Abstract
Background
Immunotherapy has determined unprecedented long-term responses in several hematological and solid tumors. In the MOUSEION-03 study, we conducted a meta-analysis to determine the possibility of achieving complete remissions (CR) with immunotherapy or immuno-oncology combinations in cancer patients.
Methods
The primary endpoint was to assess the incidence of CR in cancer patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) alone or in combination with other agents versus control treatments. The pooled odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) for CR rate were extracted.
Results
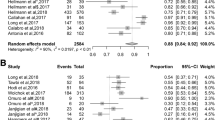
A total of 12,130 potentially relevant trials were identified; 5 phase II and 80 phase III randomized studies (37 monotherapies and 48 combinations) and 49,425 cancer patients were included. The most frequent types of malignancies were non-small cell lung cancer (n = 14,249; 29%), urothelial cancer (n = 6536; 13%), renal cell carcinoma (n = 5743; 12%), and melanoma (n = 2904; 6%). In patients treated with immunotherapy (as monotherapy or in combination with other anticancer agents), the pooled OR was 1.67 (1.52–1.84). The highest OR was registered by immune-based combinations with two ICIs (3.56, 95% CI 1.28–9.90).
Conclusions
To the best of the authors’ knowledge, no comprehensive meta-analysis on the use of ICIs and ICI-based combinations in solid tumors to systematically investigate the probability to achieve CR has been published so far. Although CR is not a common event in several cancer patients receiving immunotherapy, the MOUSEION-03 suggests that the use of ICIs may significantly increase the chance of achieving CR in comparison with control treatments.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
E Borcoman Y Kanjanapan S Champiat 2019 Novel patterns of response under immunotherapy AnnOncol 30 385 396
S Faury J Foucaud 2020 Health-related quality of life in cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a systematic review on reporting of methods in randomized controlled trials PLoS ONE 15 e0227344
C Robert 2020 A decade of immune-checkpoint inhibitors in cancer therapy Nat Commun 11 3801
P Darvin SM Toor V Sasidharan Nair E Elkord 2018 Immune checkpoint inhibitors: recent progress and potential biomarkers Exp Mol Med 50 1 11
RG Most van der BW Robinson RA Lake 2005 Combining immunotherapy with chemotherapy to treat cancer Discov Med 5 27 265 270
M Vanneman G Dranoff 2012 Combining immunotherapy and targeted therapies in cancer treatment Nat Rev Cancer 12 4 237 251
L Apetoh S Ladoire G Coukos F Ghiringhelli 2015 Combining immunotherapy and anticancer agents: the right path to achieve cancer cure? Ann Oncol 26 9 1813 1823
LH Schwartz S Litière E Vries de R Ford S Gwyther S Mandrekar 2016 RECIST 1. 1-Update and clarification: from the RECIST committee Eur J Cancer 62 132 7
D Moher A Liberati J Tetzlaff DG Altman PRISMA Group 2010 Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement Int J Surg 8 336 41
Rittmeyer A, Barlesi F, Waterkamp D, et al; OAK Study Group. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): a phase 3, open-label, multicentrerandomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2017 389:255–265.
P Schmid S Adams HS Rugo A Schneeweiss CH Barrios H Iwata 2018 Atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel in advanced triple-negative breast cancer N Engl J Med 379 2108 2121
MA Socinski RM Jotte F Cappuzzo F Orlandi D Stroyakovskiy N Nogami 2018 Atezolizumab for first-line treatment of metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC N Engl J Med 378 2288 2301
T Powles I Duran MS Heijden van der Y Loriot NJ Vogelzang U Giorgi De 2018 Atezolizumab versus chemotherapy in patients with platinum-treated locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (IMvigr211): a multicenter, open-label, phase 3 randomized controlled trial Lancet 391 748 757
Horn L, Mansfield AS, Szczęsna A, et al; IMpower133 Study Group. First-line atezolizumab plus chemotherapy in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:2220–9.
C Eng T Won Kim J Bendell G Argiles NC Tebbutt M Bartolomeo Di 2019 Atezolizumab with or without cobimetinib versus regorafenib in previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (IMblaze370): a multicenter, open-label, phase 3, randomized, controlled trial Lancet Oncol 20 849 861
H West M McCleod M Hussein 2019 Atezolizumab in combination with carboplatin plus nab-paclitaxel chemotherapy compared with chemotherapy alone as first-line treatment for metastatic non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower130): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial Lancet Oncol 20 924 937
BI Rini T Powles MB Atkins B Escudier DF McDermott C Suarez S Bracarda 2019 Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus sunitinib in patients with previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma (IMmotion151): a multicenter, open-label, phase 3, randomized controlled trial Lancet 393 2404 2415
Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, et al; IMbrave150 Investigators. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:1894–1905.
