Abstract
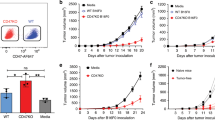
Interactions between CD40 and CD40L play a central role in the regulation of both humoral and cellular immunity. Recently, interactions between these molecules have also been implicated in the generation of protective cell-mediated tumor immunity. We have generated a tumor model in which a well-understood and clearly immunostimulatory antigen, influenza hemagglutinin has been transfected into the BALB/c-derived, MHC-class-I-positive, B7-deficient murine mammary carcinoma, MT901. In this model, expression of the influenza hemagglutinin antigen does not alter tumorigenicity in naïve but serves as a tumor-rejection target in immunized mice. T-cell-depletion experiments indicate that successful tumor protection can occur following immunization in mice depleted of CD4+ but not CD8+ T cells, suggesting that tumor protection is largely CD8-mediated and CD4-independent. Interestingly, despite the ability of tumor protection to be generated in the absence of CD4+ T cells, effective immunization was clearly dependent on CD40/CD40L as well as CD28/B7 interactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 20 January 1999 / Accepted: 2 June 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eck, S., Turka, L. Generation of protective immunity against an immunogenic carcinoma requires CD40/CD40L and B7/CD28 interactions but not CD4+ T cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother 48, 336–341 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002620050583
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002620050583