Abstract
Background
Copaíba oil is an oleoresin obtained from the Copaiffera langsdorffii genus (Leguminoseae). It is widely used in folk medicine as an antiinflammatory, healing, and antiseptic agent. Comparative pharmacologic studies between different species of copaíba oils are scarce.
Methods
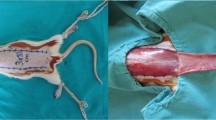
The protective effect of Copaiffera langsdorffii was evaluated on an experimental model of random skin flaps on rat dorsums.
Results
Seventy-two Wistar rats (average weight = 216.8 g) were divided randomly into four equal groups (saline control, vehicle control, GT200—Test 1, and GT400—Test 2). A caudally based rectangular flap, 2.5–8.0 cm in size, was elevated on the back of the rat using McFarlane’s method. The flap was sutured back into its original place. Copaifera and control drugs (saline and Tween 80) were administered by gavage 24, 12, and 2 h prior to the beginning of the experiment followed by daily doses for the next 7 days. To observe the effects of Copaifera, laboratory analyses included plasma and tissue levels of tiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBARS) and reduced glutathione (GSH) and tissue levels of myeloperoxidase (MPO).
Conclusion
The oil-resin of copaíba presents discrete antilipoperoxidation action, intense antioxidant action, and antiinflammatory activity during the ischemia and reperfusion of randomized cutaneous flaps. The effects of ischemia-reperfusion are complex and substances capable of increasing the tolerance of tissue to those effects by reducing the production or neutralizing the action of free radicals are needed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida KG, Fagundes DJ, Manna MC, Souza EF (2004) Ação do dimetil-sulfóxido na isquemia de retalhos randômicos de pele em ratos. Acta Cir Bras 19(6):649–657
Biondo-Simões ML, Greca FH, Paula JB, Chin EW, Santos EA, Stalhschmidt FL (2000) Effect of buflomedil on ischemic skin flaps: experimental study in rats. Acta Cir Bras 15(Suppl 3):36–40
Francisco Neto A, Silva JC, Fagundes DJ, Percário S, Novo NF, Juliano Y, Moreira Neto AA (2005) Oxidative alterations, total antioxidant status and nitric oxide study in rats submitted to ischemia and reperfusion of hind limbs. Acta Cir Bras 20(2):134–139 [in Portugeuse]
Hart K, Baur D, Hodam J, Lesoon-Wood L, Parham M, Keith K, Vasquez R, Ager E, Pizarro J (2006) Short- and long-term effects of sildenafil on skin flap survival in rats. Laryngoscope 116:522–528
Huemer GM, Wechselberger G, Otto-Schoeller A, Gurunluoglu R, Piza-Katzer H, Schoeller T (2003) Improved dorsal random-pattern skin flap survival in rats with a topically applied combination of Nonivamide and Nicoboxil. Plast Reconstr Surg 111(3):1207–1211
Bittencourt RC, Biondo-Simões ML, Paula JB, Martynetz J, Groth A (2005) Influence of minoxidil on ischemic cutaneous flaps in rats. Acta Cir Bras 20(6):450–454
Komorowska-Timek E, Timek TA, Brevetti LS, Szuba A, Stuelinger M, Hardesty RA, Buncke HJ (2004) Oral administration of L-arginine decreases necrosis of the epigastric skin flap in the rat. Ann Plast Surg 53(1):73–78
Souza Filho MV, Leal PR, Sbalchiero JC, Marques MJ (2002) Effect of ginkgo biloba extract on skin flap survival in rats. Rev Soc Bras Cir Plast 17(2):45–56
Ghavami A, Nutt MP, Hardy SP (2002) Heat shock protein and high-dose aspirin: effects on random skin flap survival in a rat model. Ann Plast Surg 48(1):60–67
McFarlane RM, DeYoung G, Henry RA (1965) The design of a pedicle flap in the rat to study necrosis and its prevention. Plast Reconstr Surg 35:177–178
