Abstract
Background
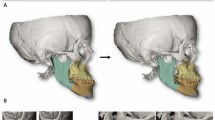
Mandibular angle ostectomy (MAO) is commonly used to correct prominent mandibular angles through an intraoral approach. However, limited vision in the operative site may lead to difficulties or complications during surgery. Therefore, it is necessary to develop an effective method for helping surgeons to perform MAO more precisely and safely.
Methods
In this study, we report a novel method of a computer image-guided surgical template for navigation of MAO, and evaluate its accuracy and clinical outcomes. Nine patients with a prominent mandibular angle were enrolled in this study. A pair of stereolithographic templates was fabricated by computer-aided image design and 3D printing. In all cases, bilateral MAO was performed under the guide of these templates. Post-operative effects were evaluated by 3D curve functions and maximal shell-to-shell deviations.
Results
All patients were satisfied with their cosmetic outcomes. The mean and SD of ICC between R-Sim and R-Post were 0.958 ± 0.011; between L-Sim and L-Post, 0.965 ± 0.014; and between R-Post and L-Post, 0.964 ± 0.013. The maximal shell-to-shell deviations between the simulated mandibular contour and post-operative mandibular contour on the right and left sides were 2.02 ± 0.32 and 1.97 ± 0.41 mm, respectively.
Conclusion
The results of this study suggest that this new technique could assist surgeons in making better pre-surgical plans and ensure more accurate and safer manipulation for completion of this procedure.
Level of Evidence V
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu D, Huang J, Shan L, Wang J (2011) Intraoral curved ostectomy for prominent mandibular angle by grinding, contiguous drilling, and chiseling. J Craniofac Surg 22:2109–2113
Satoh K (1998) Mandibular contouring surgery by angular contouring combined with genioplasty in orientals. Plast Reconstr Surg 101:461–472
Oh YW, Han KT, Ahn ST (1990) The complication of mandibular angle reduction. J Korean Soc Plast Reconstr Surg 17:645–652
Hwang K, Han JY, Kil MS, Lee SI (2002) Treatment of condyle fracture caused by mandibular angle ostectomy. J Craniofac Surg 13:709–712
Kane AA, Lo LJ, Chen YR, Hsu KH, Noordhoff MS (2000) The course of the inferior alveolar nerve in the normal human mandibular ramus and in patients presenting for cosmetic reduction of the mandibular angles. Plast Reconstr Surg 106:1162–1174; discussion 1175–1166
Zinser MJ, Mischkowski RA, Sailer HF, Zoller JE (2012) Computer-assisted orthognathic surgery: feasibility study using multiple CAD/CAM surgical splints. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 113:673–687
Choi JY, Song KG, Baek SH (2009) Virtual model surgery and wafer fabrication for orthognathic surgery. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 38:1306–1310
Xia J, Ip HH, Samman N, Wang D, Kot CS, Yeung RW, Tideman H (2000) Computer-assisted three-dimensional surgical planning and simulation: 3D virtual osteotomy. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 29:11–17
Ye N, Long H, Xue J, Wang S, Yang X, Lai W (2014) Integration accuracy of laser-scanned dental models into maxillofacial cone beam computed tomography images of different voxel sizes with different segmentation threshold settings. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 117:780–786
Adams WM (1949) Bilateral hypertrophy of the masseter muscle; an operation for correction; case report. Br J Plast Surg 2:78–81
Gui L, Yu D, Zhang Z, Changsheng LV, Tang X, Zheng Z (2005) Intraoral one-stage curved osteotomy for the prominent mandibular angle: a clinical study of 407 cases. Aesthet Plast Surg 29:552–557
Kim Y, Park B (2003) Resection of the prominent mandible angle with intraoral and external approach. Aesthetic Plast Surg 27:38–42; discussion 43
Yang DB, Park CG (1991) Mandibular contouring surgery for purely aesthetic reasons. Aesthet Plast Surg 15:53–60
Ying B, Wu S, Yan S, Hu J (2011) Intraoral multistage mandibular angle ostectomy: 10 years’ experience in mandibular contouring in Asians. J Craniofac Surg 22:230–232
Hsu YC, Li J, Hu J, Luo E, Hsu MS, Zhu S (2010) Correction of square jaw with low angles using mandibular “V-line” ostectomy combined with outer cortex ostectomy. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 109:197–202
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant from Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (No. 20130181130004). We also thank 3D Orthodontics & Craniofacial Laboratory, Shanghai TiTOK Medical Technology Co., Ltd.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, N., Long, H., Zhu, S. et al. The Accuracy of Computer Image-Guided Template for Mandibular Angle Ostectomy. Aesth Plast Surg 39, 117–123 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-014-0424-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-014-0424-1