Abstract
Background
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) or immune checkpoint blockade (ICB), either alone or in combination, confers a significant overall survival (OS) benefit for metastatic RCC in the first-line setting. However, guidance for optimal treatment selection in elderly patients remains limited.
Methods
A database search was performed to identify eligible randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating first-line regimens for patients with advanced RCC older than 65 years old. The primary outcomes were progression-free survival (PFS) and OS. Indirect comparisons of available regimens were estimated using a random-effects network meta-analysis.
Results
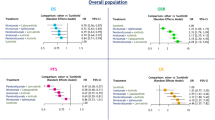
A total of 14 and five RCTs were eligible for PFS and OS analyses. Compared with sunitinib, pembrolizumab plus axitinib (HR 0.68, 95% CI 0.48–0.97) and pembrolizumab plus lenvatinib (HR 0.61, 95% CI 0.4–0.94) were associated with improved OS. Pembrolizumab plus lenvatinib, nivolumab plus cabozantinib, pembrolizumab plus axitinib, and cabozantinib alone each showed improved PFS over sunitinib. Among these, pembrolizumab plus lenvatinib showed better PFS than pembrolizumab plus axitinib (HR 0.58, 95% CI 0.37–0.91), but no PFS difference compared to nivolumab plus cabozantinib (HR 0.63, 95% CI 0.39–1.03) and cabozantinib alone (HR 0.84, 95% CI 0.40–1.77). Network ranking showed pembrolizumab plus lenvatinib provided the favored OS and PFS benefit for elderly patients.
Conclusions
The combination of ICB with TKI such as pembrolizumab plus lenvatinib needs to be considered over monotherapy in the elderly population, but further validation using real-world data or prospective trials is necessary to confirm the efficacy and safety of first-line regimens for the geriatric population with advanced RCC.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available in a public, open access repository. All data relevant to the study are included in the article or uploaded as supplementary information.
References
Canino C, Perrone L, Bosco E, Saltalamacchia G, Mosca A, Rizzo M et al (2019) Targeting angiogenesis in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 19:245–257
George DJ, Kaelin WG Jr (2003) The von hippel-lindau protein, vascular endothelial growth factor, and kidney cancer. N Engl J Med 349:419–421
Powles T (2021) Recent eUpdate to the ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines on renal cell carcinoma on cabozantinib and nivolumab for first-line clear cell renal cancer: renal cell carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 32:422–423
Vuong L, Kotecha RR, Voss MH, Hakimi AA (2019) Tumor microenvironment dynamics in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Discov 9:1349–1357
Yang J, Yan J, Liu B (2018) Targeting VEGF/VEGFR to modulate antitumor immunity. Front Immunol 9:978
Fujiwara Y, Mittra A, Naqash AR, Takebe N (2020) A review of mechanisms of resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors and potential strategies for therapy. Cancer Drug Resist 3:252–275
Rathmell WK, Rumble RB, Van Veldhuizen PJ, Al-Ahmadie H, Emamekhoo H, Hauke RJ, et al. (2022) Management of Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: ASCO Guideline. Journal of Clinical Oncology. JCO.22.00868.
