Abstract
Background
CKLF-like MARVEL transmembrane domain-containing 6 (CMTM6) is a critical regulator of tumor immunology among various cancers. However, the role and underlying molecular mechanism of CMTM6 in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) progression remains unclear.
Methods
The expression of CMTM6, PD-L1 and CD163 in OSCC tissues were detected by immunohistochemistry on tissue microarray. The effect of CMTM6 knockdown on OSCC cells and macrophage polarization were analyzed by CCK-8 assay, apoptotic assay, would-healing assay, transwell assay and qPCR. OSCC cell derived exosomes were obtained by ultracentrifugation and the mechanistic studies were conducted by qPCR and Western Blot. 4-Nitroquinoline N-oxide (4NQO) induced OSCC mice were used for verifying the effect of CMTM6 downregulation on M2 macrophage infiltration and tumor growth.
Results
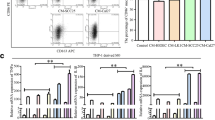
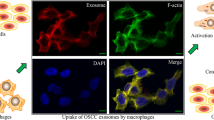
In OSCC samples, higher CMTM6 expression has been obviously associated with higher pathological stage of OSCC patients, CD163 + macrophages infiltration and PD-L1 expression. CMTM6 knockdown of OSCC cells inhibited proliferative, migrative and invasive abilities of OSCC cells, as well as inhibited M2 macrophage polarization in vitro with downregulating PD-L1 expression. Importantly, exosomes from OSCC cells shuttled CMTM6 to macrophages and promoted M2-like macrophage polarization through activating ERK1/2 signaling. In addition, in 4NQO-induced OSCC mice, CMTM6 level was positively associated with CD163, CD206 and PD-L1 as well as M2-like macrophage infiltration.
Conclusion
OSCC cell-secreted exosomal CMTM6 induces M2-like macrophages polarization to promote malignant progression via ERK1/2 signaling pathway, revealing a novel crosstalk between cancer cells and immune cells in OSCC microenvironment.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
25 November 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-021-03113-0
References
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F (2015) Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 136(5):E359-386. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29210
Krstevska V (2015) Evolution of treatment and high-risk features in resectable locally advanced Head and Neck squamous cell carcinoma with special reference to extracapsular extension of nodal disease. J BUON 20(4):943–953
Pring M, Prime S, Parkinson E, Paterson I (2006) Dysregulated TGF-beta1-induced smad signalling occurs as a result of defects in multiple components of the TGF-beta signalling pathway in human head and neck carcinoma cell lines. Int J Oncol 28(5):1279–1285
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2019) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 69(1):7–34. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21551
Burr ML, Sparbier CE, Chan YC, Williamson JC, Woods K, Beavis PA, Lam EYN, Henderson MA, Bell CC, Stolzenburg S, Gilan O, Bloor S, Noori T, Morgens DW, Bassik MC, Neeson PJ, Behren A, Darcy PK, Dawson SJ, Voskoboinik I, Trapani JA, Cebon J, Lehner PJ, Dawson MA (2017) CMTM6 maintains the expression of PD-L1 and regulates anti-tumour immunity. Nature 549(7670):101–105. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23643
Mezzadra R, Sun C, Jae LT, Gomez-Eerland R, de Vries E, Wu W, Logtenberg MEW, Slagter M, Rozeman EA, Hofland I, Broeks A, Horlings HM, Wessels LFA, Blank CU, Xiao Y, Heck AJR, Borst J, Brummelkamp TR, Schumacher TNM (2017) Identification of CMTM6 and CMTM4 as PD-L1 protein regulators. Nature 549(7670):106–110. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23669
Guan X, Zhang C, Zhao J, Sun G, Song Q, Jia W (2018) CMTM6 overexpression is associated with molecular and clinical characteristics of malignancy and predicts poor prognosis in gliomas. EBioMedicine 35:233–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.08.012