Galsky MD, Arija JÁA, Bamias A, et al; IMvigor130 Study Group. Atezolizumab with or without chemotherapy in metastatic urothelial cancer (IMvigor130): a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2020;395:1547–1557.
R Gutzmer D Stroyakovskiy H Gogas C Robert K Lewis S Protsenko 2020 Atezolizumab, vemurafenib, and cobimetinib as first-line treatment for unresectable advanced BRAFV600 mutation-positive melanoma (Imspire150): primary analysis of the randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial Lancet 395 1835 1844
EA Mittendorf H Zhang CH Barrios S Saji K Hae Jung R Hegg 2020 Neoadjuvant Atezolizumab in combination with sequential nab-paclitaxel and anthracycline-based chemotherapy versus placebo and chemotherapy in patients with early-stage triple-negative breast cancer (Impassion031): a randomized, double-blind, phase 3 trial Lancet 396 1090 1100
R Jotte F Cappuzzo I Vynnychenko 2020 Atezolizumab in combination with carboplatin and Nab-Paclitaxel in advanced squamous NSCLC (IMpower131): results from a randomized phase III trial J ThoracOncol 15 1351 1360
YJ Bang EY Ruiz E Cutsem Van 2018 Phase III, randomised trial of avelumab versus physician's choice of chemotherapy as third-line treatment of patients with advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer: primary analysis of JAVELIN Gastric 300 Ann Oncol 29 2052 2060
F Barlesi J Vansteenkiste D Spigel 2018 Avelumab versus docetaxel in patients with platinum-treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (JAVELIN Lung 200): an open-label, randomised, phase 3 study Lancet Oncol 19 1468 1479
TK Choueiri RJ Motzer BI Rini 2020 Updated efficacy results from the JAVELIN Renal 101 trial: first-line avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma Ann Oncol 31 1030 1039
T Powles SH Park E Voog C Caserta BP Valderrama H Gurney 2020 Avelumab maintenance therapy for advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma N Engl J Med 383 13 1218 1230
M Moehler M Dvorkin N Boku M Özgüroğlu MH Ryu AS Muntean 2021 Phase III trial of avelumab maintenance after first-line induction chemotherapy versus continuation of chemotherapy in patients with gastric cancers: results from JAVELIN gastric 100 J Clin Oncol 39 9 966 977
NY Lee RL Ferris A Psyrri RI Haddad M Tahara J Bourhis 2021 Avelumab plus standard-of-care chemoradiotherapy versus chemoradiotherapy alone in patients with locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre, phase 3 trial Lancet Oncol 22 4 450 462
E Pujade-Lauraine K Fujiwara JA Ledermann AM Oza R Kristeleit IL Ray-Coquard 2021 Avelumab alone or in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone in platinum-resistant or platinum-refractory ovarian cancer (JAVELIN Ovarian 200): an open-label, three-arm, randomised, phase 3 study Lancet Oncol 22 7 1034 1046
BJ Monk N Colombo AM Oza K Fujiwara MJ Birrer L Randall 2021 Chemotherapy with or without avelumab followed by avelumab maintenance versus chemotherapy alone in patients with previously untreated epithelial ovarian cancer (JAVELIN Ovarian 100): an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial Lancet Oncol 22 9 1275 1289
J Huang J Xu Y Chen W Zhuang Y Zhang Z Chen 2020 Camrelizumab versus investigator's choice of chemotherapy as second-line therapy for advanced or metastatic oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCORT): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 study Lancet Oncol 21 6 832 842
C Zhou G Chen Y Huang J Zhou L Lin J Feng 2021 Camrelizumab plus carboplatin and pemetrexed versus chemotherapy alone in chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (CameL): a randomised, open-label, multicentre, phase 3 trial Lancet Respir Med 9 3 305 314
H Luo J Lu Y Bai T Mao J Wang Q Fan 2021 Effect of Camrelizumab vs Placebo added to chemotherapy on survival and progression-free survival in patients with advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell Carcinoma: the ESCORT-1st randomized clinical trial JAMA 326 10 916 925
Y Yang S Qu J Li C Hu M Xu W Li 2021 Camrelizumab versus placebo in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin as first-line treatment for recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma (CAPTAIN-1st): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial Lancet Oncol 22 8 1162 1174
A Sezer S Kilickap M Gümüş I Bondarenko M Özgüroğlu M Gogishvili 2021 Cemiplimab monotherapy for first-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with PD-L1 of at least 50%: a multicentre, open-label, global, phase 3, randomised, controlled trial Lancet 397 10274 592 604
Paz-Ares L, Dvorkin M, Chen Y, et al; CASPIAN investigators. Durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide versus platinum-etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2019;394:1929–1939.