Massari F, Rizzo A, Mollica V, Rosellini M, Marchetti A, Ardizzoni A et al (2021) Immune-based combinations for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. Eur J Cancer 154:120–127
Mollica V, Santoni M, Matrana MR, Basso U, De Giorgi U, Rizzo A et al (2022) Concomitant proton pump inhibitors and outcome of patients treated with nivolumab alone or plus ipilimumab for advanced renal cell carcinoma. Target Oncol 17:61–68
Dizman N, Meza L, Bergerot P, Alcantara M, Dorff T, Lyou Y et al (2022) Nivolumab plus ipilimumab with or without live bacterial supplementation in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a randomized phase 1 trial. Nat Med 28:704–712
Rizzo A, Mollica V, Santoni M, Massari F (2022) Assessing PD-L1 status in mRCC treated with first-line immune-based combinations: a meta-analysis. Immunotherapy 14:617–625
Santoni M, Massari F, Bracarda S, Grande E, Matrana MR, Rizzo M et al (2022) Cabozantinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma primary refractory to first-line immunocombinations or tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Eur Urol Focus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2022.02.004
Landre T, Des Guetz G, Chouahnia K, Fossey-Diaz V, Culine S (2020) Immune checkpoint inhibitors for patients aged ≥ 75 years with advanced cancer in first- and second-line settings: a meta-analysis. Drugs Aging 37:747–754
Nebhan CA, Cortellini A, Ma W, Ganta T, Song H, Ye F et al (2021) Clinical outcomes and toxic effects of single-agent immune checkpoint inhibitors among patients aged 80 years or older with cancer: a multicenter international cohort study. JAMA Oncol 7:1856–1861
Kanesvaran R, Le Saux O, Motzer R, Choueiri TK, Scotté F, Bellmunt J et al (2018) Elderly patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: position paper from the International Society of Geriatric Oncology. Lancet Oncol 19:e317–e326
Kaymakcalan MD, Xie W, Albiges L, North SA, Kollmannsberger CK, Smoragiewicz M et al (2016) Risk factors and model for predicting toxicity-related treatment discontinuation in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy: results from the international metastatic renal cell carcinoma database consortium. Cancer 122:411–419
Varkaris A, Xu W, Davis RB, Healy B, McDermott DF (2020) Combining immune checkpoint and VEGFR inhibition in favorable risk and elderly patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer 18:179–84.e3
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD et al (2021) The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst Rev 10:89
Rohatgi A. WebPlotDigitizer. 4.5 ed (2021)
Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I et al (2019) RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 366:l4898
Rücker G, Krahn U, König J, Efthimiou O, Davies A, Papakonstantinou T, et al. (2022) Netmeta: network meta-analysis using frequentist methods.
Escudier B, Bellmunt J, Négrier S, Bajetta E, Melichar B, Bracarda S et al (2010) Phase III trial of bevacizumab plus interferon alfa-2a in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (AVOREN): final analysis of overall survival. J Clin Oncol 28:2144–2150
Escudier B, Pluzanska A, Koralewski P, Ravaud A, Bracarda S, Szczylik C et al (2007) Bevacizumab plus interferon alfa-2a for treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a randomised, double-blind phase III trial. Lancet 370:2103–2111
George DJ, Hessel C, Halabi S, Michaelson MD, Hahn O, Walsh M et al (2019) Cabozantinib versus sunitinib for untreated patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma of intermediate or poor risk: subgroup analysis of the alliance A031203 CABOSUN trial. Oncologist 24:1497–1501
Motzer RJ, Tannir NM, McDermott DF, Arén Frontera O, Melichar B, Choueiri TK et al (2018) Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 378:1277–1290
Choueiri TK, Powles T, Burotto M, Escudier B, Bourlon MT, Zurawski B et al (2021) Nivolumab plus cabozantinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 384:829–841
Motzer R, Alekseev B, Rha SY, Porta C, Eto M, Powles T et al (2021) Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab or everolimus for advanced renal cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 384:1289–1300
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Cella D, Reeves J, Hawkins R, Guo J et al (2013) Pazopanib versus sunitinib in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 369:722–731
Rini BI, Bellmunt J, Clancy J, Wang K, Niethammer AG, Hariharan S et al (2014) Randomized phase III trial of temsirolimus and bevacizumab versus interferon alfa and bevacizumab in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: INTORACT trial. J Clin Oncol 32:752–759
Choueiri TK, Motzer RJ, Rini BI, Haanen J, Campbell MT, Venugopal B et al (2020) Updated efficacy results from the JAVELIN Renal 101 trial: first-line avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Ann Oncol 31:1030–1039
Powles T, Plimack ER, Soulières D, Waddell T, Stus V, Gafanov R et al (2020) Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib monotherapy as first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-426): extended follow-up from a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 21:1563–1573
Hudes G, Carducci M, Tomczak P, Dutcher J, Figlin R, Kapoor A et al (2007) Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356:2271–2281
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O et al (2007) Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356:115–124
Hutson TE, Lesovoy V, Al-Shukri S, Stus VP, Lipatov ON, Bair AH et al (2013) Axitinib versus sorafenib as first-line therapy in patients with metastatic renal-cell carcinoma: a randomised open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 14:1287–1294
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Szczylik C, Oudard S, Siebels M et al (2007) Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 356:125–134
Motzer RJ, Nosov D, Eisen T, Bondarenko I, Lesovoy V, Lipatov O et al (2013) Tivozanib versus sorafenib as initial targeted therapy for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results from a phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 31:3791–3799
Sternberg CN, Davis ID, Mardiak J, Szczylik C, Lee E, Wagstaff J et al (2010) Pazopanib in locally advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 28:1061–1068
World Health O. World report on ageing and health. Geneva: world Health Organization; 2015.
