Abstract
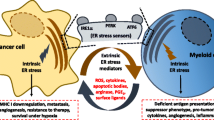
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is a cellular process that occurs as a consequence of several stress circumstances, such as the accumulation of unfolded proteins in the lumen of the ER or distinct insults that disturb the ER normal function. Different conditions in the tumor microenvironment (TME), including hypoxia, nutrient deprivation, and the elevated production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species destabilize the loading and dispatching of the newly synthesized proteins, triggering ER stress in cancer cells and tumor-infiltrating leukocytes. In order to cope with TME-induced ER stress, tumor and stromal cells initiate an adaptive response process that aims to resolve ER stress and to restore cellular homeostasis, which is referred as the unfolded protein responses (UPR). Paradoxically, the UPR can also induce cell death under severe and/or permanent ER stress. The UPR is started through three mediators, the activation of the inositol-requiring enzyme-1α, the pancreatic ER kinase-like ER kinase, and the activating transcription factor 6. In this minireview, we will discuss the pro- and anti-tumorigenic role of the UPR in cancer cells. In addition, we will describe the effects of the TME-induced ER stress in the immunosuppressive activity of tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells. Also, we will review the results of emerging therapeutic interventions that target ER stress and the UPR mediators in cancer. We postulate that the inhibition of ER stress or the UPR-related elements could represent a significant approach to increase the efficacy of various forms of cancer immunotherapy.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A-NEC:
-
Acute necrotizing enterocolitis
- ATF4:
-
Activation transcription factor 4
- ATF6:
-
Activating transcription factor 6
- C/EBP:
-
CAAT/enhancer binding protein
- cDCs:
-
Conventional dendritic cells
- CHOP:
-
CAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP) homologous protein
- CRT:
-
Calreticulin
- DAMPs:
-
Danger-associated molecular patterns
- DR5:
-
TNF-related apoptosis-induced ligand receptor 2
- EAE:
-
Autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- eIF2α:
-
Eukaryotic initiation factor 2α
- ER stress:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress
- ERAD:
-
ER-associated degradation
- HIF-1α:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha
- ICD:
-
Immunogenic cell death
- IRE-1α:
-
Inositol-requiring enzyme-1α
- Kdelr1:
-
KDEL receptor 1
- LOX-1:
-
Lectin-type oxidized LDL receptor-1
- M-MDSC:
-
Monocytic MDSC
- MDSC:
-
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells
- Nrf2:
-
NF-E2-related factor-2
- PERK:
-
Pancreatic ER kinase (PKR)-like ER kinase
- PKR:
-
Protein kinase RNA
- PMN-MDSC:
-
Granulocytic MDSC
- PRR:
-
Pathogen recognition receptors
- RIDD:
-
IRE-1-dependent decay of mRNA
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- Rpl22:
-
RP ribosomal protein L22
- t-DC:
-
Tumor-infiltrating dendritic cells
- TAM:
-
Tumor-associated macrophages
- Th2:
-
Type 2 T helper cells
- TLRs:
-
Toll-like receptors
- TME:
-
Tumor microenvironment
- TNBC:
-
Triple-negative breast cancer
- TRAF2:
-
TNF receptor-associated factor 2
- UPR:
-
Unfolded protein responses
- VEGF-A:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor A
- XBP-1:
-
X-box binding protein-1
References
Janssens S, Pulendran B, Lambrecht BN (2014) Emerging functions of the unfolded protein response in immunity. Nat Immunol 15(10):910–919
Smith MH, Ploegh HL, Weissman JS (2011) Road to ruin: targeting proteins for degradation in the endoplasmic reticulum. Science 334(6059):1086–1090. doi:10.1126/science.1209235
Bettigole SE, Glimcher LH (2015) Endoplasmic reticulum stress in immunity. Annu Rev Immunol 33:107–138. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-032414-112116
