Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the curative efficacy of osteonecrosis of the femoral head (ONFH) in a hip-preserving operative approach, by grafting a vascularized greater trochanter flap combined with a free iliac flap, in an attempt to seek an innovative approach for patients who suffered middle to late stage ONFH without total hip arthroplasty (THA) surgery.
Method
Our research included a total of 60 patients (66 hips) who accepted hip-preserving surgery by grafting a vascularized greater trochanter flap combined with a free iliac flap which was tightly filled by hammering because of ONFH (most were Association Research Circulation Osseous (ARCO) stage III patients) from January, 2006 to December, 2010. A Harris Hip Score was obtained during follow-ups, evaluating the clinical efficacy, X-rays were taken regularly for image assessing, and the SF-36 scale was used for estimating quality of life. Terminal observation time was considered when patients had symptom-dependant indications for performing another hip-preserving surgery or THA surgery.
Results
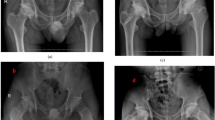
Fifty-eight patients (64 hips) were eventually contacted by telephone for an out-patient clinic return visit, with a mean follow-up time of 35.8 months (varied from 12 months to 60 months), but two patients lost contact for various reasons. The demographic data were as follows: there were 16 ARCO IIIA cases, 22 ARCO IIIB cases, and 26 ARCO IIIC cases, respectively. Postoperative X-rays revealed a well-repaired necrotic area of the femoral head and improvement of femoral-acetabulum coverage. The last follow-up mean Harris Hip Score was 86.56 ± 7.38 (excellent results reached 87.50 %), which were greatly improved compared to 50.95 ± 6.86 pre-operatively. Also the postoperative mean scores of all dimensions of the SF-36 scale were improved to some extent. Additionally the physical component summary (PSC) scores were enhanced from 42 ± 13 pre-operatively to 78 ± 11, while the postoperative mental component summary (MCS) scores (76 ± 11) largely increased in contrast to pre-operative scores (51 ± 10), with both target indices having statistical significance (p = 0.005, p = 0.01), signifying hugely improvement of the quality of life of the patients. A correlation was found between Harris Hip Score and all dimensions of SF-36 scale (r = 0.32–0.72), especially closely correlated with physical functioning (PF), role-physical (RP) and bodily pain (BP) in PCS aspect (r = 0.72, p < 0.01; r = 0.58, p < 0.01; r = 0.65, p < 0.01, respectively).
Conclusion
There is definite curative efficacy for the treatment of ONFH with an hip-preserving operative approach by grafting a vascularized greater trochanter flap combined with a free iliac flap which was tightly filled by hammering. This kind of operative approach reconstructs the biological stability of femoral head, which promotes repair of necrotic areas and indirectly preserves the femoral head of patients and a majority of hip function. It possesses vast clinical as well as practical significance, because the long-term efficacy can satisfy fundamental life requirements, especially for those young and middle-aged patients who suffer ONFH to avoid or put off the time of total hip arthroplasty(THA) surgery.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Razik F, Alexopoulos AS, El-Osta B, Connolly MJ, Brown A, Hassan S, Ravikumar K (2012) Time to internal fixation of femoral neck fractures in patients under sixty years--does this matter in the development of osteonecrosis of femoral head? Int Orthop 36(10):2127–2132. doi:10.1007/s00264-012-1612-8
Li Y, Han R, Geng C, Wang Y, Wei L (2009) A new osteonecrosis animal model of the femoral head induced by microwave heating and repaired with tissue engineered bone. Int Orthop 33(2):573–580. doi:10.1007/s00264-008-0672-2
Akinyoola AL, Adediran IA, Asaleye CM, Bolarinwa AR (2009) Risk factors for osteonecrosis of the femoral head in patients with sickle cell disease. Int Orthop 33(4):923–926. doi:10.1007/s00264-008-0584-1
Merle D’Aubigné R, Postel M, Mazabraud A, Massias P, Gueguen J (1965) Idiopathic necrosis of the femoral head in adults. Bone Joint Surg Br 47:612–633
Ohzono K, Saito M, Takaoka K, Ono K, Saito S, Nishina T, Kadowaki T (1991) Natural history of nontraumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Bone Joint Surg Br 73:68–72
Moriya M, Uchiyama K, Takahira N, Fukushima K, Yamamoto T, Hoshi K, Itoman M, Takaso M (2012) Evaluation of bipolar hemiarthroplasty for the treatment of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Int Orthop 36(10):2041–2047. doi:10.1007/s00264-012-1612-8
Kim YH, Choi Y, Kim JS (2010) Cementless total hip arthroplasty with ceramic-on-ceramic bearing in patients younger than 45 years with femoral-head osteonecrosis. Int Orthop 34(8):1123–1127. doi:10.1007/s00264-009-0878-y
Katz RL, Bourne RB, Rorabeck CH, McGee H (1992) Total hip arthroplasty in patients with avascular necrosis of the hip: follow-up observations on cementless and cemented operations. Clin Orthop Relat Res 281:145–151
Kim YH, Oh JH, Oh SH (1995) Cementless total hip arthroplasty in patients with osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin Orthop Relat Res 320:73–84
Sugioka Y, Hotokebuchi T, Tsutsui H (1992) Transtrochanteric anterior rotational osteotomy for idiopathic and streoid-induced necrosis of the femoral head. Indications and long-term results. [J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res 277:111–120
Fairbank AC, Bhatia D, Jinnah RH, Hungerford DS (1995) Long-term results of core decompression for ischaemic necrosis of the femoral head. Bone Joint Surg Br 77:42–49
