Abstract
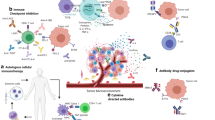
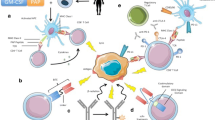
The recent FDA approval of the first therapeutic vaccine against prostate cancer has revitalized the public interest in the fields of cancer immunology and immunotherapy. Yet, clinical results are modest. A reason for this limited success may reside in the capacity of the tumor to convert inflammation in a tumor-promoting condition and eventually escape immune surveillance. Here we present the main known interactions between the prostate tumor and the immune system, showing how the malignancy can dodge the immune system by also exerting several immunosuppressive mechanisms. We also discuss experimental and clinical strategies proposed to counteract cancer immune evasion and emphasize the importance of implementing appropriate murine models like the transgenic adenocarcinoma of the mouse prostate model for investigating the biology of prostate cancer and novel immunotherapy approaches against it.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61(2):69–90. doi:10.3322/caac.20107
Miller BA, Chu KC, Hankey BF, Ries LA (2008) Cancer incidence and mortality patterns among specific Asian and Pacific Islander populations in the U.S. Cancer Causes Control 19(3):227–256. doi:10.1007/s10552-007-9088-3
Parker PM, Rice KR, Sterbis JR, Chen Y, Cullen J, McLeod DG, Brassell SA (2011) Prostate cancer in men less than the age of 50: a comparison of race and outcomes. Urology 78(1):110–115. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2010.12.046
Resnick MJ, Canter DJ, Guzzo TJ, Brucker BM, Bergey M, Sonnad SS, Wein AJ, Malkowicz SB (2009) Does race affect postoperative outcomes in patients with low-risk prostate cancer who undergo radical prostatectomy? Urology 73(3):620–623. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2008.09.035
Walsh PC, DeWeese TL, Eisenberger MA (2007) Clinical practice. Localized prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 357(26):2696–2705. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp0706784
Bill-Axelson A, Holmberg L, Ruutu M, Garmo H, Stark JR, Busch C, Nordling S, Haggman M, Andersson SO, Bratell S, Spangberg A, Palmgren J, Steineck G, Adami HO, Johansson JE (2011) Radical prostatectomy versus watchful waiting in early prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 364(18):1708–1717. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1011967
D’Amico AV (2011) Risk-based management of prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 365(2):169–171. doi:10.1056/NEJMe1103829
Tannock IF, de Wit R, Berry WR, Horti J, Pluzanska A, Chi KN, Oudard S, Theodore C, James ND, Turesson I, Rosenthal MA, Eisenberger MA (2004) Docetaxel plus prednisone or mitoxantrone plus prednisone for advanced prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 351(15):1502–1512. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa040720
Antonarakis ES, Eisenberger MA (2011) Expanding treatment options for metastatic prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 364(21):2055–2058. doi:10.1056/NEJMe1102758
Kantoff PW, Higano CS, Shore ND, Berger ER, Small EJ, Penson DF, Redfern CH, Ferrari AC, Dreicer R, Sims RB, Xu Y, Frohlich MW, Schellhammer PF (2010) Sipuleucel-T immunotherapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 363(5):411–422. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1001294
Drake CG (2010) Prostate cancer as a model for tumour immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol 10(8):580–593. doi:10.1038/nri2817
Miller AM, Pisa P (2007) Tumor escape mechanisms in prostate cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 56(1):81–87. doi:10.1007/s00262-005-0110-x
