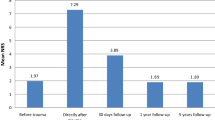
Abstract
According to the literature, hip function after hip fracture is affected by the type of surgery. Our aim was to determine the correlation between surgical treatment of hip fracture and postoperative function in the elderly. Inclusion criteria were displaced hip fracture and age over 70 years. One hundred and twenty-nine participants were randomly divided into three groups according to the type of the surgical operation they underwent (hemi-arthroplasty [Merete, Berlin, Germany], total arthroplasty [Plus; De Puy, Warsaw, IN, USA] and internal fixation [Richards plate screw; Smith & Nephew, Memphis, TN, USA]). The function of the patients was estimated using the following parameters: the Barthel Index and Harris Hip Score, the range of passive hip motion, the gait speed of individuals, after 1 and 4 years of follow-up. The Barthel Index scores after 4 years of follow-up were 85.3, 82.6, 80.1 after total arthroplasty, hemi-arthroplasty and internal fixation respectively. Similarly, the Harris Hip Scores after 4 years of follow-up were 83.7, 79.5 and 73.6. The range of passive hip motion in the three groups of patients did not differ significantly (p > 0.05). Also, patients of the total arthroplasty and hemi-arthroplasty groups walked faster than the patients of the internal fixation group 4 years after discharge (p < 0.05). In conclusion, we believe that total hip arthroplasty is the treatment of choice for displaced subcapital hip fractures in patients over 70 years old.
Résumé
Selon la littérature, la fonction de la hanche après traitement d’une fracture dépend du type d’intervention. Le but de notre étude est d’apprécier la corrélation qui existe entre le traitement chirurgical et la fonction post-opératoire chez les patients âgés. Les critères d’inclusion ont été la notion d’une fracture déplacée chez les patients âgés de plus de 70 ans. Cent vingt-neuf patients ont été randomisés en trois groupes selon le type d’intervention, prothèse intermédiaire de type Merete, prothèse totale de type Plus et fixation interne par vis plaque de type Richards. La fonction des patients a été estimée selon les paramètres suivants : index de Barthel, Score de Harris, mobilité passive de la hanche et vitesse de marche après un à quatre ans de suivi. Le score de Barthel à quatre ans, post opératoire est passé respectivement à 85,3, 82,6, 80,1 après prothèse totale, prothèse intermédiaire et fixation interne, de même en ce qui concerne le score de Harris qui est passé respectivement de 83,7, 79,5, 73,6. La mobilité passive de la hanche dans les trois groupes ne montre pas de différence significative. Les patients ayant bénéficié d’une prothèse totale ou d’une prothèse intermédiaire ont une marche plus rapide que les patients ayant bénéficié d’une fixation interne (p < 0.05). En conclusion, nous pensons que la prothèse totale de hanche est le traitement de choix pour les fractures déplacées sous capitale de la hanche chez les patients de plus de 70 ans.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhandari M, Devereaux P, Swiontkowski M, Tornetta P, Obremskey W, Koval K, Nork S, Sprague S, Schemitsch E, Guyatt G (2003) Internal fixation compared with arthroplasty for displaced fractures of the femoral neck. A meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 85A(9):1673–1681
Ceder L, Thorngren G, Wallden B (1980) Prognostic indicators and early home rehabilitation in elderly patients with hip fractures. Clin Orthop 152:173–184
Cserhati P, Fekete K, Berglund-Roden M, Wingstrand H, Thomgren K (2002) Hip fractures in Hungary and Sweden—differences in treatment and rehabilitation. Int Orthop 26(4):222–228
Cuckler JM, Tamarapalli JR (1994) An algorithm for the management of femoral neck fractures. Orthopedics 17(9):789–792
Cummings R, Phillips L, Wheat E, Black D, Goosby E, Wlodarczyk D, Trafton P, Jergesen H, Winograd C, Hulley S (1988) Recovery of function after hip fracture. The role of social supports. J Am Geriatr Soc 36(9):801–806
