Abstract
Background
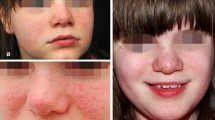
Tuberous sclerosis, an autosomal dominant neurocutaneous syndrome seen in approximately 1 in 6,000 people worldwide, is characterized by the appearance of hamartomas in multiple organs. The classic clinical triad consists of angiofibromas, epilepsy, and developmental delay. Dermatologic disorder is one of the main characteristics. Angiofibromas, a common form of presentation, causes significant cosmetic and medical problems. The current treatment for skin lesions is laser therapy. The carbon dioxide (CO2) laser has been used satisfactorily in treating these lesions, but several studies have demonstrated a high percentage of recurrences. Erbium:yttrium–aluminum–garnet (YAG) laser treatment has been used to resurface skin abnormalities in patients with dermatologic conditions. The dye laser as an alternative uses the principles of selective photothermolysis and is very effective in treating the vascular component of tuberous sclerosis. The use of all these lasers to treat skin lesions in patients affected by tuberous sclerosis has never been described in the literature.
Methods
A retrospective study, conducted from 2007 to May 2013, investigated 13 patients who had tuberous sclerosis treated with an erbium:YAG/CO2/dye laser combination.
Results
All the patients showed great improvement of their skin lesions. The results were evident immediately after the first treatment. No patient experienced complications or recurrence.
Conclusions
The combined use of the erbium:YAG/Dye/CO2 laser is a safe and effective treatment for skin lesions in patients affected by tuberous sclerosis.
Level of Evidence V
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Osborne PJ, Fryer A, Webb D (1991) Epidemiology of tuberous sclerosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 615:125–127
Grieb S, Kruse R, Bruch-Gerharz D, Reifenberger J (2008) Tuberous sclerosis: diagnostic criteria and new treatment approaches. Hautarzt 59:774–776
Wataya-Kaneda M, Tanaka M, Hamasaki T, Katayama I (2013) Trends in the prevalence of tuberous sclerosis complex manifestations: an epidemiological study of 166 Japanese patients. PLoS One 8:e63910. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0063910
Bourneville DM (1880) Sclerose tubereuse des circonvolutions cerebrales: idiotie et epilepsie hemiplegique. Arch Neurol 1:81–91
Webb DW, Clarke A, Fryer A, Osborne JP (1996) The cutaneous features of tuberous sclerosis: a population study. Br J Dermatol 135:1–5
Fernández-Guarino M, Boixeda P, Anaya MJ, Beldar P, Jaéna P (2009) Clinical findings in 67 patients with tuberous sclerosis. Actas Dermosifiliogr 100:596–601
Crino PB, Nathanson KL, Henske EP (2006) The tuberous sclerosis complex. N Engl J Med 355:1645–1656
Roach ES, Gomez MR, Northrup H (1998) Tuberous sclerosis complex consensus conference: revised clinical diagnostic criteria. J Child Neurol 13:624–628
Sergiusz J, Zwiak, Schwartz AR, Janniger CK, Bielicka-Cymerman J (2000) Usefulness of diagnostic criteria of tuberous sclerosis complex in pediatric patients. J Child Neurol 15:652
Nickel WR, Reed WB (1965) Tuberous sclerosis: special reference to the microscopic alteration in the cutaneous hemangiomas. Arch Dermatol 85:89–106
Cheadle JP, Reeve MP, Sampson JR, Kwiatkowski DJ (2000) Molecular genetics advances in tuberous sclerosis. Hum Genet 107:97–114
Kevin C (2006) The neurobiology of tuberous sclerosis complex. Semin Pediatr Neurol 13:37–42
Jozwiak J, Jozwiak S, Wlodarski P (2008) Possible mechanisms of disease development in tuberous sclerosis. Lancet Oncol 9:73–79
Mozaffari M, Hoogeveen-Westerveld M, Kwiatkowski D, Sampson J, Ekong R, Povey S, den Dunnen JT, van den Ouweland A, Halley D, Nellist M (2009) Identification of a region required for TSC1 stability by functional analysis of TSC1 missense mutations found in individuals with tuberous sclerosis complex. BMC Med Genet 10:88