Zhao W, Zhao F, Yang K, Lu Y, Zhang Y, Wang W, Xie H, Deng K, Yang C, Rong Z, Hou Y, Li K (2019) An immunophenotyping of renal clear cell carcinoma with characteristics and a potential therapeutic target for patients insensitive to immune checkpoint blockade. J Cell Biochem 120(8):13330–13341. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28607
Yafune A, Kawai M, Itahashi M, Kimura M, Nakane F, Mitsumori K, Shibutani M (2013) Global DNA methylation screening of liver in piperonyl butoxide-treated mice in a two-stage hepatocarcinogenesis model. Toxicol Lett 222(3):295–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2013.08.006
Zhu X, Qi G, Li C, Bei C, Tan C, Zhang Y, Shi W, Zeng W, Kong J, Fu Y, Tan S (2019) Expression and clinical significance of CMTM6 in hepatocellular carcinoma. DNA Cell Biol 38(2):193–197. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2018.4513
Singh Y, Pawar VK, Meher JG, Raval K, Kumar A, Shrivastava R, Bhadauria S, Chourasia MK (2017) Targeting tumor associated macrophages (TAMs) via nanocarriers. J Control Release 254:92–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.03.395
Bingle L, Brown NJ, Lewis CE (2002) The role of tumour-associated macrophages in tumour progression: implications for new anticancer therapies. J Pathol 196(3):254–265. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.1027
Weber M, Iliopoulos C, Moebius P, Buttner-Herold M, Amann K, Ries J, Preidl R, Neukam FW, Wehrhan F (2016) Prognostic significance of macrophage polarization in early stage oral squamous cell carcinomas. Oral Oncol 52:75–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2015.11.001
Biswas SK, Sica A, Lewis CE (2008) Plasticity of macrophage function during tumor progression: regulation by distinct molecular mechanisms. J Immunol 180(4):2011–2017. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.180.4.2011
Kryczek I, Zou L, Rodriguez P, Zhu G, Wei S, Mottram P, Brumlik M, Cheng P, Curiel T, Myers L, Lackner A, Alvarez X, Ochoa A, Chen L, Zou W (2006) B7–H4 expression identifies a novel suppressive macrophage population in human ovarian carcinoma. J Exp Med 203(4):871–881. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20050930
Winograd R, Byrne KT, Evans RA, Odorizzi PM, Meyer AR, Bajor DL, Clendenin C, Stanger BZ, Furth EE, Wherry EJ, Vonderheide RH (2015) Induction of T cell immunity overcomes complete resistance to PD-1 and CTLA-4 blockade and improves survival in pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Res 3(4):399–411. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.Cir-14-0215
Jiang C, Yuan F, Wang J, Wu L (2017) Oral squamous cell carcinoma suppressed antitumor immunity through induction of PD-L1 expression on tumor-associated macrophages. Immunobiology 222(4):651–657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imbio.2016.12.002
Wen ZF, Liu H, Gao R, Zhou M, Ma J, Zhang Y, Zhao J, Chen Y, Zhang T, Huang F, Pan N, Zhang J, Fox BA, Hu HM, Wang LX (2018) Tumor cell-released autophagosomes (TRAPs) promote immunosuppression through induction of M2-like macrophages with increased expression of PD-L1. J Immunother Cancer 6(1):151. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-018-0452-5
Sun LP, Xu K, Cui J, Yuan DY, Zou B, Li J, Liu JL, Li KY, Meng Z, Zhang B (2019) Cancerassociated fibroblastderived exosomal miR3825p promotes the migration and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep 42(4):1319–1328. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2019.7255
Mu X, Shi W, Xu Y, Xu C, Zhao T, Geng B, Yang J, Pan J, Hu S, Zhang C, Zhang J, Wang C, Shen J, Che Y, Liu Z, Lv Y, Wen H, You Q (2018) Tumor-derived lactate induces M2 macrophage polarization via the activation of the ERK/STAT3 signaling pathway in breast cancer. Cell Cycle 17(4):428–438. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2018.1444305
