Abstract
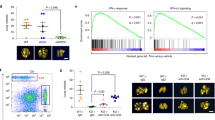
The transcription factor signal activator and transducer or transcription (STAT3), which regulates genes controlling proliferation, survival, and invasion, is activated inappropriately in many human cancers, including breast cancer. Activation of STAT3 can lead to both malignant cellular behavior and suppression of immune cell function in the tumor microenvironment. Through a chemical-biology screen, pyrimethamine (PYR), an FDA approved anti-microbial drug, was identified as an inhibitor of STAT3 function at concentrations known to be achieved safely in humans. We report that PYR shows therapeutic activity in two independent mouse models of breast cancer, with both direct tumor inhibitory and immune stimulatory effects. PYR-inhibited STAT3 activity in TUBO and TM40D-MB metastatic breast cancer cells in vitro and inhibited tumor cell proliferation and invasion into Matrigel basement membrane matrix. In tumor-transplanted mice, PYR had both direct and indirect tumor inhibitory effects. Tumor-bearing mice treated with PYR showed reduced STAT3 activation in tumor cells, attenuated tumor growth, and reduced tumor-associated inflammation. In addition, expression of Lamp1 by tumor infiltrating CD8+ T cells was elevated, indicating enhanced release of cytotoxic granules. These findings suggest that PYR may have beneficial effects in the treatment of breast cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- BTBM:
-
BALBL/c TUBO transplant breast cancer mouse model
- CTLs:
-
Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes
- FDA:
-
United States food and drug administration
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- HER2:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor 2
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin 6
- JAK:
-
Janus kinase
- NMP:
-
1Methyl-2-pyrrolodinone
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffered saline
- Poly:
-
Polyethylene glycol
- pSTAT:
-
Phospho-STAT
- PYR:
-
Pyrimethamine; 2, 4-diamino-5-p-chlorophenyl-6-ethyl-pyrimidine
- RORγT:
-
Retinoic acid-related orphan receptor gamma T
- STAT:
-
Signal activator and transducer of transcription
- TAMs:
-
Tumor associated macrophages
- TH17:
-
T-helper 17
- Tregs:
-
Regulatory T cells
References
Zhong Z, Wen Z, Darnell JE Jr (1994) Stat3: a STAT family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science 264(5155):95–98
Yu H, Pardoll D, Jove R (2009) STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev Cancer 9(11):798–809. doi:10.1038/nrc2734
Dave B, Landis MD, Tweardy DJ, Chang JC, Dobrolecki LE, Wu MF, Zhang X, Westbrook TF, Hilsenbeck SG, Liu D, Lewis MT (2012) Selective small molecule STAT3 inhibitor reduces breast cancer tumor-initiating cells and improves recurrence free survival in a human-xenograft model. PLoS One 7(8):e30207. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030207
Marotta LL, Almendro V, Marusyk A, Shipitsin M, Schemme J, Walker SR, Bloushtain-Qimron N, Kim JJ, Choudhury SA, Maruyama R, Wu Z, Gonen M, Mulvey LA, Bessarabova MO, Huh SJ, Silver SJ, Kim SY, Park SY, Lee HE, Anderson KS, Richardson AL, Nikolskaya T, Nikolsky Y, Liu XS, Root DE, Hahn WC, Frank DA, Polyak K (2011) The JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway is required for growth of CD44(+)CD24(−) stem cell-like breast cancer cells in human tumors. J Clin Investig 121(7):2723–2735. doi:10.1172/jci44745
Legorreta-Herrera M, Retana-Ugalde R, Ventura-Gallegos JL, Narvaez V (2010) Pyrimethamine induces oxidative stress in Plasmodium yoelii 17XL-infected mice: a novel immunomodulatory mechanism of action for an old antimalarial drug? Exp Parasitol 126(3):381–388. doi:10.1016/j.exppara.2010.02.013
Takakura A, Nelson EA, Haque N, Humphreys BD, Zandi-Nejad K, Frank DA, Zhou J (2011) Pyrimethamine inhibits adult polycystic kidney disease by modulating STAT signaling pathways. Hum Mol Genet 20(21):4143–4154. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddr338
Hooft van Huijsduijnen R, Guy RK, Chibale K, Haynes RK, Peitz I, Kelter G, Phillips MA, Vennerstrom JL, Yuthavong Y, Wells TN (2013) Anticancer properties of distinct antimalarial drug classes. PLoS One 8(12):e82962. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0082962