Davidson CW, Merrilees MJ, Wilkinson TJ, Mckie J, Gilchrist N (2001) Hip fracture mortality and morbidity—can we do better? N Z Med J 114(1136):329–332
Haentjens P (2003) Costs of care after hospital discharge among women with a femoral neck fracture. Clin Orthop 1(414):250–258
Harris HW (1969) Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by Moore arthroplasty. An end result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Jt Surg Am 51:737–755
Healey W, Iorio R (2004) Hip arthroplasty: optimal treatment for displaced femoral neck fractures in elderly patients. Clin Orthop 429:43–48
Koval J, Zuckerman D (1994) Hip fractures. I. Overview and evaluation and treatment of femoral neck fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2:141–149
Koval J, Skovron L, Aharnoff B, Zuckerman J (1998) Predictors of functional recovery after hip fracture in the elderly. Clin Orthop 348:22–28
Lu-Yao GL, Keller RB, Littenberg B, Wennberg J (1994) Outcomes after displaced fractures of the femoral neck. A meta-analysis of one hundred and six published reports. J Bone Jt Surg Am 76(1):15–25
Magaziner J, Simonsick M, Kashner M, Hebel J, Kenzora J (1990) Predictors of functional recovery one year following hospital discharge for hip fracture: a prospective study. J Gerontol 45(3):101–107
Marottoli A, Berkman F, Cooney M (1992) Decline in physical function following hip fracture. J Am Geriatr Soc 40(9):861–866
Mossey M, Murtan E, Knott K, Graik R (1989) Determinants of recovery 12 months after hip fracture: the importance of psychological factors. Am J Public Health 79(3):279–286
Parker J, Pryor A (2000) Internal fixation or arthroplasty for displaced cervical hip fractures in the elderly: a randomised controlled trial of 208 patients. Acta Orthop Scand 71:406–440
Ravikumar KJ, Marsh G (2000) Internal fixation versus hemi-arthroplasty versus total hip arthroplasty for displaced subcapital fractures of femur—13 year results of a prospective randomised study. Injury 31:793–797
Rogmark C, Carlsson A, Johnell O, Sembo I (2002) A prospective randomised trial of internal fixation versus arthroplasty for displaced fractures of the neck of the femur. Functional outcome for 450 patients at two years. J Bone Joint Surg Br 84(2):183–188
Shah S, Vanclay F, Cooper B (1989) Improving the sensitivity of the Barthel Index for stroke rehabilitation. J Clin Epidemiol 42:703–709
Skinner P, Riley D, Ellery J, Beaumont A, Cumine R, Shafighian B (1989) Displaced subcapital fractures of the femur: a prospective randomized comparison of internal fixation, hemi-arthroplasty and total hip replacement. Injury 20:291–293
Su H, Aharonoff GB, Hiebert R, Zuckerman J, Koval K (2000) In-hospital mortality after femoral neck fracture: do internal fixation and hemi-arthroplasty differ? Am J Orthop 32(3):151–155
Swiontkowski F (1994) Current concepts review: intracapsular fractures of the hip. J Bone Jt Surg 76A:129–138
Tanaka J, Tokimura F, Seki N (2003) Outcomes of hip fracture surgery in patients aged > or = 90 years. Orthopedics 26(1):55–58
Wade T, Collin C (1988) The Barthel ADL Index: a standard measure of physical disability? Int Disabil Stud 10:64–67
Young Y, German P, Brandt L, Kenzora J, Magaziner J (1996) The predictors of surgical procedure and the effects on functional recovery in elderly with subcapital fractures. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 51:158–164
Young Y, Brandt L, German P, Kenzora J, Magaziner J (1997) A longitudinal examination of functional recovery among older people with subcapital hip fracture. J Am Geriatr Soc 45(3):288–294
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mouzopoulos, G., Stamatakos, M., Arabatzi, H. et al. The four-year functional result after a displaced subcapital hip fracture treated with three different surgical options. International Orthopaedics (SICO 32, 367–373 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-007-0321-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-007-0321-1