Wu JS, Zheng M, Zhang M, Pang X, Li L, Wang SS, Yang X, Wu JB, Tang YJ, Tang YL, Liang XH (2018) Porphyromonas gingivalis promotes 4-Nitroquinoline-1-Oxide-induced oral carcinogenesis with an alteration of fatty acid metabolism. Frontiers in microbiology 9:2081. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02081
Tong H, Ke JQ, Jiang FZ, Wang XJ, Wang FY, Li YR, Lu W, Wan XP (2016) Tumor-associated macrophage-derived CXCL8 could induce ERalpha suppression via HOXB13 in endometrial cancer. Cancer Lett 376(1):127–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2016.03.036
Yamaguchi T, Fushida S, Yamamoto Y, Tsukada T, Kinoshita J, Oyama K, Miyashita T, Tajima H, Ninomiya I, Munesue S, Harashima A, Harada S, Yamamoto H, Ohta T (2016) Tumor-associated macrophages of the M2 phenotype contribute to progression in gastric cancer with peritoneal dissemination. Gastric Cancer 19(4):1052–1065. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-015-0579-8
Chen Y, Zhang S, Wang Q, Zhang X (2017) Tumor-recruited M2 macrophages promote gastric and breast cancer metastasis via M2 macrophage-secreted CHI3L1 protein. J Hematol Oncology 10(1):36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-017-0408-0
Weng YS, Tseng HY, Chen YA, Shen PC, Al Haq AT, Chen LM, Tung YC, Hsu HL (2019) MCT-1/miR-34a/IL-6/IL-6R signaling axis promotes EMT progression, cancer stemness and M2 macrophage polarization in triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Can 18(1):42. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-0988-0
Khabipov A, Kading A, Liedtke KR, Freund E, Partecke LI, Bekeschus S (2019) RAW 264.7 macrophage polarization by pancreatic cancer cells—a model for studying tumour-promoting macrophages. Anticancer Res 39(6):2871–2882. https://doi.org/10.2187/anticanres.13416
Lobb RJ, van Amerongen R, Wiegmans A, Ham S, Larsen JE, Moller A (2017) Exosomes derived from mesenchymal non-small cell lung cancer cells promote chemoresistance. Int J Cancer 141(3):614–620. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.30752
Wang X, Luo G, Zhang K, Cao J, Huang C, Jiang T, Liu B, Su L, Qiu Z (2018) Hypoxic tumor-derived exosomal miR-301a mediates M2 macrophage polarization via PTEN/PI3Kgamma to promote pancreatic cancer metastasis. Can Res 78(16):4586–4598. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-17-3841
Chen X, Ying X, Wang X, Wu X, Zhu Q, Wang X (2017) Exosomes derived from hypoxic epithelial ovarian cancer deliver microRNA-940 to induce macrophage M2 polarization. Oncol Rep 38(1):522–528. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2017.5697
Bardi GT, Smith MA, Hood JL (2018) Melanoma exosomes promote mixed M1 and M2 macrophage polarization. Cytokine 105:63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2018.02.002
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China grants (Nos.8207300, 81672672, 81972542 and 81902779) and National Science Foundation of Sichuan Province (Nos.2020JDRC0018 and 2020YFS0171).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xin Pang, Sha-sha Wang and Mei Zhang performed most of the experiments and wrote the manuscript. Hua-yang Fan and Jia-shun Wu performed the mice materials. Hao-fan Wang analyzed data and assisted in manuscript writing. Xin-hua Liang and Ya-ling Tang conceived the study and performed the final corrections.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, X., Wang, Ss., Zhang, M. et al. OSCC cell-secreted exosomal CMTM6 induced M2-like macrophages polarization via ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Cancer Immunol Immunother 70, 1015–1029 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-020-02741-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-020-02741-2