Kusmartsev S, Vieweg J (2009) Enhancing the efficacy of cancer vaccines in urologic oncology: new directions. Nat Rev Urol 6(10):540–549. doi:10.1038/nrurol.2009.177
Rabinovich GA, Gabrilovich D, Sotomayor EM (2007) Immunosuppressive strategies that are mediated by tumor cells. Annu Rev Immunol 25:267–296. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141609
Mellor AL, Munn DH (2008) Creating immune privilege: active local suppression that benefits friends, but protects foes. Nat Rev Immunol 8(1):74–80. doi:10.1038/nri2233
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 140(6):883–899. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.025
Coussens LM, Werb Z (2002) Inflammation and cancer. Nature 420(6917):860–867. doi:10.1038/nature01322
Sparmann A, Bar-Sagi D (2004) Ras-induced interleukin-8 expression plays a critical role in tumor growth and angiogenesis. Cancer Cell 6(5):447–458. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2004.09.028
Ellis LM, Hicklin DJ (2008) VEGF-targeted therapy: mechanisms of anti-tumour activity. Nat Rev Cancer 8(8):579–591. doi:10.1038/nrc2403
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V, Werb Z (2010) Matrix metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell 141(1):52–67. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.015
Gabrilovich DI, Nagaraj S (2009) Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 9(3):162–174. doi:10.1038/nri2506
Qian BZ, Pollard JW (2010) Macrophage diversity enhances tumor progression and metastasis. Cell 141(1):39–51. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.014
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F (2008) Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 454(7203):436–444. doi:10.1038/nature07205
Gabrilovich D (2004) Mechanisms and functional significance of tumour-induced dendritic-cell defects. Nat Rev Immunol 4(12):941–952. doi:10.1038/nri1498
De Marzo AM, Platz EA, Sutcliffe S, Xu J, Gronberg H, Drake CG, Nakai Y, Isaacs WB, Nelson WG (2007) Inflammation in prostate carcinogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 7(4):256–269. doi:10.1038/nrc2090
Zheng SL, Augustsson-Balter K, Chang B, Hedelin M, Li L, Adami HO, Bensen J, Li G, Johnasson JE, Turner AR, Adams TS, Meyers DA, Isaacs WB, Xu J, Gronberg H (2004) Sequence variants of toll-like receptor 4 are associated with prostate cancer risk: results from the CAncer Prostate in Sweden Study. Cancer Res 64(8):2918–2922
Riddell JR, Bshara W, Moser MT, Spernyak JA, Foster BA, Gollnick SO (2011) Peroxiredoxin 1 controls prostate cancer growth through Toll-like receptor 4-dependent regulation of tumor vasculature. Cancer Res 71(5):1637–1646. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3674
Kim TH, Choi SE, Ha ES, Jung JG, Han SJ, Kim HJ, Kim DJ, Kang Y, Lee KW (2011) IL-6 induction of TLR-4 gene expression via STAT3 has an effect on insulin resistance in human skeletal muscle. Acta Diabetol. doi:10.1007/s00592-011-0259-z
Reddy KR, Guan Y, Qin G, Zhou Z, Jing N (2011) Combined treatment targeting HIF-1alpha and Stat3 is a potent strategy for prostate cancer therapy. Prostate. doi:10.1002/pros.21397
Foster BA, Gingrich JR, Kwon ED, Madias C, Greenberg NM (1997) Characterization of prostatic epithelial cell lines derived from transgenic adenocarcinoma of the mouse prostate (TRAMP) model. Cancer Res 57(16):3325–3330
Tomlins SA, Rhodes DR, Perner S, Dhanasekaran SM, Mehra R, Sun XW, Varambally S, Cao X, Tchinda J, Kuefer R, Lee C, Montie JE, Shah RB, Pienta KJ, Rubin MA, Chinnaiyan AM (2005) Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription factor genes in prostate cancer. Science 310(5748):644–648. doi:10.1126/science.1117679