Bertolotti A, Zhang Y, Hendershot LM, Harding HP, Ron D (2000) Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat Cell Biol 2(6):326–332. doi:10.1038/35014014
Tabas I, Ron D (2011) Integrating the mechanisms of apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Nat Cell Biol 13(3):184–190. doi:10.1038/ncb0311-184
Yoshida H, Matsui T, Yamamoto A, Okada T, Mori K (2001) XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription factor. Cell 107(7):881–891
Shoulders MD, Ryno LM, Genereux JC, Moresco JJ, Tu PG, Wu C, Yates JR 3rd, Su AI, Kelly JW, Wiseman RL (2013) Stress-independent activation of XBP1s and/or ATF6 reveals three functionally diverse ER proteostasis environments. Cell Rep 3(4):1279–1292. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2013.03.024
Sriburi R, Jackowski S, Mori K, Brewer JW (2004) XBP1: a link between the unfolded protein response, lipid biosynthesis, and biogenesis of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol 167(1):35–41. doi:10.1083/jcb.200406136
Urano F, Wang X, Bertolotti A, Zhang Y, Chung P, Harding HP, Ron D (2000) Coupling of stress in the ER to activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase IRE1. Science 287(5453):664–666
Harding HP, Zhang Y, Bertolotti A, Zeng H, Ron D (2000) Perk is essential for translational regulation and cell survival during the unfolded protein response. Mol Cell 5(5):897–904
Chitnis NS, Pytel D, Bobrovnikova-Marjon E, Pant D, Zheng H, Maas NL, Frederick B, Kushner JA, Chodosh LA, Koumenis C, Fuchs SY, Diehl JA (2012) miR-211 is a prosurvival microRNA that regulates chop expression in a PERK-dependent manner. Mol Cell 48(3):353–364
Adachi Y, Yamamoto K, Okada T, Yoshida H, Harada A, Mori K (2008) ATF6 is a transcription factor specializing in the regulation of quality control proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell Struct Funct 33(1):75–89
Szegezdi E, Logue SE, Gorman AM, Samali A (2006) Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. EMBO Rep 7(9):880–885. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.7400779
Ahonen TJ, Xie J, LeBaron MJ, Zhu J, Nurmi M, Alanen K, Rui H, Nevalainen MT (2003) Inhibition of transcription factor Stat5 induces cell death of human prostate cancer cells. J Biol Chem 278(29):27287–27292. doi:10.1074/jbc.M304307200
Daneshmand S, Quek ML, Lin E, Lee C, Cote RJ, Hawes D, Cai J, Groshen S, Lieskovsky G, Skinner DG, Lee AS, Pinski J (2007) Glucose-regulated protein GRP78 is up-regulated in prostate cancer and correlates with recurrence and survival. Hum Pathol 38(10):1547–1552. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2007.03.014
Chen X, Iliopoulos D, Zhang Q, Tang Q, Greenblatt MB, Hatziapostolou M, Lim E, Tam WL, Ni M, Chen Y, Mai J, Shen H, Hu DZ, Adoro S, Hu B, Song M, Tan C, Landis MD, Ferrari M, Shin SJ, Brown M, Chang JC, Liu XS, Glimcher LH (2014) XBP1 promotes triple-negative breast cancer by controlling the HIF1alpha pathway. Nature 508(7494):103–107. doi:10.1038/nature13119
Cullinan SB, Diehl JA (2004) PERK-dependent activation of Nrf2 contributes to redox homeostasis and cell survival following endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Biol Chem 279(19):20108–20117. doi:10.1074/jbc.M314219200
Schewe DM, Aguirre-Ghiso JA (2008) ATF6alpha-Rheb-mTOR signaling promotes survival of dormant tumor cells in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(30):10519–10524. doi:10.1073/pnas.0800939105
Dadey DY, Kapoor V, Khudanyan A, Urano F, Kim AH, Thotala D, Hallahan DE (2016) The ATF6 pathway of the ER stress response contributes to enhanced viability in glioblastoma. Oncotarget 7(2):2080–2092. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.6712
Pereira ER, Liao N, Neale GA, Hendershot LM (2010) Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of proangiogenic factors by the unfolded protein response. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012521
