Abstract
Introduction
Failure to neutralize the different physiological forces acting on the inferior as well as the superior regions of the pubic symphysis, the long healing time, is blamed for the repeated failures of conventional superior symphyseal plating.
Material and methods
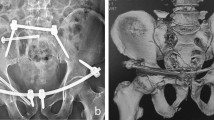
A three years prospective case series study between January 2017 and December 2019 was done, to evaluate the radiological and the functional outcomes, using Matta/Tornetta and Majeed criteria respectively, of the combination of trans-symphyseal cross-screws configuration and superior symphyseal plate in Tile-type B1 pelvic injuries.
Results
Thirty patients, 18 with anteroposterior compression type II and 12 with type III, with a mean follow-up of 20 months ±5 were included. Radiologically, 26 (86.6%) cases showed an excellent, one (3.3%) good and three (10%) fair outcome. Clinically, excellent outcome in 26 (86.6%) cases, good in two (6.6%) cases, and fair in two (6.6%). Intra-operative drill bit breakage occurred in three (10%) cases and was the only reported technical complication. Significant re-displacement was reported in three (10%) cases.
Conclusion
The open trans-symphyseal cross-screws for fixation of the superior symphyseal plate is a simple, efficient, and safe technique with the biomechanical advantages of an extra-fixation point to the inferior symphysis together with a long and a strong bony anchorage.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papakostidis C, Kanakaris NK, Kontakis G, Giannoudis PV (2009) Pelvic ring disruptions: treatment modalities and analysis of outcomes. Int Orthop 33(2):329–338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-008-0555-6
Pereira GJC, Damasceno ER, Dinhane DI, Bueno FM, Leite JBR, Ancheschi BDC (2017) Epidemiology of pelvic ring fractures and injuries. Rev Bras Ortop 52(3):260–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rboe.2017.05.012
Aggarwal S, Bali K, Krishnan V, Kumar V, Meena D, Sen RK (2011) Management outcomes in pubic diastasis: our experience with 19 patients. J Orthop Surg Res 6(1):21. https://doi.org/10.1186/1749-799X-6-21
Banierink H, Reininga IHF, Heineman E, Wendt KW, Ten Duis K, IJpma FFA (2019) Long-term physical functioning and quality of life after pelvic ring injuries. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 139(9):1225–1233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-019-03170-2
Hermans E, Brouwers L, van Gent T, Biert J, de Jongh MAC, Lansink KWW, Edwards MJR (2019) Quality of life after pelvic ring fractures: long-term outcomes. A multicentre study. Injury 50(6):1216–1222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2019.04.002
Morris SA, Loveridge J, Smart DK, Ward AJ, Chesser TJ (2012) Is fixation failure after plate fixation of the symphysis pubis clinically important? Clin Orthop Relat Res 470(8):2154–2160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-012-2427-z
Farouk O, Hassanein MY, Mohamed AM, Adam FF (2017) Preliminary results of internal fixation of symphyseal disruption using Assiut Symphyseal plate: a novel biplanar plate design. Journal of Current Medical Research and Practice 2(3):177
Becker I, Woodley SJ, Stringer MD (2010) The adult human pubic symphysis: a systematic review. J Anat 217(5):475–487. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7580.2010.01300.x
Collinge C, Archdeacon MT, Dulaney-Cripe E, Moed BR (2012) Radiographic changes of implant failure after plating for pubic symphysis diastasis: an underappreciated reality? Clin Orthop Relat Res 470(8):2148–2153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-012-2340-5
Eastman JG, Krieg JC, Routt MLC Jr (2016) Early failure of symphysis pubis plating. Injury 47(8):1707–1712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2016.05.019
Gill JR, Murphy C, Quansah B, Carrothers A (2017) Management of the open book APC II pelvis: survey results from pelvic and acetabular surgeons in the United Kingdom. J Orthop 14(4):530–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jor.2017.08.004
Vaidya R, Martin AJ, Roth M, Nasr K, Gheraibeh P, Tonnos F (2017) INFIX versus plating for pelvic fractures with disruption of the symphysis pubis. Int Orthop 41(8):1671–1678. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-016-3387-9
Gonzálvez ÁL, Reina JM, Luis PC, Baquero JJ, Fernández JS, Sánchez MÁG (2016) Is cannulated-screw fixation an alternative to plate osteosynthesis in open book fractures? A biomechanical analysis. Injury 47:S72–S77. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-1383(16)30610-6
Yao F, He Y, Qian H, Zhou D, Li Q (2015) Comparison of biomechanical characteristics and pelvic ring stability using different fixation methods to treat pubic symphysis diastasis: a finite element study. Medicine 94(49). https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000002207
Burgess AR, Eastridge BJ, Young JW, Ellison TS, Ellison PS Jr, Poka A et al (1990) Pelvic ring disruptions: effective classification system and treatment protocols. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 30(7):848–856
Park MS, Yoon SJ, Choi SM, Lee K (2017) Is there a clinical benefit of additional tension band wiring in plate fixation of the symphysis? BMC Musculoskelet Disord 18(1):40. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-017-1418-3
Matta JM, Tornetta P III (1996) Internal fixation of unstable pelvic ring injuries. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research (1976–2007) 329:129–140. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-199608000-00016
Majeed SA (1989) Grading the outcome of pelvic fractures. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. British 71(2):304–306
Icke C, Koebke J (2014) Normal stress pattern of the pubic symphysis. Anatomy & Cell Biology 47(1):40–43. https://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2014.47.1.40
Cano-Luis P, Giráldez-Sanchez MA, Martínez-Reina J, Serrano-Escalante FJ, Galleguillos-Rioboo C, Lazaro-Gonzalvez A et al (2012) Biomechanical analysis of a new minimally invasive system for osteosynthesis of pubis symphysis disruption. Injury 43:S20–S27. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-1383(13)70175-X
Chen L, Zhang G, Song D, Guo X, Yuan W (2012) A comparison of percutaneous reduction and screw fixation versus open reduction and plate fixation of traumatic symphysis pubis diastasis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 132(2):265–270
Yin C, Liu J, Peng XU, Liu Z, Jialiang LU, Pan W, Weidong MU (2014) Quantitative anatomical study of percutaneous cannulated lag screw fixation for treatment of symphysis pubis diastasis. Chinese Journal of Trauma 30(6):589–593
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beder, F.K., Hamdy, M.S., El-Desouky, I.I. et al. Symphyseal plate with trans-symphyseal cross-screws for fixation of tile-type B1 pelvic ring injuries: radiological and functional evaluation. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 44, 2745–2751 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-020-04851-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-020-04851-z