Abstract
Background
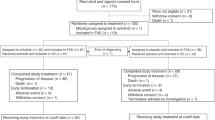
This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of anlotinib combined with programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) blockade for the treatment of small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) and non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Patients and methods
SCLC (n = 28) and NSCLC (n = 177) patients who received treatment at Hunan Cancer Hospital between June 1, 2019, and July 1, 2020, were retrospectively analyzed. Progression-free survival (PFS) and treatment responses were compared among patients who received combination therapy of anlotinib plus PD-1 inhibitor, or monotherapy of either chemotherapy or PD-1 inhibitor. Independent prognostic factors were identified by Cox regression analysis.
Results
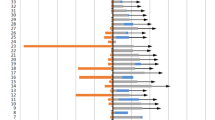
Patients with relapsed SCLC who received anlotinib plus PD-1 inhibitor as a ≥ second-line therapy (n = 14) had a significantly longer PFS than those who received PD-1 inhibitor alone (n = 14, 5.0 vs. 3.0 months; P = 0.005). For patients with previously untreated wild-type NSCLC, the combination therapy in the first-line setting (n = 6) provided a marginally longer PFS than mono-chemotherapy (n = 6, 8.0 vs. 3.0 months; P = 0.075). For patients with relapsed NSCLC, the combination therapy in the ≥ second-line setting (n = 62) resulted in significantly higher objective response rate (19.3 vs. 5.0 vs. 2.4%; P = 0.013) and longer PFS (8.0 vs. 2.0 vs. 2.0 months; P <0.001) as compared to monotherapy of either chemotherapy (n = 41) or PD-1 inhibitor (n = 62). Anlotinib and PD-1 blockade combination therapy was an independent predictive factor of longer PFS (P <0.001).
Conclusion
The combination of anlotinib and PD-1 inhibitor has promising efficacy and manageable toxicity as a second- or later-line treatment of relapsed NSCLC and possibly for relapsed SCLC.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data generated from this study are included as figures and tables in the main text and as supplementary files.
References
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F (2015) Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 136(5):E359-386. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29210
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ (2015) He J (2016) Cancer statistics in China. CA Cancer J Clin 66(2):115–132. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21338
Miller KD, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB, Rowland JH, Yabroff KR, Alfano CM, Jemal A, Kramer JL (2019) Siegel RL (2019) Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 69(5):363–385. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21565
Doroshow DB, Herbst RS (2018) Treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer in 2018. JAMA Oncol 4(4):569–570. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.5190
Sun Y, Niu W, Du F, Du C, Li S, Wang J, Li L, Wang F, Hao Y, Li C, Chi Y (2016) Safety, pharmacokinetics, and antitumor properties of anlotinib, an oral multi-target tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced refractory solid tumors. J Hematol Oncol 9(1):105. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-016-0332-8
Han B, Li K, Zhao Y, Li B, Cheng Y, Zhou J, Lu Y, Shi Y, Wang Z, Jiang L, Luo Y, Zhang Y, Huang C, Li Q, Wu G (2018) Anlotinib as a third-line therapy in patients with refractory advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a multicentre, randomised phase II trial (ALTER0302). Br J Cancer 118(5):654–661. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2017.478
Beaver JA, Hazarika M, Mulkey F, Mushti S, Chen H, He K, Sridhara R, Goldberg KB, Chuk MK, Chi DC, Chang J, Barone A, Balasubramaniam S, Blumenthal GM, Keegan P, Pazdur R, Theoret MR (2018) Patients with melanoma treated with an anti-PD-1 antibody beyond RECIST progression: a US food and drug administration pooled analysis. Lancet Oncol 19(2):229–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30846-X
Lin B, Song X, Yang D, Bai D, Yao Y, Lu N (2018) Anlotinib inhibits angiogenesis via suppressing the activation of VEGFR2, PDGFRbeta and FGFR1. Gene 654:77–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.02.026
