Abstract
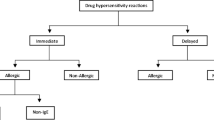
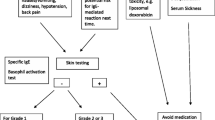
Hypersensitivity reactions (HSRs) to chemotherapy drugs, such as taxanes and platins, and to monoclonal antibodies limit their therapeutic use due to the severity of some reactions and the fear of inducing a potentially lethal reaction in highly sensitized patients. Patients who experience hypersensitivity reactions face the prospect of abandoning first-line treatment and switching to a second-line, less effective therapy. Some of these reactions are mast cell-mediated hypersensitivity reactions, a subset of which occur through an immunoglobulin (IgE)-dependent mechanism, and are thus true allergies. Others involve mast cells without a demonstrable IgE mechanism. Whether basophils can participate in these reactions has not been demonstrated. Rapid drug desensitization (RDD) is a procedure that induces temporary tolerance to a drug, allowing a medication allergic patient to receive the optimal agent for his or her disease. Through RDD, patients with IgE and non-IgE HSRs can safely be administered important medications while minimizing or completely inhibiting adverse reactions. Due to the clinical expansion and success of RDD, the molecular mechanisms inducing the temporary tolerization have been investigated and are partially understood, allowing for safer and more effective protocols. This article reviews the current literature on molecular mechanisms of RDD with an emphasis in our recent contributions to this field as well as the indications, methods and outcomes of RDD for taxanes, platins, and monoclonal antibodies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schwartz LB, Metcalfe DD, Miller JS, Earl H, Sullivan T (1987) Tryptase levels as an indicator of mast-cell activation in systemic anaphylaxis and mastocytosis. N Engl J Med 316:1622–1626. doi:10.1056/NEJM198706253162603
Vadas P, Gold M, Perelman B et al (2008) Platelet-activating factor, PAF acetylhydrolase, and severe anaphylaxis. N Engl J Med 358:28–35. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa070030
Castells M (2006) Desensitization for drug allergy. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 6:476–481. doi:10.1097/ACI.0b013e3280108716
Castells MC, Tennant NM, Sloane DE et al (2008) Hypersensitivity reactions to chemotherapy: outcomes and safety of rapid desensitization in 413 cases. J Allergy Clin Immunol 122:574–580. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2008.02.044
Lee CW, Matulonis UA, Castells MC (2005) Rapid inpatient/outpatient desensitization for chemotherapy hypersensitivity: standard protocol effective in 57 patients for 255 courses. Gynecol Oncol 99:393–399. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2005.06.028
Lee CW, Matulonis UA, Castells MC (2004) Carboplatin hypersensitivity: a 6-h 12-step protocol effective in 35 desensitizations in patients with gynecological malignancies and mast cell/IgE-mediated reactions. Gynecol Oncol 95:370–376. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2004.08.002
Wu LC (2011) Immunoglobulin E receptor signaling and asthma. J Biol Chem 286:32891–32897. doi:10.1074/jbc.R110.205104
Kepley CL (2005) Antigen-induced reduction in mast cell and basophil functional responses due to reduced Syk protein levels. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 138:29–39. doi:10.1159/000087355
Shalit M, Levi-Schaffer F (1995) Challenge of mast cells with increasing amounts of antigen induces desensitization. Clin Exp Allergy 25:896–902
Sancho-Serra Mdel C, Simarro M, Castells M (2011) Rapid IgE desensitization is antigen specific and impairs early and late mast cell responses targeting FcepsilonRI internalization. Eur J Immunol 41:1004–1013. doi:10.1002/eji.201040810