Wang J, Cai Y, Shao LJ, Siddiqui J, Palanisamy N, Li R, Ren C, Ayala G, Ittmann M (2011) Activation of NF-{kappa}B by TMPRSS2/ERG fusion Isoforms through toll-like receptor-4. Cancer Res 71(4):1325–1333. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2210
Greenberg NM, DeMayo F, Finegold MJ, Medina D, Tilley WD, Aspinall JO, Cunha GR, Donjacour AA, Matusik RJ, Rosen JM (1995) Prostate cancer in a transgenic mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(8):3439–3443
Huss WJ, Maddison LA, Greenberg NM (2001) Autochthonous mouse models for prostate cancer: past, present and future. Semin Cancer Biol 11(3):245–260. doi:10.1006/scbi.2001.0373
Shappell SB, Thomas GV, Roberts RL, Herbert R, Ittmann MM, Rubin MA, Humphrey PA, Sundberg JP, Rozengurt N, Barrios R, Ward JM, Cardiff RD (2004) Prostate pathology of genetically engineered mice: definitions and classification. The consensus report from the Bar Harbor meeting of the mouse models of human cancer consortium prostate pathology committee. Cancer Res 64(6):2270–2305
Hess Michelini R, Freschi M, Manzo T, Jachetti E, Degl’Innocenti E, Grioni M, Basso V, Bonini C, Simpson E, Mondino A, Bellone M. Concomitant tumor and minor histocompatibility antigen-specific immunity initiate rejection and maintain remission from established spontaneous solid tumors. Cancer Res 70(9):3505–3514. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4253
Han G, Foster BA, Mistry S, Buchanan G, Harris JM, Tilley WD, Greenberg NM (2001) Hormone status selects for spontaneous somatic androgen receptor variants that demonstrate specific ligand and cofactor dependent activities in autochthonous prostate cancer. J Biol Chem 276(14):11204–11213. doi:10.1074/jbc.M008207200
Huss WJ, Hanrahan CF, Barrios RJ, Simons JW, Greenberg NM (2001) Angiogenesis and prostate cancer: identification of a molecular progression switch. Cancer Res 61(6):2736–2743
Singh RP, Agarwal R (2006) Prostate cancer chemoprevention by silibinin: bench to bedside. Mol Carcinog 45(6):436–442. doi:10.1002/mc.20223
Luo JL, Tan W, Ricono JM, Korchynskyi O, Zhang M, Gonias SL, Cheresh DA, Karin M (2007) Nuclear cytokine-activated IKKalpha controls prostate cancer metastasis by repressing Maspin. Nature 446(7136):690–694. doi:10.1038/nature05656
Chin AI, Miyahira AK, Covarrubias A, Teague J, Guo B, Dempsey PW, Cheng G (2010) Toll-like receptor 3-mediated suppression of TRAMP prostate cancer shows the critical role of type I interferons in tumor immune surveillance. Cancer Res 70(7):2595–2603. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1162
Gonzalez-Reyes S, Fernandez JM, Gonzalez LO, Aguirre A, Suarez A, Gonzalez JM, Escaff S, Vizoso FJ (2011) Study of TLR3, TLR4, and TLR9 in prostate carcinomas and their association with biochemical recurrence. Cancer Immunol Immunother 60(2):217–226. doi:10.1007/s00262-010-0931-0
Paone A, Starace D, Galli R, Padula F, De Cesaris P, Filippini A, Ziparo E, Riccioli A (2008) Toll-like receptor 3 triggers apoptosis of human prostate cancer cells through a PKC-alpha-dependent mechanism. Carcinogenesis 29(7):1334–1342. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgn149
Bierie B, Moses HL (2006) Tumour microenvironment: TGFbeta: the molecular Jekyll and Hyde of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6(7):506–520. doi:10.1038/nrc1926
Massague J (2008) TGFbeta in cancer. Cell 134(2):215–230. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.001
Cardillo MR, Petrangeli E, Salvatori L, Ravenna L, Di Silverio F (2000) Transforming growth factor beta 1 and androgen receptors in prostate neoplasia. Anal Quant Cytol Histol 22(5):403–410