Chen M, Osman I, Orlow SJ (2009) Antifolate activity of pyrimethamine enhances temozolomide-induced cytotoxicity in melanoma cells. Mol Cancer Res 7(5):703–712. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0263
Giammarioli AM, Maselli A, Casagrande A, Gambardella L, Gallina A, Spada M, Giovannetti A, Proietti E, Malorni W, Pierdominici M (2008) Pyrimethamine induces apoptosis of melanoma cells via a caspase and cathepsin double-edged mechanism. Cancer Res 68(13):5291–5300. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-08-0222
Dai C, Zhang B, Liu X, Guo K, Ma S, Cai F, Yang Y, Yao Y, Feng M, Bao X, Deng K, Jiao Y, Wei Z, Junji W, Xing B, Lian W, Wang R (2013) Pyrimethamine sensitizes pituitary adenomas cells to temozolomide through cathepsin B-dependent and caspase-dependent apoptotic pathways. Int J Cancer 133(8):1982–1993. doi:10.1002/ijc.28199
Gattinoni L, Zhong XS, Palmer DC, Ji Y, Hinrichs CS, Yu Z, Wrzesinski C, Boni A, Cassard L, Garvin LM, Paulos CM, Muranski P, Restifo NP (2009) Wnt signaling arrests effector T cell differentiation and generates CD8+ memory stem cells. Nat Med 15(7):808–813. doi:10.1038/nm.1982
DeSantis CE, Bray F, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Anderson BO, Jemal A (2015) International variation in female breast cancer incidence and mortality rates. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 24(10):1495–1506. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-15-0535
Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ, Ullrich A, McGuire WL (1987) Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science 235(4785):177–182
Quaglino E, Mastini C, Forni G, Cavallo F (2008) ErbB2 transgenic mice: a tool for investigation of the immune prevention and treatment of mammary carcinomas. Curr Protoc Immunol. doi:10.1002/0471142735.im2009s82 (Chapter 20: Unit 20.9.1–20.9-10)
Kmieciak M, Payne KK, Wang XY, Manjili MH (2013) IFN-gamma Ralpha is a key determinant of CD8+ T cell-mediated tumor elimination or tumor escape and relapse in FVB mouse. PLoS One 8(12):e82544. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0082544
Melani C, Chiodoni C, Forni G, Colombo MP (2003) Myeloid cell expansion elicited by the progression of spontaneous mammary carcinomas in c-erbB-2 transgenic BALB/c mice suppresses immune reactivity. Blood 102(6):2138–2145
Hix LM, Karavitis J, Khan MW, Shi YH, Khazaie K, Zhang M (2013) Tumor STAT1 transcription factor activity enhances breast tumor growth and immune suppression mediated by myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J Biol Chem 288(17):11676–11688. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.441402
Boggio K, Nicoletti G, Di Carlo E, Cavallo F, Landuzzi L, Melani C, Giovarelli M, Rossi I, Nanni P, De Giovanni C, Bouchard P, Wolf S, Modesti A, Musiani P, Lollini PL, Colombo MP, Forni G (1998) Interleukin 12-mediated prevention of spontaneous mammary adenocarcinomas in two lines of Her-2/neu transgenic mice. J Exp Med 188(3):589–596
Rovero S, Amici A, Di Carlo E, Bei R, Nanni P, Quaglino E, Porcedda P, Boggio K, Smorlesi A, Lollini PL, Landuzzi L, Colombo MP, Giovarelli M, Musiani P, Forni G (2000) DNA vaccination against rat her-2/Neu p185 more effectively inhibits carcinogenesis than transplantable carcinomas in transgenic BALB/c mice. J Immunol 165(9):5133–5142
Shi HY, Zhang W, Liang R, Abraham S, Kittrell FS, Medina D, Zhang M (2001) Blocking tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis by maspin in a syngeneic breast cancer model. Cancer Res 61(18):6945–6951
Khan MW, Keshavarzian A, Gounaris E, Melson JE, Cheon EC, Blatner NR, Chen ZE, Tsai FN, Lee G, Ryu H, Barrett TA, Bentrem DJ, Beckhove P, Khazaie K (2013) PI3K/AKT signaling is essential for communication between tissue-infiltrating mast cells, macrophages, and epithelial cells in colitis-induced cancer. Clin Cancer Res 19(9):2342–2354. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-2623
Siddiquee K, Zhang S, Guida WC, Blaskovich MA, Greedy B, Lawrence HR, Yip ML, Jove R, McLaughlin MM, Lawrence NJ, Sebti SM, Turkson J (2007) Selective chemical probe inhibitor of STAT3, identified through structure-based virtual screening, induces antitumor activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(18):7391–7396. doi:10.1073/pnas.0609757104