Romero-Ramirez L, Cao H, Regalado MP, Kambham N, Siemann D, Kim JJ, Le QT, Koong AC (2009) X box-binding protein 1 regulates angiogenesis in human pancreatic adenocarcinomas. Transl Oncol 2(1):31–38
Blais JD, Addison CL, Edge R, Falls T, Zhao H, Wary K, Koumenis C, Harding HP, Ron D, Holcik M, Bell JC (2006) Perk-dependent translational regulation promotes tumor cell adaptation and angiogenesis in response to hypoxic stress. Mol Cell Biol 26(24):9517–9532. doi:10.1128/MCB.01145-06
Reimold AM, Iwakoshi NN, Manis J, Vallabhajosyula P, Szomolanyi-Tsuda E, Gravallese EM, Friend D, Grusby MJ, Alt F, Glimcher LH (2001) Plasma cell differentiation requires the transcription factor XBP-1. Nature 412(6844):300–307. doi:10.1038/35085509
Osorio F, Tavernier SJ, Hoffmann E, Saeys Y, Martens L, Vetters J, Delrue I, De RR, Parthoens E, Pouliot P, Iwawaki T, Janssens S, Lambrecht BN (2014) The unfolded-protein-response sensor IRE-1alpha regulates the function of CD8alpha+ dendritic cells. Nat Immunol 15(3):248–257
Iwakoshi NN, Pypaert M, Glimcher LH (2007) The transcription factor XBP-1 is essential for the development and survival of dendritic cells. J Exp Med 204(10):2267–2275. doi:10.1084/jem.20070525
Martinon F, Chen X, Lee AH, Glimcher LH (2010) TLR activation of the transcription factor XBP1 regulates innate immune responses in macrophages. Nat Immunol 11(5):411–418. doi:10.1038/ni.1857
Goodall JC, Wu C, Zhang Y, McNeill L, Ellis L, Saudek V, Gaston JS (2010) Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced transcription factor, CHOP, is crucial for dendritic cell IL-23 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(41):17698–17703
Cubillos-Ruiz JR, Silberman PC, Rutkowski MR, Chopra S, Perales-Puchalt A, Song M, Zhang S, Bettigole SE, Gupta D, Holcomb K, Ellenson LH, Caputo T, Lee AH, Conejo-Garcia JR, Glimcher LH (2015) ER stress sensor XBP1 controls anti-tumor immunity by disrupting dendritic cell homeostasis. Cell 161(7):1527–1538. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.025
Cubillos-Ruiz JR, Bettigole SE, Glimcher LH (2017) Tumorigenic and immunosuppressive effects of endoplasmic reticulum stress in cancer. Cell 168(4):692–706. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2016.12.004
Condamine T, Kumar V, Ramachandran IR, Youn JI, Celis E, Finnberg N, El-Deiry WS, Winograd R, Vonderheide RH, English NR, Knight SC, Yagita H, McCaffrey JC, Antonia S, Hockstein N, Witt R, Masters G, Bauer T, Gabrilovich DI (2014) ER stress regulates myeloid-derived suppressor cell fate through TRAIL-R-mediated apoptosis. J Clin Invest 124(6):2626–2639
Condamine T, Dominguez GA, Youn JI, Kossenkov AV, Mony S, Alicea-Torres K, Tcyganov E, Hashimoto A, Nefedova Y, Lin C, Partlova S, Garfall A, Vogl DT, Xu X, Knight SC, Malietzis G, Lee GH, Eruslanov E, Albelda SM, Wang X, Mehta JL, Bewtra M, Rustgi A, Hockstein N, Witt R, Masters G, Nam B, Smirnov D, Sepulveda MA, Gabrilovich DI (2016) Lectin-type oxidized LDL receptor-1 distinguishes population of human polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer patients. Sci Immunol. doi:10.1126/sciimmunol.aaf8943
Thevenot PT, Sierra RA, Raber PL, Al-Khami AA, Trillo-Tinoco J, Zarreii P, Ochoa AC, Cui Y, Del VL, Rodriguez PC (2014) The stress-response sensor chop regulates the function and accumulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in tumors. Immunity 41(3):389–401
Sonda N, Chioda M, Zilio S, Simonato F, Bronte V (2011) Transcription factors in myeloid-derived suppressor cell recruitment and function. Curr Opin Immunol 23(2):279–285
Yan D, Wang HW, Bowman RL, Joyce JA (2016) STAT3 and STAT6 signaling pathways synergize to promote cathepsin secretion from macrophages via IRE1alpha activation. Cell Rep 16(11):2914–2927. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2016.08.035
Mahadevan NR, Rodvold J, Sepulveda H, Rossi S, Drew AF, Zanetti M (2011) Transmission of endoplasmic reticulum stress and pro-inflammation from tumor cells to myeloid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(16):6561–6566
