Abstract
Background
The inferior pedicle mammaplasty is particularly applied to large breasts with a long sternal notch to nipple distance. The present study reports modifications developed to solve the bottoming-out deformity, the lack of upper pole fullness and the wound healing problems seen at the reverse T-zone, known disadvantages of the inferior pedicle reduction mammaplasty, and evaluates postoperative sensation.
Methods
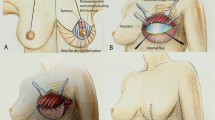
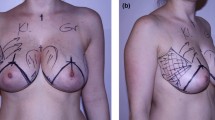
A total of 110 patients with a mean age of 32 underwent the same technique. In this technique, two pairs of quadrangular and triangular flaps were planned from the skin of resection sites. The triangular dermal flaps and quadrangular flaps were suspended from the periosteum of the 2nd and 4th ribs, respectively. The distance from the nipple to inframammary fold was measured at the postoperative 1st month and 1st year. In the postoperative period, a nipple–inframammary fold distance increase of over 2 cm was determined as bottoming-out deformity. Sensation evaluations were performed by subjective and objective tests.
Results
The mean sternal notch to nipple distance was 35.00 cm. After operation, the mean distance between the sternal notch and the nipple was 20.00 cm. NAC examination revealed normal sensation in all patients. Whereas the preoperative mean areolar threshold value was 36.70 g/mm2, the postoperative first-year mean areolar pressure threshold value was 35.50 g/mm2 (p < 0.0001). The preoperative mean nipple pressure threshold value was 25.30 g/mm2, whereas the postoperative first-year mean nipple pressure threshold value was 26.00 g/mm2 (p = 0.5471). The postoperative first-month mean sternal notch to nipple distance value of the patients was 20.00 cm, whereas the postoperative first-year mean sternal notch to nipple distance value of the patients was 20.00 cm, (p = 0.0648). The postoperative first-month mean nipple to submammary fold distance value of the patients was 10.50 cm, the postoperative first-year mean nipple to submammary fold distance value of the patients was 11.00 cm (p < 0.0001) There were no patients determined as having bottoming-out deformity. No breast asymmetry was encountered at the late follow-up period. All patients, except the scarred ones, were satisfied with the results.
Conclusıon
In this study, we achieved an internal fascial reconstruction using a pair of triangular and quadrangular dermal flaps suspended to the rib periosteum. We believe that our modifications will contribute to decreasing the disadvantages of the inferior pedicle breast reduction technique.
Level of Evidence V
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson DL et al (2005) Improving long-term breast shape with the medial pedicle wise pattern breast reduction. Plast Reconstr Surg 115(7):1937–1943
Ribeiro L (1975) A new technique for reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 55(3):330–334
Courtiss EH, Goldwyn RM (1977) Reduction mammaplasty by the inferior pedicle technique. An alternative to free nipple and areola grafting for severe macromastia or extreme ptosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 59(4):500–507
Robbins TH (1977) A reduction mammaplasty with the areola-nipple based on an inferior dermal pedicle. Plast Reconstr Surg 59(1):64–67
Georgiade NG et al (1979) Reduction mammaplasty utilizing an inferior pedicle nipple-areolar flap. Ann Plast Surg 3(3):211–218
Reich J (1979) The advantages of a lower central breast segment in reduction mammaplasty. Aesthetic Plast Surg 3(1):47–56
Hall-Findlay EJ (2002) Pedicles in vertical breast reduction and mastopexy. Clin Plast Surg 29(3):379–391
Yuksel F et al (2012) Experience with vertical mammaplasty: advantages and drawbacks of Hall-Findlay’s superomedial pedicle technique and improving the results by adding modifications to the technique. Aesthetic Plast Surg 36(6):1329–1333
Widgerow AD (2005) Breast reduction with inferior pedicle fascial suspension. Aesthetic Plast Surg 29(6):532–537 discussion 538-9
Weinstein S (1993) Fifty years of somatosensory research: from the Semmes-Weinstein monofilaments to the Weinstein Enhanced Sensory Test. J Hand Ther 6(1):11–22 discussion 50
Levin S, Pearsall G, Ruderman RJ (1978) Von Frey’s method of measuring pressure sensibility in the hand: an engineering analysis of the Weinstein-Semmes pressure aesthesiometer. J Hand Surg Am 3(3):211–216
Schlenz I et al (2005) Alteration of nipple and areola sensitivity by reduction mammaplasty: a prospective comparison of five techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg 115(3):743–751 discussion 752–4
Hamdi M et al (2001) A prospective quantitative comparison of breast sensation after superior and inferior pedicle mammaplasty. Br J Plast Surg 54(1):39–42
Wise RJ (1956) A preliminary report on a method of planning the mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg (1946) 17(5):367–375
Pennington DG (2006) Improving the results of inferior pedicle breast reduction using pedicle suspension and plication. Aesthetic Plast Surg 30(4):390–394
Zic R et al (2013) The “dermal cage”: a modification of the inferior pedicle breast reduction. Aesthetic Plast Surg 37(2):364–371
Echo A, Guerra G, Yuksel E (2011) The dermal suspension sling: shaping the inferior pedicle during breast reduction. Aesthetic Plast Surg 35(4):608–616
Frey M (1999) A new technique of reduction mammaplasty: dermis suspension and elimination of medial scars. Br J Plast Surg 52(1):45–51
Baumeister RG (2003) Curtain type combined pedicled reduction mammoplasty with internal suspension for extensive hypertrophic and ptotic breasts. Br J Plast Surg 56(2):114–119
Aydin H et al (2003) Reduction mammaplasty using inferior pedicle technique combined with dermal suspension. Plast Reconstr Surg 111(3):1362–1363
Rubin JP, Gusenoff JA, Coon D (2009) Dermal suspension and parenchymal reshaping mastopexy after massive weight loss: statistical analysis with concomitant procedures from a prospective registry. Plast Reconstr Surg 123(3):782–789
Brown RH, Izaddoost S, Bullocks JM (2010) Preventing the “bottoming out” and “star-gazing” phenomena in inferior pedicle breast reduction with an acellular dermal matrix internal brassiere. Aesthetic Plast Surg 34(6):760–767
Mallucci P, Branford OA (2012) Concepts in aesthetic breast dimensions: analysis of the ideal breast. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 65(1):8–16
Jaspars JJ et al (1997) The cutaneous innervation of the female breast and nipple-areola complex: implications for surgery. Br J Plast Surg 50(4):249–259
Mofid MM et al (2002) Quantitation of breast sensibility following reduction mammaplasty: a comparison of inferior and medial pedicle techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg 109(7):2283–2288
Acknowledgments
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflict of interest
All named authors hereby declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose. None of the authors have a financial interest in any of the products, devices, or drugs mentioned in this article.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Temel, M., Karakaş, A.O., Dokuyucu, R. et al. ‘‘The Dermal Internal Brassiere Flap,’’ A New Modification of Inferior Pedicle Breast Reduction Technic. Aesth Plast Surg 39, 350–358 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-015-0483-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-015-0483-y