Cardillo MR, Petrangeli E, Perracchio L, Salvatori L, Ravenna L, Di Silverio F (2000) Transforming growth factor-beta expression in prostate neoplasia. Anal Quant Cytol Histol 22(1):1–10
Shariat SF, Kattan MW, Traxel E, Andrews B, Zhu K, Wheeler TM, Slawin KM (2004) Association of pre- and postoperative plasma levels of transforming growth factor beta(1) and interleukin 6 and its soluble receptor with prostate cancer progression. Clin Cancer Res 10(6):1992–1999
Pu H, Collazo J, Jones E, Gayheart D, Sakamoto S, Vogt A, Mitchell B, Kyprianou N (2009) Dysfunctional transforming growth factor-beta receptor II accelerates prostate tumorigenesis in the TRAMP mouse model. Cancer Res 69(18):7366–7374. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0758
Yang L, Huang J, Ren X, Gorska AE, Chytil A, Aakre M, Carbone DP, Matrisian LM, Richmond A, Lin PC, Moses HL (2008) Abrogation of TGF beta signaling in mammary carcinomas recruits Gr-1+ CD11b+ myeloid cells that promote metastasis. Cancer Cell 13(1):23–35. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2007.12.004
Li MO, Flavell RA (2008) TGF-beta: a master of all T cell trades. Cell 134(3):392–404. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.025
Thomas DA, Massague J (2005) TGF-beta directly targets cytotoxic T cell functions during tumor evasion of immune surveillance. Cancer Cell 8(5):369–380. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2005.10.012
Donkor MK, Sarkar A, Savage PA, Franklin RA, Johnson LK, Jungbluth AA, Allison JP, Li MO (2011) T cell surveillance of oncogene-induced prostate cancer is impeded by T cell-derived TGF-beta1 cytokine. Immunity 35(1):123–134. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2011.04.019
Diener KR, Woods AE, Manavis J, Brown MP, Hayball JD (2009) Transforming growth factor-beta-mediated signaling in T lymphocytes impacts on prostate-specific immunity and early prostate tumor progression. Lab Invest 89(2):142–151. doi:10.1038/labinvest.2008.123
Zhang Q, Yang X, Pins M, Javonovic B, Kuzel T, Kim SJ, Parijs LV, Greenberg NM, Liu V, Guo Y, Lee C (2005) Adoptive transfer of tumor-reactive transforming growth factor-beta-insensitive CD8 + T cells: eradication of autologous mouse prostate cancer. Cancer Res 65(5):1761–1769. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3169
Tang B, de Castro K, Barnes HE, Parks WT, Stewart L, Bottinger EP, Danielpour D, Wakefield LM (1999) Loss of responsiveness to transforming growth factor beta induces malignant transformation of nontumorigenic rat prostate epithelial cells. Cancer Res 59(19):4834–4842
Guo Y, Kyprianou N (1999) Restoration of transforming growth factor beta signaling pathway in human prostate cancer cells suppresses tumorigenicity via induction of caspase-1-mediated apoptosis. Cancer Res 59(6):1366–1371
Guo Y, Jacobs SC, Kyprianou N (1997) Down-regulation of protein and mRNA expression for transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta1) type I and type II receptors in human prostate cancer. Int J Cancer 71(4):573–579. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19970516)71:4<573::AID-IJC11>3.0.CO;2-D
Zeng L, Rowland RG, Lele SM, Kyprianou N (2004) Apoptosis incidence and protein expression of p53, TGF-beta receptor II, p27Kip1, and Smad4 in benign, premalignant, and malignant human prostate. Hum Pathol 35(3):290–297
Friese MA, Wischhusen J, Wick W, Weiler M, Eisele G, Steinle A, Weller M (2004) RNA interference targeting transforming growth factor-beta enhances NKG2D-mediated antiglioma immune response, inhibits glioma cell migration and invasiveness, and abrogates tumorigenicity in vivo. Cancer Res 64(20):7596–7603. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1627