Zanetti M, Rodvold JJ, Mahadevan NR (2016) The evolving paradigm of cell-nonautonomous UPR-based regulation of immunity by cancer cells. Oncogene 35(3):269–278. doi:10.1038/onc.2015.108
Brunsing R, Omori SA, Weber F, Bicknell A, Friend L, Rickert R, Niwa M (2008) B- and T-cell development both involve activity of the unfolded protein response pathway. J Biol Chem 283(26):17954–17961. doi:10.1074/jbc.M801395200
Solanki NR, Stadanlick JE, Zhang Y, Duc AC, Lee SY, Lauritsen JP, Zhang Z, Wiest DL (2016) Rpl22 loss selectively impairs alphabeta T cell development by dysregulating endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling. J Immunol 197(6):2280–2289. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1600815
Kamimura D, Katsunuma K, Arima Y, Atsumi T, Jiang JJ, Bando H, Meng J, Sabharwal L, Stofkova A, Nishikawa N, Suzuki H, Ogura H, Ueda N, Tsuruoka M, Harada M, Kobayashi J, Hasegawa T, Yoshida H, Koseki H, Miura I, Wakana S, Nishida K, Kitamura H, Fukada T, Hirano T, Murakami M (2015) KDEL receptor 1 regulates T-cell homeostasis via PP1 that is a key phosphatase for ISR. Nat Commun 6:7474. doi:10.1038/ncomms8474
Omar I, Lapenna A, Cohen-Daniel L, Tirosh B, Berger M (2016) Schlafen2 mutation unravels a role for chronic ER stress in the loss of T cell quiescence. Oncotarget 7(26):39396–39407. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.9818
Takano S, Ando T, Hiramatsu N, Kanayama A, Maekawa S, Ohnuma Y, Enomoto N, Ogawa H, Paton AW, Paton JC, Kitamura M, Nakao A (2008) T cell receptor-mediated signaling induces GRP78 expression in T cells: the implications in maintaining T cell viability. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 371(4):762–766. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.04.132
Pino SC, O’Sullivan-Murphy B, Lidstone EA, Thornley TB, Jurczyk A, Urano F, Greiner DL, Mordes JP, Rossini AA, Bortell R (2008) Protein kinase C signaling during T cell activation induces the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Cell Stress Chaperones 13(4):421–434. doi:10.1007/s12192-008-0038-0
Scheu S, Stetson DB, Reinhardt RL, Leber JH, Mohrs M, Locksley RM (2006) Activation of the integrated stress response during T helper cell differentiation. Nat Immunol 7(6):644–651. doi:10.1038/ni1338
Kamimura D, Bevan MJ (2008) Endoplasmic reticulum stress regulator XBP-1 contributes to effector CD8+ T cell differentiation during acute infection. J Immunol 181(8):5433–5441
Pino SC, O’Sullivan-Murphy B, Lidstone EA, Yang C, Lipson KL, Jurczyk A, diIorio P, Brehm MA, Mordes JP, Greiner DL, Rossini AA, Bortell R (2009) CHOP mediates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in Gimap5-deficient T cells. PLoS One 4(5):e5468. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0005468
Xu Y, Zhao F, Qiu Q, Chen K, Wei J, Kong Q, Gao B, Melo-Cardenas J, Zhang B, Zhang J, Song J, Zhang DD, Zhang J, Fan Y, Li H, Fang D (2016) The ER membrane-anchored ubiquitin ligase Hrd1 is a positive regulator of T-cell immunity. Nat Commun 7:12073. doi:10.1038/ncomms12073
Lu P, Struijs MC, Mei J, Witte-Bouma J, Korteland-van Male AM, de Bruijn AC, van Goudoever JB, Renes IB (2013) Endoplasmic reticulum stress, unfolded protein response and altered T cell differentiation in necrotizing enterocolitis. PLoS One 8(10):e78491. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0078491
Kono H, Rock KL (2008) How dying cells alert the immune system to danger. Nat Rev Immunol 8(4):279–289. doi:10.1038/nri2215
Krysko DV, Garg AD, Kaczmarek A, Krysko O, Agostinis P, Vandenabeele P (2012) Immunogenic cell death and DAMPs in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 12(12):860–875. doi:10.1038/nrc3380
Luo Y, Li SJ, Yang J, Qiu YZ, Chen FP (2013) HMGB1 induces an inflammatory response in endothelial cells via the RAGE-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 438(4):732–738. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.07.098
