Abstract
Purpose
This study was designed to investigate accuracy of the tibial component in the coronal plane when the lateral condylar eminence was determined as the proximal reference of proximal tibial cutting in varus-deformed knees.
Methods
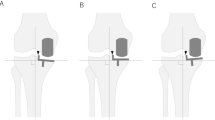
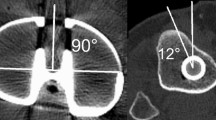
Varus-deformed tibiae were designed using the entire tibia sawbone models of four categories (varus 0°, 5°, 10° and 15°). Each of ten sawbones was allocated into four in each group. All sawbones were osteotomised with the proximal reference of proximal tibial cutting as the lateral intercondylar eminence. The thickness of the cut tibial medial and lateral condyles were measured. After implantation of the tibial component, anteroposterior (AP) radiographs were obtained. An independent examiner evaluated angles between the perpendicular line to the tibial tray and the shaft/mechanical axes of the tibia.
Results
The mean angular difference between the axis perpendicular to the prosthesis and the mechanical/shaft axes of the tibia were not significant in any group. When the tibial component coronal alignment was measured based on the tibial mechanical axis, no significant difference was observed in any group, but when based on the shaft axis of the tibia, it was significantly different between Group A and Group D.
Conclusions
Accuracy of the tibial component alignment was acceptable in varus-deformed knees when the lateral intercondylar eminence was used as a reference for tibial osteotomy, although any prolonged clinical benefits will require long-term in vivo study.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fang DM, Ritter MA, Davis KE (2009) Coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty: just how important is it? J Arthroplasty 24:39–43
Mihalko WM, Boyle J, Clark LD, Krackow KA (2005) The variability of intramedullary alignment of the femoral component during total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 20:25–28
Ritter MA, Davis KE, Meding JB, Pierson JL, Berend ME, Malinzak RA (2011) The effect of alignment and BMI on failure of total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 93:1588–1596
Ensini A, Catani F, Leardini A, Romagnoli M, Giannini S (2007) Alignments and clinical results in conventional and navigated total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 457:156–162
Pitto RP, Graydon AJ, Bradley L, Malak SF, Walker CG, Anderson IA (2006) Accuracy of a computer-assisted navigation system for total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 88:601–605
Spencer JM, Chauhan SK, Sloan K, Taylor A, Beaver RJ (2007) Computer navigation versus conventional total knee replacement: no difference in functional results at two years. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 89:477–480
Han HSCY, YoonKS LLH, Jo HC, Kan SB (2007) Accuracy of intramedulary versus extramedullary tibial alignment guides : a randomized, prospective study in bilateral total knee arthroplasty. J Korean Knee Soc 19:181–186
Rand JA, Coventry MB (1988) Ten-year evaluation of geometric total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 232:168–173
Bono JV, Roger DJ, Laskin RS, Peterson MG, Paulsen CA (1995) Tibial intramedullary alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Am J Knee Surg 8:7–11, discussion 11–12
Ishii Y, Ohmori G, Bechtold JE, Gustilo RB (1995) Extramedullary versus intramedullary alignment guides in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 318:167–175
Maestro A, Harwin SF, Sandoval MG, Vaquero DH, Murcia A (1998) Influence of intramedullary versus extramedullary alignment guides on final total knee arthroplasty component position: a radiographic analysis. J Arthroplasty 13:552–558
Reed MR, Bliss W, Sher JL, Emmerson KP, Jones SM, Partington PF (2002) Extramedullary or intramedullary tibial alignment guides: a randomised, prospective trial of radiological alignment. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 84:858–860
Teter KE, Bregman D, Colwell CW Jr (1995) Accuracy of intramedullary versus extramedullary tibial alignment cutting systems in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 321:106–110
Yang SH, Liu TK (1998) Intramedullary versus extramedullary tibial alignment guides in total knee arthroplasty. J Formos Med Assoc 97:564–568
Oswald MH, Jakob RP, Schneider E, Hoogewoud HM (1993) Radiological analysis of normal axial alignment of femur and tibia in view of total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 8:419–426
Ko PS, Tio MK, Ban CM, Mak YK, Ip FK, Lam JJ (2001) Radiologic analysis of the tibial intramedullary canal in Chinese varus knees: implications in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 16:212–215
Moreland JR, Bassett LW, Hanker GJ (1987) Radiographic analysis of the axial alignment of the lower extremity. J Bone Joint Surg Am 69:745–749
Nagamine R, Miura H, Bravo CV, Urabe K, Matsuda S, Miyanishi K, Hirata G, Iwamoto Y (2000) Anatomic variations should be considered in total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci 5:232–237
Matsuda S, Mizu-uchi H, Miura H, Nagamine R, Urabe K, Iwamoto Y (2003) Tibial shaft axis does not always serve as a correct coronal landmark in total knee arthroplasty for varus knees. J Arthroplasty 18:56–62
Chiu KY, Yau WP, Ng TP, Tang WM (2008) The accuracy of extramedullary guides for tibial component placement in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 32:467–471
Fukagawa S, Matsuda S, Mitsuyasu H, Miura H, Okazaki K, Tashiro Y, Iwamoto Y (2011) Anterior border of the tibia as a landmark for extramedullary alignment guide in total knee arthroplasty for varus knees. J Orthop Res 29:919–924
Tsukeoka T, Lee TH, Tsuneizumi Y, Suzuki M (2014) The tibial crest as a practical useful landmark in total knee arthroplasty. Knee 21:283–289
Haaker RG, Stockheim M, Kamp M, Proff G, Breitenfelder J, Ottersbach A (2005) Computer-assisted navigation increases precision of component placement in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 433:152–159
Nabeyama R, Matsuda S, Miura H, Mawatari T, Kawano T, Iwamoto Y (2004) The accuracy of image-guided knee replacement based on computed tomography. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 86:366–371
Sparmann M, Wolke B, Czupalla H, Banzer D, Zink A (2003) Positioning of total knee arthroplasty with and without navigation support. A prospective, randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 85:830–835
Bellemans J, Vandenneucker H, Vanlauwe J (2007) Robot-assisted total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 464:111–116
Bae DK, Song SJ (2011) Computer assisted navigation in knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Surg 3:259–267
Jeffcote B, Shakespeare D (2003) Varus/valgus alignment of the tibial component in total knee arthroplasty. Knee 10:243–247
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SM., Kim, KW., Cha, SM. et al. Proximal tibial resection in varus-deformed tibiae during total knee arthroplasty: an in vitro study using sawbone model. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 39, 429–434 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-014-2485-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-014-2485-9