Powles T, van der Heijden MS, Castellano D, et al; DANUBE study investigators. Durvalumab alone and durvalumab plus tremelimumab versus chemotherapy in previously untreated patients with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (DANUBE): a randomised, open-label, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:1574–1588.
C Robert L Thomas I Bondarenko 2011 Ipilimumab plus dacarbazine for previously untreated metastatic melanoma N Engl J Med 364 2517 2526
M Reck A Luft A Szczesna 2016 Phase III randomized trial of Ipilimumab plus etoposide and platinum versus Placebo plus etoposide and platinum in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer J Clin Oncol 34 3740 3748
R Govindan A Szczesna MJ Ahn 2017 Phase III Trial of Ipilimumab Combined With Paclitaxel and Carboplatin in Advanced Squamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer J ClinOncol 35 3449 3457
C Robert GV Long B Brady C Dutriaux M Maio L Mortier 2015 Nivolumab in previously untreated melanoma without BRAF mutation N Engl J Med 372 4 320 330
JS Weber SP D'Angelo D Minor FS Hodi R Gutzmer B Neyns 2015 Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced melanoma who progressed after anti-CTLA-4 treatment (CheckMate 037): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial Lancet Oncol 16 4 375 384
H Borghaei L Paz-Ares L Horn 2015 Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer N Engl J Med 373 1627 1639
J Brahmer KL Reckamp P Baas 2015 Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced squamous-cell non-small-cell lung cancer N Engl J Med 373 123 135
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, McDermott DF, et al; CheckMate 025 Investigators. Nivolumab versus Everolimus in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2015; 373:1803–13.
Motzer RJ, Tannir NM, McDermott DF, et al; CheckMate 214 Investigators. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2018; 378:1277–1290.
ML Gillison G Blumenschein Jr J Fayette J Guigay AD Colevas L Licitra 2018 CheckMate 141: 1-Year update and subgroup analysis of Nivolumab as first-line therapy in patients with recurrent/Metastatic head and neck cancer Oncologist 23 9 1079 1082
MD Hellmann L Paz-Ares R Bernabe Caro B Zurawski SW Kim E Carcereny Costa 2019 Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer N Engl J Med 381 21 2020 2031
K Kato BC Cho M Takahashi M Okada CY Lin K Chin 2019 Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma refractory or intolerant to previous chemotherapy (ATTRACTION-3): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial Lancet Oncol 20 11 1506 1517
YL Wu S Lu Y Cheng C Zhou J Wang T Mok 2019 Nivolumab versus docetaxel in a predominantly Chinese patient population with previously treated advanced NSCLC: CheckMate 078 randomized phase III clinical trial J Thorac Oncol 14 5 867 875
DA Reardon AA Brandes A Omuro P Mulholland M Lim A Wick 2020 Effect of Nivolumab vs Bevacizumab in patients with recurrent Glioblastoma: the checkMate 143 phase 3 randomized clinical trial JAMA Oncol 6 7 1003 1010
T Tsujikawa T Crocenzi JN Durham EA Sugar AA Wu B Onners 2020 Evaluation of Cyclophosphamide/GVAX pancreas followed by Listeria-Mesothelin (CRS-207) with or without Nivolumab in patients with pancreatic cancer Clin Cancer Res 26 14 3578 3588
J Hamanishi N Takeshima N Katsumata K Ushijima T Kimura S Takeuchi 2021 Nivolumab Versus Gemcitabine or pegylated liposomal doxorubicin for patients with platinum-resistant ovarian cancer: open-label, randomized trial in Japan (NINJA) J Clin Oncol 39 33 3671 3681
P Baas A Scherpereel AK Nowak N Fujimoto S Peters AS Tsao 2021 First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab in unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma (CheckMate 743): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial Lancet 397 10272 375 386
M Reck TE Ciuleanu M Cobo M Schenker B Zurawski J Menezes 2021 First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab with two cycles of chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone (four cycles) in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: CheckMate 9LA 2-year update ESMO Open 6 5 100273