Taurin S, Yang CH, Reyes M, Cho S, Coombs DM, Jarboe EA, Werner TL, Peterson CM, Janat-Amsbury MM (2018) Endometrial cancers harboring mutated fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 protein are successfully treated with a new small tyrosine kinase inhibitor in an orthotopic mouse model. Int J Gynecol Cancer Soc 28(1):152–160. https://doi.org/10.1097/IGC.0000000000001129
Han B, Li K, Wang Q, Zhang L, Shi J, Wang Z, Cheng Y, He J, Shi Y, Zhao Y, Yu H, Zhao Y, Chen W, Luo Y, Wu L, Wang X, Pirker R, Nan K, Jin F, Dong J, Li B, Sun Y (2018) Effect of anlotinib as a third-line or further treatment on overall survival of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: the ALTER 0303 phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol 4(11):1569–1575. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.3039
Zhou M, Chen X, Zhang H, Xia L, Tong X, Zou L, Hao R, Pan J, Zhao X, Chen D, Song Y, Qi Y, Tang L, Liu Z, Gao R, Shi Y, Yang Z (2019) China national medical products administration approval summary: anlotinib for the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer after two lines of chemotherapy. Cancer Commun 39(1):36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40880-019-0383-7
Cheng YWQ, Li K et al (2018) Anlotinib as third-line or further-line treatment in relapsed SCLC: a multicentre, randomized, double-blind Phase 2 trial. J Thorac Oncol 13(10):S351–S352
Cheng Y, Wang Q, Li K, Shi J, Liu Y, Wu L, Han B, Chen G, He J, Wang J, Lou D, Yu H, Qin H, Li XL (2019) Overall survival (OS) update in ALTER 1202: anlotinib as third-line or further-line treatment in relapsed small-cell lung cancer (SCLC). Ann Oncol 30:v711. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdz264.002
Zhang K, Ma X, Gao H, Wang H, Qin H, Yang S, Liu X (2020) Efficacy and safety of anlotinib in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a real-world study. Cancer Manag Res 12:3409–3417. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S246000
Shao L, Wang W, Song Z, Zhang Y (2019) The efficacy and safety of anlotinib treatment for advanced lung cancer. Onco Targets Ther 12:6549–6554. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S205674
Gandhi L, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Gadgeel S, Esteban E, Felip E, De Angelis F, Domine M, Clingan P, Hochmair MJ, Powell SF, Cheng SY, Bischoff HG, Peled N, Grossi F, Jennens RR, Reck M, Hui R, Garon EB, Boyer M, Rubio-Viqueira B, Novello S, Kurata T, Gray JE, Vida J, Wei Z, Yang J, Raftopoulos H, Pietanza MC, Garassino MC, Investigators K (2018) Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. New Engl J Med 378(22):2078–2092. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1801005
Reck M, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG, Hui R, Csoszi T, Fulop A, Gottfried M, Peled N, Tafreshi A, Cuffe S, O’Brien M, Rao S, Hotta K, Leiby MA, Lubiniecki GM, Shentu Y, Rangwala R, Brahmer JR, Investigators K (2016) Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. New Engl J Med 375(19):1823–1833. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1606774
Rittmeyer A, Barlesi F, Waterkamp D, Park K, Ciardiello F, von Pawel J, Gadgeel SM, Hida T, Kowalski DM, Dols MC, Cortinovis DL, Leach J, Polikoff J, Barrios C, Kabbinavar F, Frontera OA, De Marinis F, Turna H, Lee JS, Ballinger M, Kowanetz M, He P, Chen DS, Sandler A, Gandara DR, Group OAKS (2017) Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): a phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 389(10066):255–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32517-X
Fehrenbacher L, Spira A, Ballinger M, Kowanetz M, Vansteenkiste J, Mazieres J, Park K, Smith D, Artal-Cortes A, Lewanski C, Braiteh F, Waterkamp D, He P, Zou W, Chen DS, Yi J, Sandler A, Rittmeyer A, Group PS (2016) Atezolizumab versus docetaxel for patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (POPLAR): a multicentre, open-label, phase 2 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 387(10030):1837–1846. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00587-0
Reck M, Vicente D, Ciuleanu T, Gettinger S, Peters S, Horn L et al (2018) Efficacy and safety of nivolumab (nivo) monotherapy versus chemotherapy (chemo) in recurrent small cell lung cancer (SCLC): Results from CheckMate 331. Ann Oncol 29:X43
