Abstract.
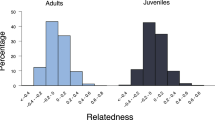
Female greater horseshoe bats (Rhinolophus ferrumequinum) exhibit strong natal philopatry to their maternity roost over many years, leading to the aggregation of matrilineal kin. Maternity colonies may, therefore, be expected to comprise highly related individuals, and, as such, provide conditions suitable for the evolution of kin-selected behaviours. To test these predictions, we examined relatedness and behaviour among matrilineal kin within a colony in south-west Britain. Genetic analysis of 15 matrilines, identified from microsatellite genotyping and long-term ringing surveys, revealed average relatedness levels of 0.17 to 0.64. In contrast, background relatedness among colony females approximated to zero (0.03). These results suggest that inclusive fitness benefits may only be accrued through discriminate cooperation within matrilines, and not at the wider colony level. To examine whether the potential for such benefits is realised through kin- biased cooperation during foraging, females from two matrilines were radio-tracked simultaneously over 3 years. Pairwise home-range overlap correlated significantly with Hamilton's relatedness coefficient. The greatest spatial associations were observed between females and their adult daughters, which shared both foraging grounds and night roosts, sometimes over several years. Tagged females, however, generally foraged and roosted alone, suggesting that kin-biased spatial association probably does not result from either information-transfer or cooperative territorial defence. Such patterns may instead result from a mechanism of maternal inheritance of preferred foraging and roosting sites.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rossiter, S.J., Jones, G., Ransome, R.D. et al. Relatedness structure and kin-biased foraging in the greater horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus ferrumequinum). Behav Ecol Sociobiol 51, 510–518 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00265-002-0467-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00265-002-0467-1