S Sugawara JS Lee JH Kang HR Kim N Inui T Hida 2021 Nivolumab with carboplatin, paclitaxel, and bevacizumab for first-line treatment of advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer Ann Oncol 32 9 1137 1147
DR Spigel D Vicente TE Ciuleanu S Gettinger S Peters L Horn 2021 Second-line nivolumab in relapsed small-cell lung cancer: CheckMate 331☆ Ann Oncol 32 5 631 641
YY Janjigian K Shitara M Moehler M Garrido P Salman L Shen 2021 First-line nivolumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for advanced gastric, gastro-oesophageal junction, and oesophageal adenocarcinoma (CheckMate 649): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial Lancet 398 10294 27 40
TK Choueiri T Powles M Burotto B Escudier MT Bourlon B Zurawski 2021 Nivolumab plus cabozantinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma N Engl J Med 384 9 829 841
A Ribas I Puzanov R Dummer D Schadendorf O Hamid C Robert 2015 Pembrolizumab versus investigator-choice chemotherapy for ipilimumab-refractory melanoma (KEYNOTE-002): a randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial Lancet Oncol 16 8 908 918
RS Herbst P Baas DW Kim E Felip JL Pérez-Gracia JY Han 2016 Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): a randomised controlled trial Lancet 387 10027 1540 1550
Paz-Ares L, Luft A, Vicente D, et al; KEYNOTE-407 Investigators. Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy for Squamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med 2018;379:2040–2051.
Gandhi L, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Gadgeel S, et al; KEYNOTE-189 Investigators. Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med 2018;378:2078–2092.
Burtness B, Harrington KJ, Greil R, et al; KEYNOTE-048 Investigators. Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2019;394:1915–1928.
Y Fradet J Bellmunt DJ Vaughn JL Lee L Fong NJ Vogelzang 2019 Randomized phase III KEYNOTE-045 trial of pembrolizumab versus paclitaxel, docetaxel, or vinflunine in recurrent advanced urothelial cancer: results of >2 years of follow-up Ann Oncol 30 6 970 976
Cohen EEW, Soulières D, Le Tourneau C, et al; KEYNOTE-040 investigators. Pembrolizumab versus methotrexate, docetaxel, or cetuximab for recurrent or metastatic head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-040): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2019;393:156–167.
Mok TSK, Wu YL, Kudaba I, et al; KEYNOTE-042 Investigators. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for previously untreated, PD-L1-expressing, locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-042): a randomised, open-label, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019;393:1819–1830.
Rini BI, Plimack ER, Stus V, et al; KEYNOTE-426 Investigators. Pembrolizumab plus Axitinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1116–1127.
T Powles ER Plimack D Soulières T Waddell V Stus R Gafanov 2020 Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib monotherapy as first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-426): extended follow-up from a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial Lancet Oncol 21 12 1563 1573
L Paz-Ares D Vicente A Tafreshi A Robinson H Soto Parra J Mazières 2020 A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in patients with metastatic squamous NSCLC: protocol-Specified final analysis of KEYNOTE-407 J Thorac Oncol 15 10 1657 1669
P Schmid J Cortes L Pusztai H McArthur S Kümmel J Bergh 2020 Pembrolizumab for early triple-negative breast cancer N Engl J Med 382 9 810 821
K Shitara E Cutsem Van YJ Bang C Fuchs L Wyrwicz KW Lee 2020 Efficacy and safety of pembrolizumab or pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy vs chemotherapy alone for patients with first-line, advanced gastric cancer: the KEYNOTE-062 phase 3 randomized clinical trial JAMA Oncol 6 10 1571 1580