Koo KHI, Kim R, Ko GH, Song HR, Jeong ST, Cho SH (1995) Preventing collapse in early osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A randomised clinical trial of core decompression. Bone Joint Surg Br 77:870–874
Mont MA, Carbone JJ, Firbank AC (1996) Core decompression versus nonoperative management for osteonecrosis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res 324:169–178
Buckley PD, Gearen PF, Petty RW (1991) Structural bone-graft-ing for early atraumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Bone Joint Surg Am 73:1357–1364
Scully SP, Aaron RK, Urbaniak JR (1998) Survival analysis of hips treated with core decompression or vascularized fibular grafting because of avascular necrosis. Bone Joint Surg Am 80:1270–1275
Smith KR, Bonfiglio M, Montgomery WJ (1980) Non-traumatic necrosis of the femoral head treated with tibial bone-grafting: A follow-up note. Bone Joint Surg Am 62:845–847
Meyers MH (1978) The treatment of osteonecrosis of the hip with fresh osteochondral allografts and with the muscle pedicle graft technique. Clin Orthop 130:202–209
Matsusaki H, Noguchi M, Kawakami T et al (2005) Use of vascularized pedicle iliac bone graft combined with transtrochanteric rotational osteotomy in the treatment of avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 125(2):95–101
Yasunaga Y, Hisatome T, Ikuta Y et al (2001) A histological study of the necrotic area after transtrochanteric anterior rotational osteotomy for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Br 83(2):167–170
Clark JC, Dass CR, Choong PF (2008) A review of clinical and molecular prognostic factors in osteosarcoma. Cancer Res Clin Oncol 134(3):281–297
Floerkemeier T, Lutz A, Nackenhorst U, Thorey F, Waizy H, Windhagen H, von Lewinski G (2011) Core decompression and osteonecrosis intervention rod in osteonecrosis of the femoral head: clinical outcome and finite element analysis. Int Orthop 35(10):1461–1466. doi:10.1007/s00264-010-1138-x
Baksi DP, Pal AK, Baksi DD (2009) Long-term results of decompression and muscle-pedicle bone grafting for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Int Orthop 33(1):41–47
Dass CR, Nadesapillai AP, Robin D et al (2005) Downregulation of uPAR confirms link in growth and metastasis of osteosarcoma. Clin Exp Metastasis 22(8):643–652
Keizer SB, Kock NB, Dijkstra PD, Taminiau AH, Nelissen RG (2006) Treatment of avascular necrosis of the hip by a non-vascularised cortical graft. Bone Joint Surg Br 88:460–466
Dailiana ZH, Toth AP, Gunneson E, Berend KR, Urbaniak JR (2007) Free vascularized fibular grafting following failed core decompression for femoral head osteonecrosis. Arthroplasty 22:679–688
Israelite C, Nelson CL, Ziarani CF, Landa J, Steinberg ME (2005) Bilateral core decompression for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin Orthop Relat Res 441:285–290
Athanasios E, Bassounas A, Apostolos H, Karantanas B, Dimit-rios I, Fotiadis C, Konstantinos N, Malizos D (2007) Femoral head osteonecrosis: volumetric MRI assessment and outcome. Eur J Radiol 63:10–15
Mont MA, Hungerford DS (1995) Non-traumatic avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Bone Joint Surg Am 77:459–474
Zhao FC, Li ZR, Zhang NF, Wang BL, Sun W, Cheng LM, Liu ZH (2010) Lesion size changes in osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a long-term prospective study using MRI. Int Orthop 34(6):799–804. doi:10.1007/s00264-009-0829-7
Korompilias AV, Lykissas MG, Beris AE et al (2009) Vascularised fibular graft in the management of femoral head osteonecrosis: twenty years later. J Bone Joint Surg Br 91(3):287–293
Mont MA, Jones LG, Seyler TM et al (2007) New treatment approaches for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Instr Course Lect 56(2):197–212
Kawate K, Yajima H, Sugimoto K et al (2007) Indications for free vascularized fibular grafting for the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral hend. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 8(1):78
Jin H, Xia B, Yu N, He B, Shen Y, Xiao L, Tong P (2012) The effects of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell arterial perfusion on vascular repair and angiogenesis in osteonecrosis of the femoral head in dogs. Int Orthop 36(12):2589–2596. doi:10.1007/s00264-012-1674-7
Yin S, Zhang C, Jin D, Chen S, Sun Y, Sheng J (2011) Treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in lymphoma patients by free vascularised fibular grafting. Int Orthop 35(8):1125–1130. doi:10.1007/s00264-010-1031-7
Ueo T, Tsutsumi S, Yamamuro T et al (1985) Biomechanical aspect of the development of aseptic necrosis of the femoral head. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 04(3):145–149
Mihara K, Hirano T (1998) Standing Is a Causative Fact or in Osteonecr osis of the Femoral Head in Gr owing Rats. Pediatr Orthop 18:665–669
Shimizu K, Moriya H, Akita T, Sakamoto M, Suguro T (1994) Pre-diction of collapse with magnetic resonance imaging of avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Bone Joint Surg Am 76:215–223
Gamradt SC, Lieberman JR (2004) Genetic modification of stem cells to en2 hance bone rapair. Ann Biomed Eng 1:136–147
Gaskill TR, Urbaniak JR, Aldridge JM et al (2009) Vascularized fibular transfer for femoral head osteonecrosis: donor and graft site morbidity. Bone Joint Surg Am 91(8):1861–1867
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, YR., He, S., Feng, WJ. et al. Vascularised greater trochanter bone graft, combined free iliac flap and impaction bone grafting for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 37, 391–398 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-012-1773-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-012-1773-5