Abstract.
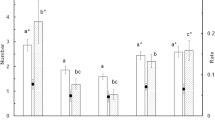
The Hipposideridae and Rhinolophidae are closely related families of bats that have similar echolocation (long-duration pure-tone signal, high duty cycle) and auditory systems (Doppler-shift compensation, auditory fovea). Rhinolophid bats are known to forage in highly cluttered areas where they capture fluttering insects, whereas the foraging habitat of hipposiderid bats is not well understood. Compared to rhinolophids, hipposiderid calls are shorter in duration, have lower duty cycles, and they exhibit only partial Doppler-shift compensation. These differences suggest that the foraging habitat of the two families may also differ. We tested this hypothesis by studying foraging and echolocation of Hipposideros speoris at a site with a range of vegetation types. Bats foraged only while in flight and used all available closed and edge habitats, including areas adjacent to open space. Levels of clutter were high in forest and moderate in other foraging areas. Prey capture (n=42) occurred in edge vegetation where it bordered open space. Echolocation signals of H. speoris lacked an initial upward frequency-modulated sweep and were of moderate duration (5.1–8.7 ms). Sequences had high duty cycles (23–41%) and very high pulse repetition rates (22.8–60.6 Hz). Variation in signal parameters during search phase flight across foraging habitats was low. H. speoris showed a greater flexibility in its use of foraging habitat than is known for any rhinolophid species. Our study confirmed that there are differences in habitat use between hipposiderid and rhinolophid bats and we suggest that this divergence is a consequence of differences in their echolocation and auditory systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pavey, C.R., Grunwald, JE. & Neuweiler, G. Foraging habitat and echolocation behaviour of Schneider's leafnosed bat, Hipposideros speoris, in a vegetation mosaic in Sri Lanka. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 50, 209–218 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002650100363
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002650100363