T André KK Shiu TW Kim BV Jensen LH Jensen C Punt 2020 Pembrolizumab in Microsatellite-Instability-High Advanced Colorectal Cancer N Engl J Med 383 23 2207 2218
CM Rudin MM Awad A Navarro M Gottfried S Peters T Csőszi 2020 Pembrolizumab or placebo plus etoposide and platinum as first-line therapy for extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: randomized, double-blind, phase III KEYNOTE-604 study J Clin Oncol 38 21 2369 2379
PF Ferrucci AM Giacomo Di M Vecchio Del V Atkinson H Schmidt J Schachter 2020 KEYNOTE-022 part 3: a randomized, double-blind, phase 2 study of pembrolizumab, dabrafenib, and trametinib in BRAF-mutant melanoma J Immunother Cancer 8 2 e001806
H Nishiyama Y Yamamoto N Sassa K Nishimura K Fujimoto S Fukasawa 2020 Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy in recurrent, advanced urothelial cancer in Japanese patients: a subgroup analysis of the phase 3 KEYNOTE-045 trial Int J Clin Oncol 25 1 165 174
SM Tolaney R Barroso-Sousa T Keenan T Li L Trippa I Vaz-Luis 2020 Effect of eribulin with or without pembrolizumab on progression-free survival for patients with hormone receptor-positive, ERBB2-negative metastatic breast cancer: a randomized clinical trial JAMA Oncol 6 10 1598 1605
R Motzer B Alekseev SY Rha C Porta M Eto T Powles 2021 Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab or everolimus for advanced renal cell carcinoma N Engl J Med 384 14 1289 1300
D Rodríguez-Abreu SF Powell MJ Hochmair S Gadgeel E Esteban E Felip 2021 Pemetrexed plus platinum with or without pembrolizumab in patients with previously untreated metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC: protocol-specified final analysis from KEYNOTE-189 Ann Oncol 32 7 881 895
MM Awad SM Gadgeel H Borghaei A Patnaik JC Yang SF Powell 2021 Long-term overall survival from KEYNOTE-021 Cohort G: pemetrexed and carboplatin with or without pembrolizumab as first-line therapy for advanced nonsquamous NSCLC J Thorac Oncol 16 1 162 168
N Colombo C Dubot D Lorusso MV Caceres K Hasegawa R Shapira-Frommer 2021 Pembrolizumab for persistent, recurrent, or metastatic cervical cancer N Engl J Med 385 20 1856 1867
T Powles T Csőszi M Özgüroğlu N Matsubara L Géczi SY Cheng 2021 Pembrolizumab alone or combined with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy as first-line therapy for advanced urothelial carcinoma (KEYNOTE-361): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial Lancet Oncol 22 7 931 945
Sun JM, Shen L, Shah MA, Enzinger P, Adenis A, Doi T, et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for first-line treatment of advanced oesophageal cancer (KEYNOTE-590): a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2021 ;398(10302):759–771.
EP Winer O Lipatov SA Im A Goncalves E Muñoz-Couselo KS Lee 2021 Pembrolizumab versus investigator-choice chemotherapy for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (KEYNOTE-119): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial Lancet Oncol 22 4 499 511
S Lu J Wang Y Yu X Yu Y Hu X Ai 2021 Tislelizumab Plus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for locally advanced or metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC (RATIONALE 304): a randomized phase 3 trial J Thorac Oncol 16 9 1512 1522
A Ribas R Kefford MA Marshall CJ Punt JB Haanen M Marmol 2013 Phase III randomized clinical trial comparing tremelimumab with standard-of-care chemotherapy in patients with advanced melanoma J Clin Oncol 31 5 616 622
T Powles J Walker J Andrew Williams J Bellmunt 2020 The evolving role of PD-L1 testing in patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma Cancer Treat Rev 82 101925
F Massari A Rizzo V Mollica M Rosellini A Marchetti A Ardizzoni M Santoni 2021 Immune-based combinations for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials Eur J Cancer 154 120 127
M Miguel de E Calvo 2020 Clinical challenges of immune checkpoint inhibitors Cancer Cell 38 326 333
Dizman, N.; Arslan, Z.E.; Feng, M.; Pal, S.K. Sequencing Therapies for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Urol. Clin. North Am. 2020, 47, :305–318.
