Abstract.
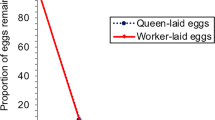
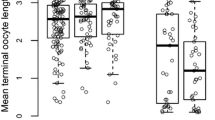
Workers of the Asian hive bee, Apis cerana, are shown to have relatively high rates of worker ovary activation. In colonies with an active queen and brood nest, 1–5% of workers have eggs in their ovarioles. When A. cerana colonies are dequeened, workers rapidly activate their ovaries. After 4 days 15% have activated ovaries and after 6 days, 40%. A cerana police worker-laid eggs in the same way that A. florea and A. mellifera do, but are perhaps slightly more tolerant of worker-laid eggs than the other species. Nevertheless, no worker's sons were detected in a sample of 652 pupal males sampled from 4 queenright colonies. A cerana continue to police worker-laid eggs, even after worker oviposition has commenced in a queenless colony.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oldroyd, B.P., Halling, L.A., Good, G. et al. Worker policing and worker reproduction in Apis cerana . Behav Ecol Sociobiol 50, 371–377 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002650100376
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002650100376