Wu JD, Higgins LM, Steinle A, Cosman D, Haugk K, Plymate SR (2004) Prevalent expression of the immunostimulatory MHC class I chain-related molecule is counteracted by shedding in prostate cancer. J Clin Invest 114(4):560–568. doi:10.1172/JCI22206
Guerra N, Tan YX, Joncker NT, Choy A, Gallardo F, Xiong N, Knoblaugh S, Cado D, Greenberg NM, Raulet DH (2008) NKG2D-deficient mice are defective in tumor surveillance in models of spontaneous malignancy. Immunity 28(4):571–580. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2008.02.016
Burnet M (1957) Cancer; a biological approach. I. The processes of control. Br Med J 1(5022):779–786
Dunn GP, Bruce AT, Ikeda H, Old LJ, Schreiber RD (2002) Cancer immunoediting: from immunosurveillance to tumor escape. Nat Immunol 3(11):991–998. doi:10.1038/ni1102-991
Vesely MD, Kershaw MH, Schreiber RD, Smyth MJ (2011) Natural innate and adaptive immunity to cancer. Annu Rev Immunol 29:235–271. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-031210-101324
Shankaran V, Ikeda H, Bruce AT, White JM, Swanson PE, Old LJ, Schreiber RD (2001) IFNgamma and lymphocytes prevent primary tumour development and shape tumour immunogenicity. Nature 410(6832):1107–1111. doi:10.1038/35074122
Boshoff C, Weiss R (2002) AIDS-related malignancies. Nat Rev Cancer 2(5):373–382. doi:10.1038/nrc797
Moloney FJ, Comber H, O’Lorcain P, O’Kelly P, Conlon PJ, Murphy GM (2006) A population-based study of skin cancer incidence and prevalence in renal transplant recipients. Br J Dermatol 154(3):498–504. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.07021.x
Birkeland SA, Storm HH, Lamm LU, Barlow L, Blohme I, Forsberg B, Eklund B, Fjeldborg O, Friedberg M, Frodin L et al (1995) Cancer risk after renal transplantation in the Nordic countries, 1964–1986. Int J Cancer 60(2):183–189
Rizzo JD, Curtis RE, Socie G, Sobocinski KA, Gilbert E, Landgren O, Travis LB, Travis WD, Flowers ME, Friedman DL, Horowitz MM, Wingard JR, Deeg HJ (2009) Solid cancers after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood 113(5):1175–1183. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-05-158782
Finak G, Bertos N, Pepin F, Sadekova S, Souleimanova M, Zhao H, Chen H, Omeroglu G, Meterissian S, Omeroglu A, Hallett M, Park M (2008) Stromal gene expression predicts clinical outcome in breast cancer. Nat Med 14(5):518–527. doi:10.1038/nm1764
Pages F, Galon J, Dieu-Nosjean MC, Tartour E, Sautes-Fridman C, Fridman WH (2010) Immune infiltration in human tumors: a prognostic factor that should not be ignored. Oncogene 29(8):1093–1102. doi:10.1038/onc.2009.416
Curiel TJ, Coukos G, Zou L, Alvarez X, Cheng P, Mottram P, Evdemon-Hogan M, Conejo-Garcia JR, Zhang L, Burow M, Zhu Y, Wei S, Kryczek I, Daniel B, Gordon A, Myers L, Lackner A, Disis ML, Knutson KL, Chen L, Zou W (2004) Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced survival. Nat Med 10(9):942–949. doi:10.1038/nm1093
Gao Q, Qiu SJ, Fan J, Zhou J, Wang XY, Xiao YS, Xu Y, Li YW, Tang ZY (2007) Intratumoral balance of regulatory and cytotoxic T cells is associated with prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. J Clin Oncol 25(18):2586–2593. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.09.4565
Elkentaoui H, Robert G, Pasticier G, Bernhard JC, Couzi L, Merville P, Ravaud A, Ballanger P, Ferriere JM, Wallerand H (2010) Therapeutic management of de novo urological malignancy in renal transplant recipients: the experience of the French Department of Urology and Kidney Transplantation from Bordeaux. Urology 75(1):126–132. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2009.06.106