O’Reilly SM, Barnes DM, Camplejohn RS, Bartkova J, Gregory WM, Richards MA (1991) The relationship between c-erbB-2 expression, S-phase fraction and prognosis in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 63(3):444–446
Kallioniemi OP, Holli K, Visakorpi T, Koivula T, Helin HH, Isola JJ (1991) Association of c-erbB-2 protein over-expression with high rate of cell proliferation, increased risk of visceral metastasis and poor long-term survival in breast cancer. Int J Cancer 49(5):650–655
Gasparini G, Boracchi P, Verderio P, Bevilacqua P (1994) Cell kinetics in human breast cancer: comparison between the prognostic value of the cytofluorimetric S-phase fraction and that of the antibodies to Ki-67 and PCNA antigens detected by immunocytochemistry. Int J Cancer 57(6):822–829
Page DL (1991) Prognosis and breast cancer. Recognition of lethal and favorable prognostic types. Am J Surg Pathol 15(4):334–349
Gupta P, Srivastava SK (2014) HER2 mediated de novo production of TGFbeta leads to SNAIL driven epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of breast cancer. Mol Oncol 8(8):1532–1547. doi:10.1016/j.molonc.2014.06.006
Cheng JC, Qiu X, Chang HM, Leung PC (2013) HER2 mediates epidermal growth factor-induced down-regulation of E-cadherin in human ovarian cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 434(1):81–86. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.03.062
Jeon M, Lee J, Nam SJ, Shin I, Lee JE, Kim S (2015) Induction of fibronectin by HER2 overexpression triggers adhesion and invasion of breast cancer cells. Exp Cell Res 333(1):116–126. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.02.019
Mills CD, Kincaid K, Alt JM, Heilman MJ, Hill AM (2000) M-1/M-2 macrophages and the Th1/Th2 paradigm. J Immunol 164(12):6166–6173
Bonavita E, Galdiero MR, Jaillon S, Mantovani A (2015) Phagocytes as corrupted policemen in cancer-related inflammation. Adv Cancer Res 128:141–171. doi:10.1016/bs.acr.2015.04.013
Wang Y, Sun J, Zheng R, Shao Q, Gao W, Song B, Chen X, Qu X (2016) Regulatory T cells are an important prognostic factor in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neoplasma 63(5):789–798. doi:10.4149/neo_2016_517
Blatner NR, Gounari F, Khazaie K (2013) The two faces of regulatory T cells in cancer. Oncoimmunology 2(5):e23852. doi:10.4161/onci.23852
Keerthivasan S, Aghajani K, Dose M, Molinero L, Khan MW, Venkateswaran V, Weber C, Emmanuel AO, Sun T, Bentrem DJ, Mulcahy M, Keshavarzian A, Ramos EM, Blatner N, Khazaie K, Gounari F (2014) Beta-catenin promotes colitis and colon cancer through imprinting of proinflammatory properties in T cells. Sci Transl Med. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3007607
Levy DE, Inghirami G (2006) STAT3: a multifaceted oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(27):10151–10152. doi:10.1073/pnas.0604042103
Berishaj M, Gao SP, Ahmed S, Leslie K, Al-Ahmadie H, Gerald WL, Bornmann W, Bromberg JF (2007) STAT3 is tyrosine-phosphorylated through the interleukin-6/glycoprotein 130/Janus kinase pathway in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 9(3):R32. doi:10.1186/bcr1680
Hartman ZC, Yang XY, Glass O, Lei G, Osada T, Dave SS, Morse MA, Clay TM, Lyerly HK (2011) HER2 overexpression elicits a proinflammatory IL-6 autocrine signaling loop that is critical for tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 71(13):4380–4391. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-11-0308
Shields BJ, Wiede F, Gurzov EN, Wee K, Hauser C, Zhu HJ, Molloy TJ, O’Toole SA, Daly RJ, Sutherland RL, Mitchell CA, McLean CA, Tiganis T (2013) TCPTP regulates SFK and STAT3 signaling and is lost in triple-negative breast cancers. Mol Cell Biol 33(3):557–570. doi:10.1128/MCB.01016-12
Tremblay ML (2013) On the role of tyrosine phosphatases as negative regulators of STAT signaling in breast cancers: new findings and future perspectives. Breast Cancer Res 15(4):312. doi:10.1186/bcr3437
Walker SR, Liu S, Xiang M, Nicolais M, Hatzi K, Giannopoulou E, Elemento O, Cerchietti L, Melnick A, Frank DA (2015) The transcriptional modulator BCL6 as a molecular target for breast cancer therapy. Oncogene 34(9):1073–1082. doi:10.1038/onc.2014.61