Morales AR, Shah N, Castells M (2005) Antigen-IgE desensitization in signal transducer and activator of transcription 6-deficient mast cells by suboptimal doses of antigen. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 94:575–580. doi:10.1016/S1081-1206(10)61136-2
Eisenhauer EA, ten Bokkel Huinink WW, Swenerton KD et al (1994) European-Canadian randomized trial of paclitaxel in relapsed ovarian cancer: high-dose versus low-dose and long versus short infusion. J Clin Oncol 12:2654–2666
Kwon JS, Elit L, Finn M, Hirte H, Mazurka J, Moens F, Trim K (2002) A comparison of two prophylactic regimens for hypersensitivity reactions to paclitaxel. Gynecol Oncol 84:420–425. doi:10.1006/gyno.2001.6546
Markman M, Kennedy A, Webster K, Kulp B, Peterson G, Belinson J (2000) Paclitaxel-associated hypersensitivity reactions: experience of the gynecologic oncology program of the Cleveland Clinic Cancer Center. J Clin Oncol 18:102–105
Wiernik PH, Schwartz EL, Strauman JJ, Dutcher JP, Lipton RB, Paietta E (1987) Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of taxol. Cancer Res 47:2486–2493
Schrijvers D, Wanders J, Dirix L, Prove A, Vonck I, van Oosterom A, Kaye S (1993) Coping with toxicities of docetaxel (Taxotere). Ann Oncol 4:610–611
Weiss RB, Donehower RC, Wiernik PH et al (1990) Hypersensitivity reactions from taxol. J Clin Oncol 8:1263–1268
Price KS, Castells MC (2002) Taxol reactions. Allergy Asthma Proc 23:205–208
Decorti G, Bartoli Klugmann F, Candussio L, Baldini L (1996) Effect of paclitaxel and Cremophor EL on mast cell histamine secretion and their interaction with adriamycin. Anticancer Res 16:317–320
Eschalier A, Lavarenne J, Burtin C, Renoux M, Chapuy E, Rodriguez M (1988) Study of histamine release induced by acute administration of antitumor agents in dogs. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 21:246–250
Essayan DM, Kagey-Sobotka A, Colarusso PJ, Lichtenstein LM, Ozols RF, King ED (1996) Successful parenteral desensitization to paclitaxel. J Allergy Clin Immunol 97:42–46
Szebeni J, Muggia FM, Alving CR (1998) Complement activation by Cremophor EL as a possible contributor to hypersensitivity to paclitaxel: an in vitro study. J Natl Cancer Inst 90:300–306
Weiszhar Z, Czucz J, Revesz C, Rosivall L, Szebeni J, Rozsnyay Z (2012) Complement activation by polyethoxylated pharmaceutical surfactants: Cremophor-EL, Tween-80 and Tween-20. Eur J Pharm Sci 45:492–498. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2011.09.016
Feldweg AM, Lee CW, Matulonis UA, Castells M (2005) Rapid desensitization for hypersensitivity reactions to paclitaxel and docetaxel: a new standard protocol used in 77 successful treatments. Gynecol Oncol 96:824–829. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2004.11.043
Aabo K, Adams M, Adnitt P et al (1998) Chemotherapy in advanced ovarian cancer: four systematic meta-analyses of individual patient data from 37 randomized trials. Advanced Ovarian Cancer Trialists’ Group. Br J Cancer 78:1479–1487
Gadducci A, Tana R, Teti G, Zanca G, Fanucchi A, Genazzani AR (2008) Analysis of the pattern of hypersensitivity reactions in patients receiving carboplatin retreatment for recurrent ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer 18:615–620
Gomez R, Harter P, Luck HJ, Traut A, Kommoss S, Kandel M, du Bois A (2009) Carboplatin hypersensitivity: does introduction of skin test and desensitization reliably predict and avoid the problem? A prospective single-center study. Int J Gynecol Cancer 19:1284–1287. doi:10.1111/IGC.0b013e3181a418ff
Makrilia N, Syrigou E, Kaklamanos I, Manolopoulos L, Saif MW (2010) Hypersensitivity reactions associated with platinum antineoplastic agents: a systematic review. Met Based Drugs. doi: 10.1155/2010/207084
Markman M, Kennedy A, Webster K, Elson P, Peterson G, Kulp B, Belinson J (1999) Clinical features of hypersensitivity reactions to carboplatin. J Clin Oncol 17:1141