Tyner TR, Shahbazian R, Nakashima J, Kane S, Sian K, Yamaguchi KT (2004) Propofol improves skin flap survival in a rat model: correlating reduction in flap-induced neutrophil activity. Ann Plast Surg 53(3):273–277
Sarifakioglu N, Gokrem S, Ates L, Akbuga UB, Aslan G (2004) The influence of sildenafil on random skin flap survival in rats: an experimental study. Br J Plast Surg 57:769–772
Esteves Junior I, Ferreira LM, Liebano RE (2004) Calcitonin gene-related peptide by iontophoresis on the viability of the randon skin flaps in rats. Acta Cir Bras 19(6):626–629
Fonseca AV, Ferreira LM, Gomes HC, Percario S (2004) Terazosin and propanolol as blockers to the deleterious effect of nicotine in a random skin flap in the rat. Acta Cir Bras 19(3):186–195
Yoshida WB, Campos EB (2005) Ischemia and reperfusion in skin flaps: effects of mannitol and vitamin C in reducing necrosis area in a rat experimental model. Acta Cir Bras 20(5):358–363
Junior IE, Masson IB, Ferreira LM, Liebano RE, Baldan C, Gomes AC (2005) Topical administration of hydralazine hydrochloride on the viability of randon skin flaps in rats. Acta Cir Bras 20(2):164–167 [in Portugeuse]
Aydogan H, Gurlek A, Parlakpinar H, Askar I, Bay-Karabulut A, Aydogan N, Fariz A, Acet A (2007) Beneficial effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) on the ischaemia-reperfusion injury in rat skin flaps. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 60(5):563–568
Ersoy A, Sevin K, Sevin A, Serel S (2007) Effects of clopidogrel on survival of rat skin flaps. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 60(8):861–863
Paiva LA, Gurgel LA, Silva RM, Tomé AR, Gramosa NV, Silveira ER, Santos FA, Rao VS (2002) Anti-inflammatory effect of kaurenoic acid, a diterpene from Copaifera langsdorffii on acetic acid-induced colitis in rats. Vascul Pharmacol 39(6):303–307
Oshaki A, Yan LT, Ito S, Edatsugi H, Iwata D, Komoda Y (1994) The isolation and in vivo potent antitumor activity of clerodane diterpenoids from the oleoresin of Brazilian medicinal plant Copaifera langsdorffii Desfon. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 4:2889–2892
Lima ES, Abdalla DSP (2001) Lipídic peroxidation: evaluation mechanisms in biological samples. Rev Bras Ci Farm 37(3):293–303
Paiva LA, Rao VS, Gramosa NV, Silveira ER (1998) Gastroprotective effect of Copaifera langsdorffii oleo-resin on experimental gastric ulcer models in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 62(1):73–78
Paiva LA, Gurgel LA, De Sousa ET, Silveira ER, Silva RM, Santos FA, Rao VS (2004) Protective effect of Copaifera langsdorffii oleo-resin against acetic acid-induced colitis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 93(1):51–56
Cymrot M, Percário S, Ferreira LM (2004) Oxidative stress and total antioxidant status in ischemic skin flaps in rats. Acta Cir Bras 19(1):18–26
Rover Júnior L, Höehr NF, Vellasco AP (2001) Anti-oxidant system involving the metabolic cycle of glutathione associated with electroanalytical methods in the assessment of oxidative stress. Quim Nova 24(1):112–119
Franck T, Kohnen S, Grulke S, Neven P, Goutman Y, Peters F, Pirotte B, Deby-Dupont G, Serteyn D (2007) Inhibitory effect of curcuminoids and tetrahydrocorcuminoids on equine activated neutrophils and myeloperoxidase activity. Physiol Res 57(4):577–587
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Lima Silva, J.J., Guimarães, S.B., da Silveira, E.R. et al. Effects of Copaifera langsdorffii Desf. on Ischemia-Reperfusion of Randomized Skin Flaps in Rats. Aesth Plast Surg 33, 104–109 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-008-9263-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-008-9263-2