Walker SR, Frank DA (2015) Targeting BCL6 and STAT3 in triple negative breast cancer: the one-two punch? Oncoscience 2(11):912. doi:10.18632/oncoscience.270
Silva CM (2004) Role of STATs as downstream signal transducers in Src family kinase-mediated tumorigenesis. Oncogene 23(48):8017–8023. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208159
Borgen E, Pantel K, Schlimok G, Muller P, Otte M, Renolen A, Ehnle S, Coith C, Nesland JM, Naume B (2006) A European interlaboratory testing of three well-known procedures for immunocytochemical detection of epithelial cells in bone marrow. Results from analysis of normal bone marrow. Cytom Part B Clin Cytom 70(6):400–409. doi:10.1002/cyto.b.20114
Yuan ZL, Guan YJ, Wang L, Wei W, Kane AB, Chin YE (2004) Central role of the threonine residue within the p+ 1 loop of receptor tyrosine kinase in STAT3 constitutive phosphorylation in metastatic cancer cells. Mol Cell Biol 24(21):9390–9400. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.21.9390-9400.2004
Khorramizadeh MR, Saadat F, Vaezzadeh F, Safavifar F, Bashiri H, Jahanshiri Z (2007) Suppression of telomerase activity by pyrimethamine: implication to cancer. Iran Biomed J 11(4):223–228
Teng Y, Ross JL, Cowell JK (2014) The involvement of JAK-STAT3 in cell motility, invasion, and metastasis. Jak-stat 3(1):e28086. doi:10.4161/jkst.28086
Xie TX, Wei D, Liu M, Gao AC, Ali-Osman F, Sawaya R, Huang S (2004) Stat3 activation regulates the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and tumor invasion and metastasis. Oncogene 23(20):3550–3560. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207383
Sossey-Alaoui K, Su G, Malaj E, Roe B, Cowell JK (2002) WAVE3, an actin-polymerization gene, is truncated and inactivated as a result of a constitutional t(1;13)(q21;q12) chromosome translocation in a patient with ganglioneuroblastoma. Oncogene 21(38):5967–5974. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205734
Pollard TD, Borisy GG (2003) Cellular motility driven by assembly and disassembly of actin filaments. Cell 112(4):453–465
Takenawa T, Suetsugu S (2007) The WASP–WAVE protein network: connecting the membrane to the cytoskeleton. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(1):37–48. doi:10.1038/nrm2069
Cavallo F, De Giovanni C, Nanni P, Forni G, Lollini PL (2011) 2011: the immune hallmarks of cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 60(3):319–326. doi:10.1007/s00262-010-0968-0
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144(5):646–674. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
Mempel TR, Pittet MJ, Khazaie K, Weninger K, Weissleder R, Von Boehmer H, Von Andrian U (2006) Regulatory T cells reversibly suppress CD8 killer cell function independent of effector differentiation. Immunity 25(1):129–141
Blatner NR, Bonertz A, Beckhove P, Cheon EC, Krantz SB, Strouch M, Weitz J, Koch M, Halverson AL, Bentrem DJ, Khazaie K (2010) In colorectal cancer mast cells contribute to systemic regulatory T-cell dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(14):6430–6435. doi:10.1073/pnas.0913683107
Blatner NR, Mulcahy MF, Dennis KL, Scholtens D, Bentrem DJ, Phillips JD, Ham S, Sandall BP, Khan MW, Mahvi DM, Halverson AL, Stryker SJ, Boller AM, Singal A, Sneed RK, Sarraj B, Ansari MJ, Oft M, Iwakura Y, Zhou L, Bonertz A, Beckhove P, Gounari F, Khazaie K (2012) Expression of RORgammat marks a pathogenic regulatory T cell subset in human colon cancer. Sci Transl Med. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3004566
Gounaris E, Blatner NR, Dennis K, Magnusson F, Gurish MF, Strom TB, Beckhove P, Gounari F, Khazaie K (2009) T-regulatory cells shift from a protective anti-inflammatory to a cancer-promoting proinflammatory phenotype in polyposis. Cancer Res 69(13):5490–5497
Acknowledgments
K. Khazaie was supported by NIH, R01CA160436-05, R01 AA023417-03. F. Gounari was supported by NIH, R01 AI 108682-02.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M.W., Saadalla, A., Ewida, A.H. et al. The STAT3 inhibitor pyrimethamine displays anti-cancer and immune stimulatory effects in murine models of breast cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 67, 13–23 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-017-2057-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-017-2057-0