Abstract
Cluster of differentiation 47 (CD47) is a transmembrane protein ubiquitously expressed on human cells but overexpressed on many different tumor cells. The interaction of CD47 with signal-regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) triggers a “don’t eat me” signal to the macrophage, inhibiting phagocytosis. Thus, overexpression of CD47 enables tumor cells to escape from immune surveillance via the blockade of phagocytic mechanisms. We report here the development and characterization of CC-90002, a humanized anti-CD47 antibody. CC-90002 is unique among previously reported anti-CD47 bivalent antibodies that it does not promote hemagglutination while maintaining high-affinity binding to CD47 and inhibition of the CD47–SIRPα interaction. Studies in a panel of hematological cancer cell lines showed concentration-dependent CC-90002-mediated phagocytosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia (AML), lenalidomide-resistant multiple myeloma (MM) cell lines and AML cells from patients. In vivo studies with MM cell line-derived xenograft models established in immunodeficient mice demonstrated significant dose-dependent antitumor activity of CC-90002. Treatment with CC-90002 significantly prolonged survival in an HL-60-disseminated AML model. Mechanistic studies confirmed the binding of CC-90002 to tumor cells and concomitant recruitment of F4-80 positive macrophages into the tumor and an increase in expression of select chemokines and cytokines of murine origin. Furthermore, the role of macrophages in the CC-90002-mediated antitumor activity was demonstrated by transient depletion of macrophages with liposome-clodronate treatment. In non-human primates, CC-90002 displayed acceptable pharmacokinetic properties and a favorable toxicity profile. These data demonstrate the potential activity of CC-90002 across hematological malignancies and provided basis for clinical studies CC-90002-ST-001 (NCT02367196) and CC-90002-AML-001 (NCT02641002).


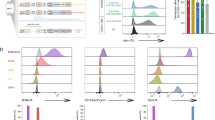
source of CD47. Data were normalized to a no antibody control. E. CC-90002 does not promote hemagglutination of human RBCs. Human RBCs were treated with a titration of CD47 antibodies. Evidence of hemagglutination was demonstrated by the presence of non-settled RBCs, appearing as a haze compared to a punctate red dot of non-hemagglutinated RBCs. The anti-CD47 antibody 9E4 was a positive control. 2A1m and 2A1-xi (chimeric): murine anti-CD47 antibodies. QN-IgG1 and QN-IgG4P: variants of CC-90002




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sharpe AH, Pauken KE (2018) The diverse functions of the PD1 inhibitory pathway. Nat Rev Immunol 18:153–167. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2017.108
Taylor PR, Martinez-Pomares L, Stcey M, Lin HH, Brown GD, Gordon S (2005) Macrophage receptors and immune recognition. Ann Rev Immunol 23:901–944. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115816
Russ A, Hua AB, Montfort WR, Rahman B, Riaz IB, Khalid MU et al (2018) Blocking “don’t eat me” signal of CD47-SIRPα in hematological malignancies, an in-depth review. Blood Rev 32:480–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.blre.2018.04.005
Matlung HL, Szilagyi K, Barclay NA, van den Berg TK (2017) The CD47-SIRPα signaling axis as an innate immune checkpoint in cancer. Immunol Rev 276:145–164. https://doi.org/10.1111/imr.12527
Fujioka Y, Matozaki T, Noguchi T, Iwamatsu A, Yamao T, Takahashi N et al (1996) A novel membrane glycoprotein, SHPS-1, that binds the SH2-domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 in response to mitogens and cell adhesion. Mol Cell Biol 16:6887–6899. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.16.12.6887
Kikuchi Y, Uno S, Kinoshita Y, Yoshimura Y, Iida S-i, Wakahara Y et al (2005) Apoptosis inducing bivalent single-chain antibody fragments against CD47 showed antitumor potency for multiple myeloma. Leukemia Res 29:445–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2004.09.005
Yuan J, He H, Chen C, Wu J, Rao J, Yan H (2019) Combined high expression of CD47 and CD68 is a novel prognostic factor for breast cancer patients. Cancer Cell Int 11(19):238. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-019-0957-0
Yoshida K, Tsujimoto H, Matsumura K, Kinoshita M, Takahata R, Matsumoto Y et al (2015) CD47 is an adverse prognostic factor and a therapeutic target in gastric cancer. Cancer Med 4:1322–1333. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.478
Majeti R, Chao MP, Alizadeh AA, Pang WW, Jaiswal S, Gibbs KD Jr et al (2009) CD47 is an adverse prognostic factor and therapeutic antibody target on human acute myeloid leukemia stem cells. Cell 138:286–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.045