Jain RK (2001) Normalizing tumor vasculature with anti-angiogenic therapy: a new paradigm for combination therapy. Nat Med 7(9):987–989. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0901-987
Liu S, Qin T, Liu Z, Wang J, Jia Y, Feng Y, Gao Y, Li K (2020) anlotinib alters tumor immune microenvironment by downregulating PD-L1 expression on vascular endothelial cells. Cell Death Dis 11(5):309. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2511-3
Yang Y, Li L, Jiang Z, Wang B, Pan Z (2020) Anlotinib optimizes anti-tumor innate immunity to potentiate the therapeutic effect of PD-1 blockade in lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother CII 69(12):2523–2532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-020-02641-5
Socinski MA, Jotte RM, Cappuzzo F, Orlandi F, Stroyakovskiy D, Nogami N, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Moro-Sibilot D, Thomas CA, Barlesi F, Finley G, Kelsch C, Lee A, Coleman S, Deng Y, Shen Y, Kowanetz M, Lopez-Chavez A, Sandler A, Reck M, Group IMS (2018) Atezolizumab for first-line treatment of metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC. New Engl J Med 378(24):2288–2301. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1716948
Han B, Chu T, Zhong R, Zhong H, Zhang B, Zhang W, Shi C, Qian J, Han Y (2019) P1.04–02 efficacy and safety of sintilimab with anlotinib as first-line therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J Thorac Oncol 14(10):S439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2019.08.905
Manegold C, Dingemans AC, Gray JE, Nakagawa K, Nicolson M, Peters S, Reck M, Wu YL, Brustugun OT, Crinò L, Felip E, Fennell D, Garrido P, Huber RM, Marabelle A, Moniuszko M, Mornex F, Novello S, Papotti M, Pérol M, Smit EF, Syrigos K, van Meerbeeck JP, van Zandwijk N, Yang JC, Zhou C, Vokes E (2017) The potential of combined immunotherapy and antiangiogenesis for the synergistic treatment of advanced NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol 12(2):194–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2016.10.003
Zhao S, Ren S, Jiang T, Zhu B, Li X, Zhao C, Jia Y, Shi J, Zhang L, Liu X, Qiao M, Chen X, Su C, Yu H, Zhou C, Zhang J, Camidge DR, Hirsch FR (2019) Low-dose apatinib optimizes tumor microenvironment and potentiates antitumor effect of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in lung cancer. Cancer Immunol Res 7(4):630–643. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.cir-17-0640
Yi M, Jiao D, Qin S, Chu Q, Wu K, Li A (2019) Synergistic effect of immune checkpoint blockade and anti-angiogenesis in cancer treatment. Mol Cancer 18(1):60. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-0974-6
Wang Q, Gao J, Di W, Wu X (2020) Anti-angiogenesis therapy overcomes the innate resistance to PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in VEGFA-overexpressed mouse tumor models. Cancer Immunol Immunother CII 69(9):1781–1799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-020-02576-x
Yang S, Zhang W, Chen Q, Guo Q (2020) Clinical investigation of the efficacy and safety of anlotinib with immunotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer as third-line therapy: a retrospective study. Cancer Manag Res 12:10333–10340. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S280096
Farago AF, Keane FK (2018) Current standards for clinical management of small cell lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res 7(1):69–79. https://doi.org/10.21037/tlcr.2018.01.16
Peifer M, Fernandez-Cuesta L, Sos ML, George J, Seidel D, Kasper LH, Plenker D, Leenders F, Sun R, Zander T, Menon R, Koker M, Dahmen I, Muller C, Di Cerbo V, Schildhaus HU, Altmuller J, Baessmann I, Becker C, de Wilde B, Vandesompele J, Bohm D, Ansen S, Gabler F, Wilkening I, Heynck S, Heuckmann JM, Lu X, Carter SL, Cibulskis K, Banerji S, Getz G, Park KS, Rauh D, Grutter C, Fischer M, Pasqualucci L, Wright G, Wainer Z, Russell P, Petersen I, Chen Y, Stoelben E, Ludwig C, Schnabel P, Hoffmann H, Muley T, Brockmann M, Engel-Riedel W, Muscarella LA, Fazio VM, Groen H, Timens W, Sietsma H, Thunnissen E, Smit E, Heideman DA, Snijders PJ, Cappuzzo F, Ligorio C, Damiani S, Field J, Solberg S, Brustugun OT, Lund-Iversen M, Sanger J, Clement JH, Soltermann A, Moch H, Weder W, Solomon B, Soria JC, Validire P, Besse B, Brambilla E, Brambilla C, Lantuejoul S, Lorimier P, Schneider PM, Hallek M, Pao W, Meyerson M, Sage J, Shendure J, Schneider R, Buttner R, Wolf J, Nurnberg P, Perner S, Heukamp LC, Brindle PK, Haas S, Thomas RK (2012) Integrative genome analyses identify key somatic driver mutations of small-cell lung cancer. Nat Genet 44(10):1104–1110. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2396