Capo-Chichi JM, Tcherkezian J, Hamdan FF, Décarie JC, Dobrzeniecka S, Patry L, Nadon MA, Mucha BE, Major P, Shevell M, Ouled Amar Bencheikh B, Joober R, Samuels ME, Rouleau GA, Roux PP, Michaud JL (2013) Disruption of TBC1D7, a subunit of the TSC1–TSC2 protein complex, in intellectual disability and megalencephaly. J Med Genet 50(11):740–744
Kevin C (2010) Tuberous sclerosis complex: a brave new world? Curr Opin Neurol 23:189–193
Sancak O, Nellist M, Goedbloed M et al (2005) Mutational analysis of the TSC1 and TSC2 genes in a diagnostic setting: genotype–phenotype correlations and comparison of diagnostic DNA techniques in tuberous sclerosis complex. Eur J Hum Genet 13:731–741
Zhao XY, Yang S, Zhou HL, Zhu YG, Wei L, Du WH, Ren YQ, Liang YH, Hou YX, Chen JJ, Zhang XJ (2006) Two novel TSC2 mutations in Chinese patients with tuberous sclerosis complex and a literature review of 20 patients reported in China. Br J Dermatol 155:1070–1073
Yuan CD, Chang XL, Gao M, Xiao FL, Wu YQ, Liu Q, Shen SK, Liu JL, Du WH, Liu JJ, Yang S, Zhang XJ, Zhou FS, Fang QY (2008) A novel mutation (insTCCG) in the TSC2 gene in a Chinese patient with tuberous sclerosis complex. J Dermatol Sci 49:92–94
Dvir E, Hirshowitz B (1979) Cryosurgery for the facial lesions of tuberous sclerosis. Harefuah 97:245–246
Dvir E, Hirshowitz B (1980) The use of cryosurgery in treating the fibrous papules of tuberous sclerosis. Ann Plast Surg 4:158–160
Menon PA (1982) Dermabrasion for the management of angiofibromas in tuberous sclerosis. J Dermatol Surg Oncol 8:984–985
Cristodor P, Esmaeili M, Glăja R, Brînzeu DT, Ursoniu S (2007) Dermabrasion in two cases of tuberous sclerosis. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi 111:918–921
Drake DB, Morgan RF, Cooper PH (1992) Shave excision and dermabrasion for facial angiofibroma in tuberous sclerosis. Ann Plast Surg 28:377–380
Fischer K, Blain B, Zhang F, Richards L, Lineaweaver WC (2001) Treatment of facial angiofibromas of tuberous sclerosis by shave excision and dermabrasion in a dark-skinned patient. Ann Plast Surg 46:332–335
Capurro S, Fiallo P (2001) Timed surgery for treatment of angiofibromas in tuberous sclerosis. Dermatol Surg 27:486–488
Fischer K, Blain B, Zhang F, Richards L, Lineaweaver WC (2001) Treatment of facial angiofibromas of tuberous sclerosis by shave excision and dermabrasion in a dark-skinned patient. Ann Plast Surg 46:332–335
Truchuelo T, Díaz-Ley B, Ríos L, Alcántara J, Jaén P (2012) Facial angiofibromas treated with topical rapamycin: an excellent choice with fast response. Dermatol Online J 18:15
Foster RS, Bint LJ, Halbert AR (2012) Topical 0.1 % rapamycin for angiofibromas in paediatric patients with tuberous sclerosis: a pilot study of four patients. Australas J Dermatol 53:52–56. doi:10.1111/j.1440-0960.2011.00837.x Epub 29 Dec 2011
Wheless JW, Almoazen H (2013) A novel topical rapamycin cream for the treatment of facial angiofibromas in tuberous sclerosis complex. J Child Neurol 28(7):933–936
Pasyk KA, Argenta LC (1988) Argon laser surgery of skin lesions in tuberous sclerosis. Ann Plast Surg 20:426–433
Berlin AL, Billick RC (2002) Use of CO2 laser in the treatment of periungual fibromas associated with tuberous sclerosis. Dermatol Surg 28:434–436
Belmar P, Boixeda P, Baniandrés O, Fernández-Lorente M, Arrazola JM (2005) Long-term follow-up of angiofibromas treated with CO2 laser in 23 patients with tuberous sclerosis. Actas Dermosifiliogr 96:498–503
Pantelis A, Bootz F, Kühnel T (2007) Laser skin resurfacing and fibrin sealing as successful treatment for facial angiofibromas in tuberous sclerosis. HNO 55:1009–1011
Eisen DB, Fazel N (2008) Treatment of gingival fibromas using CO2 laser and electrosurgery in a patient with tuberous sclerosis. Dermatol Online J 14:7