Maindrault-Goebel F, Andre T, Tournigand C, Louvet C, Perez-Staub N, Zeghib N, De Gramont A (2005) Allergic-type reactions to oxaliplatin: retrospective analysis of 42 patients. Eur J Cancer 41:2262–2267. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2005.06.021
Polyzos A, Tsavaris N, Gogas H et al (2009) Clinical features of hypersensitivity reactions to oxaliplatin: a 10-year experience. Oncology 76:36–41. doi:10.1159/000178163
Sakaeda T, Kadoyama K, Yabuuchi H, Niijima S, Seki K, Shiraishi Y, Okuno Y (2011) Platinum agent-induced hypersensitivity reactions: data mining of the public version of the FDA adverse event reporting system, AERS. Int J Med Sci 8:332–338
Lee C, Gianos M, Klaustermeyer WB (2009) Diagnosis and management of hypersensitivity reactions related to common cancer chemotherapy agents. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 102: 179–187; quiz 87–89, 222. doi:10.1016/S1081-1206(10)60078-6
Schwartz JR, Bandera C, Bradley A, Brard L, Legare R, Granai CO, Dizon DS (2007) Does the platinum-free interval predict the incidence or severity of hypersensitivity reactions to carboplatin? The experience from Women and Infants’ Hospital. Gynecol Oncol 105:81–83. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2006.10.047
Hesterberg PE, Banerji A, Oren E, Penson RT, Krasner CN, Seiden MV, Wong JT (2009) Risk stratification for desensitization of patients with carboplatin hypersensitivity: clinical presentation and management. J Allergy Clin Immunol 123(1262–7):e1. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2009.02.042
Polyzos A, Tsavaris N, Kosmas C et al (2001) Hypersensitivity reactions to carboplatin administration are common but not always severe: a 10-year experience. Oncology 61:129–133
Dizon DS, Sabbatini PJ, Aghajanian C, Hensley ML, Spriggs DR (2002) Analysis of patients with epithelial ovarian cancer or fallopian tube carcinoma retreated with cisplatin after the development of a carboplatin allergy. Gynecol Oncol 84:378–382. doi:10.1006/gyno.2001.6519
Chung CH, O’Neil BH (2009) Infusion reactions to monoclonal antibodies for solid tumors: immunologic mechanisms and risk factors. Oncology (Williston Park) 23:14–17
Hansel TT, Kropshofer H, Singer T, Mitchell JA, George AJ (2010) The safety and side effects of monoclonal antibodies. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9:325–338. doi:10.1038/nrd3003
Brennan PJ, Rodriguez Bouza T, Hsu FI, Sloane DE, Castells MC (2009) Hypersensitivity reactions to mAbs: 105 desensitizations in 23 patients, from evaluation to treatment. J Allergy Clin Immunol 124:1259–1266. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2009.09.009
Brown SG (2004) Clinical features and severity grading of anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 114:371–376. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2004.04.029
Legere HJ 3rd, Palis RI, Rodriguez Bouza T, Uluer AZ, Castells MC (2009) A safe protocol for rapid desensitization in patients with cystic fibrosis and antibiotic hypersensitivity. J Cyst Fibros 8:418–424. doi:10.1016/j.jcf.2009.08.002
Breslow RG, Caiado J, Castells MC (2009) Acetylsalicylic acid and montelukast block mast cell mediator-related symptoms during rapid desensitization. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 102:155–160. doi:10.1016/S1081-1206(10)60247-5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is part of the Symposium in Writing: AllergoOncology: The Role of Th2 responses in cancer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castells, M., Sancho-Serra, M.d.C. & Simarro, M. Hypersensitivity to antineoplastic agents: mechanisms and treatment with rapid desensitization. Cancer Immunol Immunother 61, 1575–1584 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-012-1273-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-012-1273-x