Galli S, Zlobec I, Schürch C, Perren A, Ochsenbein AF, Banz Y (2015) CD47 protein expression in acute myeloid leukemia: a tissue microarray-based analysis. Leuk Res 39:749–756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2015.04.007
Willingham SB, Volkmer JP, Gentles AJ, Sahoo D, Dalerba P, Mitra SS et al (2012) The CD47-signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) interaction is a therapeutic target for human solid tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:6662–6667. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1121623109
Liu J, Wang L, Zhao F, Tseng S, Narayan C, Shura L et al (2015) Pre-Clinical development of a humanized anti-CD47 antibody with anti-cancer therapeutic potential. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0137345
Weiskopf K, Jahchan NS, Schnorr PJ, Cristea S, Ring AM, Maute RL et al (2016) CD47-blocking immunotherapies stimulate macrophage-mediated destruction of small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Invest 126:2610–2620. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI81603
Ring NG, Herndler-Brandstetter D, Weiskopf K, Shan L, Volkmer J, George BM et al (2017) Anti-SIRPα antibody immunotherapy enhances neutrophil and macrophage antitumor activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:E10578-10585. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1710877114
Petrova PS, Viller NN, Wong M, Pang X, Lin GHY, Dodge K et al (2017) TTI-621 (SIRPαFc): a CD47-blocking innate immune checkpoint inhibitor with broad antitumor activity and minimal erythrocyte binding. Clin Cancer Res 23:1068–1079. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1700
Uno S, Kinoshita Y, Azuma Y, Tsunenari T, Yoshimura Y, Iida S et al (2007) Antitumor activity of a monoclonal antibody against CD47 in xenograft models of human leukemia. Oncol Rep 17:1189–1194
Murata Y, Saito Y, Kotani T et al (2018) CD47-Signal regulatory protein α signaling system and its application to cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Sci 109:2349–2357. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13663
Puro RJ, Bouchlaka MN, Hiebsch RR, Capoccia BJ, Donio MJ, Manning PT et al (2020) Development of AO-176, a next-generation humanized anti-CD47 antibody with novel anticancer properties and negligible red blood cell binding. Mol Cancer Ther 19:835–846. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-19-1079
Peluso MO, Adam A, Armet CM, Zhang L, O’Conner RW, Lee BH et al (2020) The Fully human anti-CD47 antibody SRF231 exerts dual-mechanism antitumor activity via engagement of the activating receptor CD32a. J ImmunoTherapy Cancer 8:e000413. https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2019-000413
Lin GHY, Chai V, Lee V et al (2017) TTI-621 (SIRPαFc), a CD47-blocking cancer immunotherapeutic, triggers phagocytosis of lymphoma cells by multiple polarized macrophage subsets. PLoS ONE 12:e0187262. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0187262
Zhang X, Fan J, Wang S, Li Y, Wang Y, Li S et al (2017) Targeting CD47 and autophagy elicited enhanced antitumor effects in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Res 5:363–375. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-16-0398
Ma L, Zhu M, Gai J, Li G, Chang Q, Qiao P et al (2020) Preclinical development of a novel CD47 nanobody with less toxicity and enhanced anti-cancer therapeutic potential. J Nanobiotechnology 18:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-020-0571-2
Tseng D, Volkmer JP, Willingham SB, Contreras-Trujillo H, Fathman JW, Fernhoff NB et al (2013) Anti-CD47 antibody-mediated phagocytosis of cancer by macrophages primes an effective antitumor T-cell response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:11103–11108. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1305569110
Veillette A, Tang Z (2019) Signaling regulatory protein (SIRP)α-CD47 blockade joins the ranks of immune checkpoint inhibition. J Clin Oncol 37:1012–1014. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.19.00121
Oldenborg PA, Zheleznyak A, Fang YF, Lagenaur CF, Gresham HD, Lindberg FP (2000) Role of CD47 as a marker of self on red blood cells. Science 288:2051–2054. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.288.5473.2051
Veillette A, Chen J (2018) SIRPα-CD47 immune checkpoint blockade in anticancer therapy. Trends Immunol 39:173–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2017.12.005
Sikic BI, Lakhani N, Patnaik A, Shah SA, Chandana SR et al (2019) First-in-human, first-in-class phase I trial of the anti-CD47 antibody Hu5F9-G4 in patients with advanced cancers. J Clin Oncol 37(12):946–953. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.18.02018