Bittencourt RCA, Huilgol SC, Seed PT, Calonje E, Markey AC, Barlow RJ (2001) Treatment of angiofibromas with a scanning carbon dioxide laser: a clinicopathologic study with long-term follow-up. J Am Acad Dermatol 45:731–735
Kaufman AJ, Grekin RC, Geisse JK, Frieden IJ (1995) Treatment of adenoma sebaceum the copper vapor laser. J Am Acad Dermatol 33:770–774
Janniger CK, Goldberg DJ (1990) Angiofibromas in tuberous sclerosis: comparison and treatment by carbon dioxide and argon laser. J Dermatol Surg Oncol 16:317–320
Mills CM, Lanigan SW (1995) Treatment of multiple angiofibroma with the pulsed dye laser. J Dermatol Treat 6:237–238
Weinberger CH, Endrizzi B, Hook KP, Lee PK (2009) Treatment of angiofibromas of tuberous sclerosis with 5-aminolevulinic acid blue light photodynamic therapy followed by immediate pulsed dye laser. Dermatol Surg 35:1849–1851
Boixeda P, Sanchez-Miralles E, Azana JM et al (1994) CO2, argon, and pulsed dye laser treatment of angiofibromas. J Dermatol Surg Oncol 20:808–812
Papadavid E, Markey A, Bellaney G, Walker NPJ (2002) Carbon dioxide and pulsed dye laser treatment of angiofibromas in 29 patients with tuberous sclerosis. Br J Dermatol 147:337–342
Ulrich H, Baumler W, Hohenleutner U, Landthaler M (2005) Neodymium-YAG laser for hemangiomas and vascular malformations: long-term results. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 3:436–440
Civas E, Koc E, Aksoy B, Aksoy HM (2009) Clinical experience in the treatment of different vascular lesions using a neodymium-doped yttrium-aluminum-garnet laser. Dermatol Surg 35:1933–1941
Bradley PF (1997) A review of the use of the neodymium YAG laser in oral and maxillofacial surgery. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 35:26–35
Lipper GM, Perez M (2006) Nonablative acne scar reduction after a series of treatments with a short-pulsed 1,064-nm neodymium:YAG laser. Dermatol Surg 32:998–1006
Lee DH, Choi YS, Min SU, Yoon MY, Suh DH (2009) Comparison of a 585-nm pulsed dye laser and a 1,064-nm Nd:YAG laser for the treatment of acne scars: a randomized split-face clinical study. Am Acad Dermatol 60:801–807
Vesnaver A, Dovsak DA (2006) Treatment of vascular lesions in the head and neck using Nd:YAG laser. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 34:17–24
Campolmi P, Bonam P, Cannarozzo G (2003) Laser e sorgenti luminose in dermatologia. Masson, Milano, pp 33–38
Goldman MP, Fitzpatrick RE (2000) Chirurgia laser in dermatologia. Mosby, Milano, pp 408–412
Fitzpatrick RE, Goldman MP (1994) CO2 laser surgery and skin resurfacing with carbon dioxide and erbium lasers. In: Goldman MP, Fitzpatrick RE (eds) Cutaneous laser surgery: the art and science of selective photothermolysis. Mosby, St. Louis, pp 198–256
Collawn SS (1999) Combination therapy: utilization of CO2 and Erbium: YAG lasers for skin resurfacing. Ann Plast Surg 42(1):21–26
Weiss ET, Geronemus RG (2010) New technique using combined pulsed dye laser and fractional resurfacing for treating facial angiofibromas in tuberous sclerosis. Lasers Surg Med 42:357–360. doi:10.1002/lsm.20939
Landthaler M, Hohenleutner U (2006) Laser therapy of vascular lesions (review). Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 22:324–332
Srinivas CR, Kumaresan M (2011) Lasers for vascular lesions: standard guidelines of care. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 77:349–368. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.79728
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00266-017-0878-z.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fioramonti, P., De Santo, L., Ruggieri, M. et al. Co2/Erbium:YAG/Dye Laser Combination: An Effective and Successful Treatment for Angiofibromas in Tuberous Sclerosis. Aesth Plast Surg 38, 192–198 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-013-0252-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-013-0252-8