CDC. Indicator Definitions - Older Adults. 2015.
Hermansen CK, Donskov F (2021) Outcomes based on age in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with first line targeted therapy or checkpoint immunotherapy: older patients more prone to toxicity. J Geriatr Oncol 12:827–833
Araujo DV, Wells JC, Hansen AR, Dizman N, Pal SK, Beuselinck B et al (2021) Efficacy of immune-checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) in the treatment of older adults with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC)—an international mRCC database consortium (IMDC) analysis. J Geriatr Oncol 12:820–826
Santoni M, Buti S, Conti A, Porta C, Procopio G, Sternberg CN et al (2015) Prognostic significance of host immune status in patients with late relapsing renal cell carcinoma treated with targeted therapy. Target Oncol 10:517–522
Daste A, Domblides C, Gross-Goupil M, Chakiba C, Quivy A, Cochin V et al (2017) Immune checkpoint inhibitors and elderly people: a review. Eur J Cancer 82:155–166
Hale P, Hahn AW, Rathi N, Pal SK, Haaland B, Agarwal N (2019) Treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma in older patients: a network meta-analysis. J Geriatr Oncol 10:149–154
Massari F, Mollica V, Rizzo A, Cosmai L, Rizzo M, Porta C (2020) Safety evaluation of immune-based combinations in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Opin Drug Saf 19:1329–1338
Tomita Y, Motzer RJ, Choueiri TK, Rini BI, Miyake H, Uemura H et al (2022) Efficacy and safety of avelumab plus axitinib in elderly patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: extended follow-up results from JAVELIN Renal 101. ESMO Open 7:100450
Schulz GB, Rodler S, Szabados B, Graser A, Buchner A, Stief C et al (2020) Safety, efficacy and prognostic impact of immune checkpoint inhibitors in older patients with genitourinary cancers. J Geriatr Oncol 11:1061–1066
Rini BI, Powles T, Atkins MB, Escudier B, McDermott DF, Suarez C et al (2019) Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus sunitinib in patients with previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma (IMmotion151): a multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 393:2404–2415
Rini BI, Stenzl A, Zdrojowy R, Kogan M, Shkolnik M, Oudard S et al (2016) IMA901, a multipeptide cancer vaccine, plus sunitinib versus sunitinib alone, as first-line therapy for advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma (IMPRINT): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 17:1599–1611
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This research was not supported by a specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YF helped in conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, resources, statistical analysis, writing—original draft, and visualization. HM contributed to formal analysis, investigation, data curation, statistical analysis, writing—review & editing. BCL performed conceptualization, writing—review & editing, visualization, and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have a conflict of interest to report for the submitted work.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not required.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fujiwara, Y., Miyashita, H. & Liaw, B.C. First-line therapy for elderly patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma in the immuno-oncology era: a network meta-analysis. Cancer Immunol Immunother 72, 1355–1364 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-022-03341-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-022-03341-y