X Gao DF McDermott 2018 Ipilimumab in combination with nivolumab for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma Exp Opin Biol Ther 18 947 957
Y Yang 2015 Cancer immunotherapy: harnessing the immune system to battle cancer J Clin Invest 125 3335 3337
P Bergerot P Lamb E Wang SK Pal 2019 Cabozantinib in Combination with Immunotherapy for Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma and Urothelial Carcinoma: Rationale and Clinical Evidence Mol Cancer Ther 18 2185 2193
AL Cheng C Hsu SL Chan SP Choo M Kudo 2020 Challenges of combination therapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors for hepatocellular carcinoma J Hepatol 72 307 319
S Lemery P Keegan R Pazdur 2017 First FDA approval agnostic of cancer site - when a biomarker defines the indication N Engl J Med 377 1409 1412
A Rizzo M Santoni V Mollica F Logullo M Rosellini A Marchetti L Faloppi N Battelli F Massari 2021 Peripheral neuropathy and headache in cancer patients treated with immunotherapy and immuno-oncology combinations: the MOUSEION-02 study Exp Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 17 12 1455 1466 https://doi.org/10.1080/17425255.2021.2029405
DJ Herzyk HG Haggerty 2018 Cancer immunotherapy: factors important for the evaluation of safety in nonclinical studies AAPS J 20 2 28 https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-017-0184-3
D Hu W Zhang J Tang Z Zhou X Liu Y Shen 2021 Improving safety of cancer immunotherapy via delivery technology Biomaterials 265 120407https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120407
F Massari V Mollica A Rizzo L Cosmai M Rizzo C Porta 2020 Safety evaluation of immune-based combinations in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis Exp Opin Drug Saf 19 1329 1338
IY Sheng BI Rini 2019 Immunotherapy for renal cell carcinoma Exp Opin Biol Ther 19 897 905
Z Wang J Duan S Cai M Han H Dong J Zhao B Zhu S Wang M Zhuo J Sun 2019 Assessment of blood tumor mutational burden as a potential biomarker for immunotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer with use of a next-generation sequencing cancer gene panel JAMA Oncol 5 696 702
AM Goodman S Kato L Bazhenova SP Patel GM Frampton V Miller PJ Stephens GA Daniels R Kurzrock 2017 Tumor mutational burden as an independent predictor of response to immunotherapy in diverse cancers Mol Cancer Ther 16 2598 2608
ZR Chalmers CF Connelly D Fabrizio L Gay SM Ali R Ennis A Schrock B Campbell A Shlien J Chmielecki 2017 Analysis of 100,000 human cancer genomes reveals the landscape of tumor mutational burden Genome Med 9 34
V Mollica M Santoni MR Matrana U Basso U Giorgi De A Rizzo M Maruzzo A Marchetti M Rosellini S Bleve D Maslov K Tawagi E Philon Z Blake F Massari 2022 Concomitant proton pump inhibitors and outcome of patients treated with nivolumab alone or plus ipilimumab for advanced renal cell carcinoma Target Oncol 17 1 61 68 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-021-00861-y
J Li Q He X Yu K Khan X Weng M Guan 2019 Complete response associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis of nine randomized controlled trials Cancer Manag Res 18 11 1623 1629 https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S188551
Acknowledgements
Fernando Sabino Marques Monteiro has received research support from Janssen, Merck Sharp and Dhome and honoraria from Janssen, Ipsen, Bristol Myers Squibb and Merck Sharp and Dhome. All unrelated to the present paper. Andrey Soares has received honoraria: Janssen, Pfizer, Bayer, Novartis, AstraZeneca, Astellas Pharma, Pierre Fabre, Merck Serono, Sanofi,Roche, Ipsen, Zodiac. Consulting or Advisory Role: Astellas Pharma, Janssen, Roche, Bayer, Lilly, AstraZeneca, Novartis, MSD, Bristol Myers Squibb, Zodiac, Amgem, Ipsen, United, Zodiac. Research Funding: Bristol Myers Squibb (Inst), Astellas (Inst), AstraZeneca (Inst). Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: AstraZeneca,Pfizer, AstellasPharma, Bristol Myers Squibb, Bayer, Roche, Janssen, Merck Serono, Sanofi, Ipsen, Zodiac. Enrique Grande has received honoraria for speaker engagements, advisory roles or funding of continuous medical education from Adacap, AMGEN, Angelini, Astellas, Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Blueprint, Bristol Myers Squibb, Caris Life Sciences, Celgene, Clovis-Oncology, Eisai, Eusa Pharma, Genetracer, Guardant Health, HRA-Pharma, IPSEN, ITM-Radiopharma, Janssen, Lexicon, Lilly, Merck KGaA, MSD, Nanostring Technologies, Natera, Novartis, ONCODNA (Biosequence), Palex, Pharmamar, Pierre Fabre, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi-Genzyme, Servier, Taiho, and Thermo Fisher Scientific. EG has received research grants from Pfizer, Astra Zeneca, Astellas, and Lexicon Pharmaceuticals. Francesco Massari reports personal fees from Astellas, BMS, Janssen, Ipsen, MSD, and Pfizer outside the submitted work.
Funding
None to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.S, A.R. and F.M. wrote the main manuscript text. All authors reviewed the manuscript
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Santoni, M., Rizzo, A., Kucharz, J. et al. Complete remissions following immunotherapy or immuno-oncology combinations in cancer patients: the MOUSEION-03 meta-analysis. Cancer Immunol Immunother 72, 1365–1379 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-022-03349-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-022-03349-4