Abstract
Purpose
Active knee flexion is more important for daily activities than passive knee flexion. The hypothesis is that the intra-operative parameters such as osteotomized bone thickness and soft tissue balance affect the postoperative active flexion angle in total knee arthroplasty (TKA). Therefore, we evaluate the influence of intra-operative parameters on postoperative early recovery of active flexion after posterior-stabilized (PS) TKA.
Methods
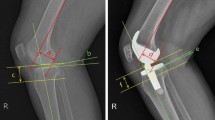
The subjects were 45 osteoarthritic knees undergoing primary PS TKA with anterior-reference technique. Intra-operative soft tissue balance was measured using an offset type tensor, and each osteotomized bone thickness was also measured. Pre- and postoperative active knee flexion angles were measured using lateral radiographs. Liner regression analysis was used to determine the influence of these intra-operative parameters on postoperative active flexion angles or recovery of active flexion angles.
Results
Pre-operative flexion angle was positively correlated with postoperative flexion angle (R = 0.52, P = 0.0002). Postoperative flexion angle was negatively correlated with the osteotomized bone thickness of femoral medial posterior condyle (R = −0.37, P = 0.012), and femoral lateral posterior condyle (R = −0.36, P = 0.015). Recovery of flexion angle was slightly negatively correlated with gap difference calculated by subtracting joint gap at extension from that at flexion between osteotomized surfaces (R = −0.30, P = 0.046).
Conclusions
The osteotomized bone thickness of the femoral posterior condyle is a significant independent factor of postoperative flexion angles. This indicates that the restoration of the posterior condyle offset may lead to larger postoperative active flexion angles in PS TKA.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Insall J, Scott WN, Ranawat CS (1979) The total condylar knee prosthesis: a report of two hundred and twenty cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am 61-A:173–180
Anouchi YS, McShane M, Kelly F Jr, Elting J, Stiehl J (1996) Range of motion in total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 331:87–91
Lizaur A, Marco L, Cebrian R (1997) Preoperative factors influencing the range of movement after total knee arthroplasty for severe osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 79-B:626–629
Harvey IA, Barry K, Kirby SP, Johnson R, Elloy MA (1993) Factors affecting the range of movement of total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br 75-B:950–955
Parsley BS, Engh GA, Dwyer KA (1992) Preoperative flexion. Dose it influence postoperative flexion after posterior-cruciate retaining total knee arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res 275:204–210
Ritter MA, Stringer EA (1999) Predictive range of motion after total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 143:115–119
Matsumoto T, Tsumura N, Kubo S, Shiba R, Kurosaka M, Yoshiya S (2005) Influence of hip position on knee flexion angle in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 20:669–673
Dennis DA (2001) Problems after knee arthroplasty. The stiff total knee arthroplasty: causes and cures. Orthopedics 24:901–902
Kawamura H, Bourne RB (2001) Factors affecting range of flexion after total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci 6:248–252
Schurman DJ, Matityahu A, Goodman SB, Maloney W, Woolson S, Shi H, Bloch DA (1998) Prediction of postoperative knee flexion in Insall-Burstein ll total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 353:175–184
Schurman DJ, Parker JN, Orstein D (1985) Total condylar knee replacement. A study of factors influencing range of motion as late as two years after arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 67-A:1006–1014
Joshi AB, Lee CM, Markovic L, Murphy JCM, Hardinge K (1994) Total knee arthroplasty after patellectomy. J Bone Joint Surg Br 76-B:926–929
Bellemans J, Banks S, Victor J, Vandenneucker H, Moemans A (2002) Fluoroscopic analysis of the kinematics of deep flexion in total knee arthroplasty. Influence of posterior condylar offset. J Bone Joint Surg Br 84-B:50–53
Fehring TK, Odum S, Griffin WL, Mason JB, Nadaud M (2001) Early failures in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 392:315–318
Sharkey PF, Hozack WJ, Rothman RH, Shastri S, Jacoby SM (2002) Insall award paper. Why are total knee arthroplasties failing today? Clin Orthop Relat Res 404:7–13
Muratsu H, Tsumura N, Yamaguchi M, Mizuno K, Kuroda R, Harada T, Yoshiya S, Kurosaka M (2003) Patellar eversion affects soft tissue balance in total knee arthroplasty. Trans Orthop Res 28:242
Matsumoto T, Muratsu H, Tsumura N, Mizuno K, Kuroda R, Yoshiya S, Kurosaka M (2006) Joint gap kinematics in posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty measured by a new tensor with the navigation system. J Biomech Eng 128:867–871
Matsumoto T, Mizuno K, Muratsu H, Tsumura N, Fukase N, Kubo S, Yoshiya S, Kurosaka M, Kuroda R (2007) Influence of intra-operative joint gap on post-operative flexion angle in osteoarthritis patients undergoing posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 15:1013–1018
Takayama K, Matsumoto T, Kubo S, Muratsu H, Ishida K, Matsushita T, Kurosaka M, Kuroda R (2012) Influence of intra-operative joint gaps on post-operative flexion angle in posterior-cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20:532–537
Berger RA, Rubash HE, Seel MJ, Thompson WH, Crossett LS (1993) Determining the rotational alignment of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty using the epicondylar axis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 286:40–47
Matsumoto T, Kuroda R, Kubo S, Muratsu H, Mizuno K, Kurosaka M (2009) The intra-operative joint gap in cruciate-retaining compared with posterior-stabilized total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 91-B:475–480
Muratsu H, Matsumoto T, Kubo S, Maruo A, Miya H, Kurosaka M, Kuroda R (2010) Femoral component placement changes soft tissue balance in posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Clin Biomech 25:926–930
Edwards JZ, Greene KA, Davis RS, Kovacik MW, Noe DA, Askew MJ (2004) Measuring flexion in knee arthroplasty patients. J Arthroplasty 19:369–372
Laidlaw MS, Rolston LR, Bozic KJ, Ries MD (2010) Assessment of tibiofemoral position in total knee arthroplasty using the active flexion lateral radiograph. Knee 17:38–42
Massin P, Gournay A (2006) Optimization of the posterior condylar offset, tibial slope, and condylar roll-back in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 21:889–896
Kim YH, Sohn KS, Kim JS (2005) Range of motion of standard and high-flexion posterior stabilized total knee prostheses. A prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87-A:1470–1475
Hanratty BM, Thompson NW, Wilson RK, Beverland DE (2007) The influence of posterior condylar offset on knee flexion after total knee replacement using a cruciate-sacrificing mobile-bearing implant. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89-B:915–918
Clarke HD (2012) Changes in posterior condylar offset after total knee arthroplasty cannot be determined by radiographic measurements alone. J Arthroplasty 27:1155–1158
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Mrs. Janina Tubby for her assistance in preparation of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagai, K., Muratsu, H., Matsumoto, T. et al. Influence of intra-operative parameters on postoperative early recovery of active knee flexion in posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 37, 2153–2157 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-013-2018-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-013-2018-y