Narla RK, Modi H, Wong L, Abassian M, Bauer, D, Desai P, et al (2017) The humanized anti‐CD47 monoclonal antibody, CC‐90002, has antitumor activity in vitro and in vivo. In: Proceedings: AACR Annual Meeting Abstract 4694
Kippartick KE, Wring SA, Walker DH, Macklin MD, Payne JA, Su JL et al (1997) Rapid development of affinity matured monoclonal antibodies using RIMMS. Hybridoma 16(4):381–389. https://doi.org/10.1089/hyb.1997.16.381
Lopez-Girona A, Mendy D, Ito T, Miller K, Gandhi AK, Kang J et al (2012) Cereblon is a direct protein target for immunomodulatory and antiproliferative activities of lenalidomide and pomalidomide. Leukemia 26:2326–2335. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.119
Labrijn AF, Buijsse AO, van den Bremer ET, Verwilligen AY, Bleeker WK, Thorpe SJ et al (2009) Therapeutic IgG4 antibodies engage in Fab-arm exchange with endogenous human IgG4 in vivo. Nat Biotechnol 27:767–771. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1553
Kikuchi Y, Uno S, Yoshimura Y, Otabe K, Iida S, Oheda M et al (2004) A bivalent single-chain Fv fragment against CD47 induces apoptosis for leukemic cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 315:912–918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.01.128
Hao NB, Lü MH, Fan YH, Cao YL, Zhang ZR, Yang SM (2012) Macrophages in tumor microenvironments and the progression of tumors. Clin Dev Immunol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/948098
Martinez FO, Helming L, Gordon S (2009) Alternative activation of macrophages: an immunologic functional perspective. Annu Rev Immunol 27:451–483. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.021908.132532
Nardin A, Abastado JP (2008) Macrophages and cancer. Front Biosci 13:3494–3505. https://doi.org/10.2741/2944
Mukaida N, Sasaki S, Baba T (2014) Chemokines in cancer development and progression and their potential as targeting molecules for cancer treatment. Mediators Inflamm 2014:170381. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/170381
Subramanian S, Parthasarathy R, Sen S, Boder ET, Discher DE (2006) Species- and cell type-specific interactions between CD47 and human SIRPalpha. Blood 107:2548–2556. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-04-1463
Manna PP, Frazier WA (2004) CD47 mediates killing of breast tumor cells via Gi-dependent inhibition of protein kinase A. Cancer Res 64:1026–1036. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-1708
Leclair P, Lim CJ (2020) CD47 (Cluster of differentiation 47): an anti-phagocytic receptor with a multitude of signaling functions. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul) 24:243–252. https://doi.org/10.1080/19768354.2020.1818618
Zhu YX, Shi CX, Bruins LA, Wang X, Riggs DL, Porter B et al (2019) Identification of lenalidomide resistance pathways in myeloma and targeted resensitization using cereblon replacement, inhibition of STAT3 or targeting of IRF4. Blood Cancer J 9:19. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41408-019-0173-0
Sallman DA, Asch AS, Lee A, Donnellan WB, Marcucci G et al (2019) The first-in-class anti-CD47 antibody Magrolimab (5F9) in combination with azacitidine is effective in MDS and AML patients: Ongoing Phase 1b results. Blood 134(Suppl-1):569
Opperman KS, Vandyke K, Clark KC, Coulter EA, Hewett DR, Mrozik KM et al (2019) Clodronate-liposome mediated macrophage depletion abrogates multiple myeloma tumor establishment in vivo. Neoplasia 21:777–787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2019.05.006
Iwamoto C, Takenaka K, Urata S et al (2014) The BALB/c-specific polymorphic SIRPa enhances its affinity for human CD47, inhibiting phagocytosis against human cells to promote xenogeneic engraftment. Exp Hematol 42:163–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exphem.2013.11.005
Myers LM, Tal MC, Torrez Dulgeroff LB et al (2019) A functional subset of CD8+ T cells during chronic exhaustion is defined by SIRPα expression. Nat Commun 10:794. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-08637-9
Deuse T, Hu X, Agbor-Enoh S et al (2021) The SIRPa-CD47 checkpoint in NK cells. J Exp Med 218:e20200839. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20200839
Acknowledgements
The authors thank other team members from Celgene Corporation, including John Boylan, WenQing Yang, Maria Wang and Dale Baker for their contributions to the strategy and execution of the experiments
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts or competing of interests.
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narla, R.K., Modi, H., Bauer, D. et al. Modulation of CD47-SIRPα innate immune checkpoint axis with Fc-function detuned anti-CD47 therapeutic antibody. Cancer Immunol Immunother 71, 473–489 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-021-03010-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-021-03010-6