Tufi R, Panaretakis T, Bianchi K, Criollo A, Fazi B, Di Sano F, Tesniere A, Kepp O, Paterlini-Brechot P, Zitvogel L, Piacentini M, Szabadkai G, Kroemer G (2008) Reduction of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ levels favors plasma membrane surface exposure of calreticulin. Cell Death Differ 15(2):274–282. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4402275
Panaretakis T, Kepp O, Brockmeier U, Tesniere A, Bjorklund AC, Chapman DC, Durchschlag M, Joza N, Pierron G, van Endert P, Yuan J, Zitvogel L, Madeo F, Williams DB, Kroemer G (2009) Mechanisms of pre-apoptotic calreticulin exposure in immunogenic cell death. EMBO J 28(5):578–590. doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.1
Kepp O, Semeraro M, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Bloy N, Buque A, Huang X, Zhou H, Senovilla L, Kroemer G, Galluzzi L (2015) eIF2alpha phosphorylation as a biomarker of immunogenic cell death. Semin Cancer Biol 33:86–92. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.02.004
Martins I, Kepp O, Schlemmer F, Adjemian S, Tailler M, Shen S, Michaud M, Menger L, Gdoura A, Tajeddine N, Tesniere A, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G (2011) Restoration of the immunogenicity of cisplatin-induced cancer cell death by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Oncogene 30(10):1147–1158. doi:10.1038/onc.2010.500
Menger L, Vacchelli E, Adjemian S, Martins I, Ma Y, Shen S, Yamazaki T, Sukkurwala AQ, Michaud M, Mignot G, Schlemmer F, Sulpice E, Locher C, Gidrol X, Ghiringhelli F, Modjtahedi N, Galluzzi L, Andre F, Zitvogel L, Kepp O, Kroemer G (2012) Cardiac glycosides exert anticancer effects by inducing immunogenic cell death. Sci Transl Med 4(143):143ra199. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3003807
Tang CH, Ranatunga S, Kriss CL, Cubitt CL, Tao J, Pinilla-Ibarz JA, Del Valle JR, Hu CC (2014) Inhibition of ER stress-associated IRE-1/XBP-1 pathway reduces leukemic cell survival. J Clin Invest 124(6):2585–2598. doi:10.1172/JCI73448
Ri M, Tashiro E, Oikawa D, Shinjo S, Tokuda M, Yokouchi Y, Narita T, Masaki A, Ito A, Ding J, Kusumoto S, Ishida T, Komatsu H, Shiotsu Y, Ueda R, Iwawaki T, Imoto M, Iida S (2012) Identification of toyocamycin, an agent cytotoxic for multiple myeloma cells, as a potent inhibitor of ER stress-induced XBP1 mRNA splicing. Blood Cancer J 2(7):e79. doi:10.1038/bcj.2012.26
Atkins C, Liu Q, Minthorn E, Zhang SY, Figueroa DJ, Moss K, Stanley TB, Sanders B, Goetz A, Gaul N, Choudhry AE, Alsaid H, Jucker BM, Axten JM, Kumar R (2013) Characterization of a novel PERK kinase inhibitor with antitumor and antiangiogenic activity. Cancer Res 73(6):1993–2002
Yu Q, Zhao B, Gui J, Katlinski KV, Brice A, Gao Y, Li C, Kushner JA, Koumenis C, Diehl JA, Fuchs SY (2015) Type I interferons mediate pancreatic toxicities of PERK inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112(50):15420–15425. doi:10.1073/pnas.1516362112
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the National Cancer Institute, NIH Grant No. CA18485 to Paulo C. Rodriguez, PhD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have conflict of interests to disclose.
Additional information
This paper is a Focussed Research Review based on a presentation given at the conference Regulatory Myeloid Suppressor Cells: From Basic Discovery to Therapeutic Application which was hosted by the Wistar Institute in Philadelphia, PA, USA, 16th–19th June, 2016. It is part of a Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy series of Focussed Research Reviews.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohamed, E., Cao, Y. & Rodriguez, P.C. Endoplasmic reticulum stress regulates tumor growth and anti-tumor immunity: a promising opportunity for cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother 66, 1069–1078 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-017-2019-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-017-2019-6