Abstract
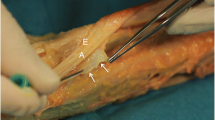
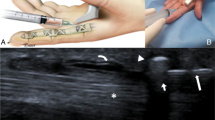
The methods and clinical outcomes of intra-sheath triamcinolone injection in the treatment of de Quervain’s disease are described. We used 38 hands of 36 patients. A mixture of 1 ml of triamcinolone and 1 ml of 1% lidocaine hydrochloride was injected, with an interval of 2 weeks. The fluid was injected into one point above the induration for the first 18 hands and into two points over the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus tendon in the induration for hands 19–38. The efficacy rate was 89%, with the treatment results of the two-point injection better than those of the one-point injection. Recurrence was observed in ten hands, and complications in 13 hands; however, over 90% of patients were satisfied with the injection. The accurate injection of triamcinolone into the sheath of both the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus tendon was considered very effective for de Quervain’s disease.
Résumé
L’injection de triamcinolone dans la maladie de de Quervain a déjà été décrite. 38 mains sur 36 patients ont été traitées par un mélange d’1 ml de triamcinolone et 1 ml d’1% de lidocaine hydrochlorique injectées à l’intervalle de deux semaines. Le liquide a été injecté au dessus de l’induration : à deux niveaux différents en dessous pour les 18 premières mains et en deux points différents au dessus du court extenseur et de l’abducteur du pouce pour les 20 suivants. Le taux de succès a été de 89 avec deux points d’injection, taux supérieur à un point, une récidive a été observée dans 10 mains et des complications dans 13 mains. Cependant, plus de 90% des patients sont satisfaits de cette injection. En conclusion : l’injection triamcinolone dans la gaine de l’extenseur du pouce et de l’abducteur peuvent être considérés comme efficaces dans la maladie de de Quervain.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahuja NK, Chung KC (2004) Fritz de Quervain, MD (1868–1940) Stenosing tendovaginitis at the radial styloid process. J Hand Surg [Am] 29:1164–1170
Bonnici AV, Spenser JD (1988) Survey of “Trigger finger” in adults. J Hand Surg [Br] 13:202–203
De Quervain F (1895) Uber eine Form von chronischer Tendovaginitis. Corresp Blatt Schweizer Arzte 25:389–394
Froimson A (1993) Tenosynovitis and tennis elbow. In: Green DP (ed) Operative hand surgery, vol. 2, 3rd edn. Churchill Livingstone, New York, pp 1989–2006
Giles KW (1960) Anatomical variations affecting the surgery of de Quervain’s disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br 42:352–355
Harvey FJ, Harvey PM, Horsley MW (1990) de Quervain’s disease: surgical or nonsurgical treatment. J Hand Surg [Am] 15:83–87
Jackson WT, Viegas SF, Coon TM et al (1986) Anatomical variation in the first extensor compartment of the wrist: a clinical and anatomical study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 68:923–926
Lapidus PW (1953) Stenosing tenosynovitis. Surg Clin North Am 33:1317–1347
Leslie BM, Ericson WB Jr, Morehead JR (1990) Incidence of a septum within the first dorsal compartment of the wrist. J Hand Surg [Am] 15:88–91
Newport L, Lane LB, Stuchin SA (1990) Treatment of trigger finger by steroid injection. J Hand Surg [Am] 15:748–750
Quinnel RC (1980) Conservative management of trigger finger. Practitioner 224:187–190
Richie CA 3rd, Eriner WW Jr (2003) Corticosteroid injection for treatment of de Quervain’s tenosynovitis: a pooled quantitative literature evaluation. J Am Board Fam Pract 16:102–106
Ta KT, Eidelman D, Thomson JG (1999) Patient satisfaction and outcomes of surgery for de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. J Hand Surg [Am] 24:1071–1077
Weiss AC, Akeiman E, Tabatabai M (1994) Treatment of de Quervain’s disease. J Hand Surg [Am] 19:595–598
Witt J, Pess G, Gelberman RH (1991) Treatment of de Quervain tenosynovitis: a prospective study of the results of injection of steroids and immobilization in splint. J Bone Joint Surg Am 73:219–222
Zingas C, Failla JM, Holsbeek MV (1998) Injection accuracy of clinical relief of de Quervain’s tendinitis. J Hand Surg [Am] 23:89–96
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sawaizumi, T., Nanno, M. & Ito, H. De Quervain’s disease: efficacy of intra-sheath triamcinolone injection. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 31, 265–268 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-006-0165-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-006-0165-0