Horn L, Mansfield AS, Szczesna A, Havel L, Krzakowski M, Hochmair MJ, Huemer F, Losonczy G, Johnson ML, Nishio M, Reck M, Mok T, Lam S, Shames DS, Liu J, Ding B, Lopez-Chavez A, Kabbinavar F, Lin W, Sandler A, Liu SV, Group IMS (2018) First-line atezolizumab plus chemotherapy in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. New Engl J Med 379(23):2220–2229. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1809064
Pujol JL, Greillier L, Audigier-Valette C, Moro-Sibilot D, Uwer L, Hureaux J, Guisier F, Carmier D, Madelaine J, Otto J, Gounant V, Merle P, Mourlanette P, Molinier O, Renault A, Rabeau A, Antoine M, Denis MG, Bommart S, Langlais A, Morin F, Souquet PJ (2019) A Randomized Non-Comparative Phase II Study of Anti-Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 Atezolizumab or chemotherapy as second-line therapy in patients with small cell lung cancer: results from the IFCT-1603 trial. J Thorac Oncol 14(5):903–913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2019.01.008
Antonia SJ, Lopez-Martin JA, Bendell J, Ott PA, Taylor M, Eder JP, Jager D, Pietanza MC, Le DT, de Braud F, Morse MA, Ascierto PA, Horn L, Amin A, Pillai RN, Evans J, Chau I, Bono P, Atmaca A, Sharma P, Harbison CT, Lin CS, Christensen O, Calvo E (2016) Nivolumab alone and nivolumab plus ipilimumab in recurrent small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 032): a multicentre, open-label, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Oncol 17(7):883–895. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30098-5
Horn L, Spigel DR, Vokes EE, Holgado E, Ready N, Steins M, Poddubskaya E, Borghaei H, Felip E, Paz-Ares L, Pluzanski A, Reckamp KL, Burgio MA, Kohlhaeufl M, Waterhouse D, Barlesi F, Antonia S, Arrieta O, Fayette J, Crino L, Rizvi N, Reck M, Hellmann MD, Geese WJ, Li A, Blackwood-Chirchir A, Healey D, Brahmer J, Eberhardt WEE (2017) Nivolumab versus docetaxel in previously treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: two-year outcomes from two randomized, open-label, phase III trials (checkmate 017 and checkmate 057). J Clin Oncol 35(35):3924–3933. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2017.74.3062
Funding
This work was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number: 81760529), and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (grant numbers: 2018RS3106, 2018SK50901, kq1801102, 2019-TJ-N04, 2019JJ50357, 2019SK4010, 2020JJ5340, and 2020JJ3025). The funding agencies had no role in the study design, data collection, analysis, interpretation, manuscript writing, and decision to submit the article for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Author contribution
YZ conceptualized, supervised and acquired funding for the study. XZ, LZ, YL curated and analyzed the clinical data and wrote the original manuscript draft. QX, HY, RJ, YZ, QL and JW contributed to the curation and analysis of clinical data. AL and XM contributed to the analysis of the data and manuscript preparation. YL and NY gave critical comments and suggestions. all authors reviewed and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Analyn Lizaso and Xinru Mao are employed by Burning Rock Biotech. All the other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Hunan Cancer Hospital (approval number: 2017YYQ-SSB-126). Informed consent
Informed consent
Informed consent was waived by the ethics committee due to the retrospective nature of the study.
Consent for publication
We confirm that the manuscript has been reviewed and approved by all named authors for publication.
Clinical trials registration
Clinical trials registration The ATHENA Study, NCT04322617.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Zeng, L., Li, Y. et al. Anlotinib combined with PD-1 blockade for the treatment of lung cancer: a real-world retrospective study in China. Cancer Immunol Immunother 70, 2517–2528 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-021-02869-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-021-02869-9