylane. Arch Facial Plast Surg 9:299–300
Menon H, Thomas M, D’silva J (2010) Low dose of hyaluronidase to treat over correction of HA filler-a case report. J Plast Reconstr Aesthetic Surg 63:416–417
Buhren BA, Schrumpf H, Hoff NP, Bölke E, Hilton S, Gerber PA (2016) Hyaluronidase: from clinical applications to molecular and cellular mechanisms. Eur J Med Res 21:5
King M, Convery C, Davies E (2018) The use of hyaluronidase in aesthetic practice. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 11(6):428–434
Bektas G (2019) Lateral crural steal and set back combination for different types of nasal tip. Akd Tıp D / Akd Med J / 1:143–150
Knapp TR, Vistnes LM (1985) The augmentation of soft tissue with injectable collagen. Clin Plast Surg 12:221–225
Webster RC, Hamdan US, Gaunt JM et al (1986) Rhinoplastic revisions with injectable silicone. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 112:269–276
Han SK, Shin SH, Kang HJ et al (2006) Augmentation rhinoplasty using injectable tissue-engineered soft tissue. Ann Plast Surg 56:251–255
Beer KR (2006) Nasal reconstruction using 20mg/mL cross-linked hyaluronic acid. J Drugs Dermatol 5:465–466
Heden P (2016) Nasal reshaping with hyaluronic acid: an alternative or complement to surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 4(11):e1120
Rohrich RJ, Ghavami A, Crosby MA (2007) The role of hyaluronic acid fillers (Restylane) in facial cosmetic surgery: review and technical considerations. Plast Reconstr Surg 120(6 Suppl):41S–54S
Johnson ON 3rd, Kontis TC (2016 Oct) Nonsurgical rhinoplasty. Facial Plast Surg 32(5):500–506
Kurkjian TJ, Ahmad J, Rohrich RJ (2014 Feb) Soft-tissue fillers in rhinoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 133(2):121–126
Papakonstantinou E, Roth M, Karakiulakis G (2012) HA: a key molecule in skin aging. Dermatoendocrinol 4(3):253–258
de Lacerda DA, Zancanaro P (2007) Filler rhinoplasty. Dermatol Surg. 33(Suppl 2):S207–S212 discussion S212
Bray D, Hopkins C, Roberts DN (2010 Jun) Injection rhinoplasty: non-surgical nasal augmentation and correction of post-rhinoplasty contour asymmetries with hyaluronic acid: how we do it. Clin Otolaryngol 35(3):227–230
Filippova OV, Afonichev KA, Krasnogorsky IN, Vashetko RV (2017) Clinical and morphological characteristics of the vascular bed of hypertrophic scar tissue in different periods of its formation. Pediatr Traumatol Orthop Reconstr Surg 5(3):25–35
Bailey SH, Fagien S, Rohrich RJ (2014) Changing role of hyaluronidase in plastic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 133(2):127e–132e
Robati RM, Moeineddin F, Almasi-Nasrabadi M. The risk of skin necrosis following hyaluronic acid filler injection in patients with a history of cosmetic rhinoplasty. Aesthet Surg J. 2018.
Kim DW, Yoon ES, Ji YH, Park SH, Lee BI, Dhong ES (2011) Vascular complications of HA fillers and the role of hyaluronidase in management. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 64(12):1590–1595
Lambros V (2004) The use of hyaluronidase to reverse the effects of hyaluronic acid filler. Plast Reconstr Surg 114(1):277
Soparkar CN, Patrinely JR, Tschen J (2004) Erasing restylane. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 20(4):317–318
Cohen JL, Biesman BS, Dayan SH, DeLorenzi C, Lambros VS, Nestor MS et al (2015) Treatment of Hyaluronic Acid Filler-Induced Impending Necrosis With Hyaluronidase: Consensus Recommendations. Aesthet Surg J 35(7):844–849
DeLorenzi C (2014) Transarterial degradation of hyaluronic acid filler by hyaluronidase. Dermatol Surg 40(8):832–841
DeLorenzi C (2017) New High Dose Pulsed Hyaluronidase Protocol for Hyaluronic Acid Filler Vascular Adverse Events. Aesthet Surg J 37(7):814–825
Longaker MT, Chiu ES, Adzick NS, Stern M, Harrison MR, Stern R (1991) Studies in fetal wound healing. V. A prolonged presence of hyaluronic acid characterizes fetal wound fluid. Ann Surg 213:292–296
Brody H (2005) Use of hyaluronidase in the treatment of granulomatous hyaluronic acid reactions or unwanted hyaluronic acid misplacement. Dermatol Surg 31:893–897
Fallacara A, Baldini E, Manfredini S, Vertuani S (2018) Hyaluronic acid in the third millennium. Polymers 10:701
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Human and Animal Rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bektas, G., Cinpolat, A. & Rizvanovic, Z. Nasal Filling in Plastic Surgery Practice: Primary Nasal Filling, Nasal Filling for Post-rhinoplasty Defects, Rhinoplasty After Hyaluronidase Injection in Dissatisfied Nasal Filling Patients. Aesth Plast Surg 44, 2208–2218 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01895-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01895-9