Kasiske BL, Snyder JJ, Gilbertson DT, Wang C (2004) Cancer after kidney transplantation in the United States. Am J Transplant 4(6):905–913. doi:10.1111/j.1600-6143.2004.00450.x
Tsaur I, Karalis A, Probst M, Blaheta RA, Scheuermann EH, Gossmann J, Kachel HG, Hauser IA, Jonas D, Obermuller N (2010) Development of urological cancers in renal transplant recipients: 30-year experience at the Frankfurt Transplant Center. Cancer Sci 101(11):2430–2435. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01676.x
Miller AM, Lundberg K, Ozenci V, Banham AH, Hellstrom M, Egevad L, Pisa P (2006) CD4+CD25high T cells are enriched in the tumor and peripheral blood of prostate cancer patients. J Immunol 177(10):7398–7405
Fox SB, Launchbury R, Bates GJ, Han C, Shaida N, Malone PR, Harris AL, Banham AH (2007) The number of regulatory T cells in prostate cancer is associated with the androgen receptor and hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-2alpha but not HIF-1alpha. Prostate 67(6):623–629. doi:10.1002/pros.20538
Vuk-Pavlovic S, Bulur PA, Lin Y, Qin R, Szumlanski CL, Zhao X, Dietz AB (2010) Immunosuppressive CD14+ HLA-DRlow/- monocytes in prostate cancer. Prostate 70(4):443–455. doi:10.1002/pros.21078
Degl’Innocenti E, Grioni M, Boni A, Camporeale A, Bertilaccio MT, Freschi M, Monno A, Arcelloni C, Greenberg NM, Bellone M (2005) Peripheral T cell tolerance occurs early during spontaneous prostate cancer development and can be rescued by dendritic cell immunization. Eur J Immunol 35(1):66–75. doi:10.1002/eji.200425531
Degl’Innocenti E, Grioni M, Capuano G, Jachetti E, Freschi M, Bertilaccio MT, Hess-Michelini R, Doglioni C, Bellone M (2008) Peripheral T-cell tolerance associated with prostate cancer is independent from CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells. Cancer Res 68(1):292–300. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2429
Drake CG, Doody AD, Mihalyo MA, Huang CT, Kelleher E, Ravi S, Hipkiss EL, Flies DB, Kennedy EP, Long M, McGary PW, Coryell L, Nelson WG, Pardoll DM, Adler AJ (2005) Androgen ablation mitigates tolerance to a prostate/prostate cancer-restricted antigen. Cancer Cell 7(3):239–249. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2005.01.027
Anderson MJ, Shafer-Weaver K, Greenberg NM, Hurwitz AA (2007) Tolerization of tumor-specific T cells despite efficient initial priming in a primary murine model of prostate cancer. J Immunol 178(3):1268–1276
Bai A, Higham E, Eisen HN, Wittrup KD, Chen J (2008) Rapid tolerization of virus-activated tumor-specific CD8+ T cells in prostate tumors of TRAMP mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(35):13003–13008. doi:10.1073/pnas.0805599105
Zheng X, Gao JX, Zhang H, Geiger TL, Liu Y, Zheng P (2002) Clonal deletion of simian virus 40 large T antigen-specific T cells in the transgenic adenocarcinoma of mouse prostate mice: an important role for clonal deletion in shaping the repertoire of T cells specific for antigens overexpressed in solid tumors. J Immunol 169(9):4761–4769
Salgaller ML, Lodge PA, McLean JG, Tjoa BA, Loftus DJ, Ragde H, Kenny GM, Rogers M, Boynton AL, Murphy GP (1998) Report of immune monitoring of prostate cancer patients undergoing T-cell therapy using dendritic cells pulsed with HLA-A2-specific peptides from prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA). Prostate 35(2):144–151. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0045(19980501)35:2<144:AID-PROS8>3.0.CO;2-J
Deeb KK, Michalowska AM, Yoon CY, Krummey SM, Hoenerhoff MJ, Kavanaugh C, Li MC, Demayo FJ, Linnoila I, Deng CX, Lee EY, Medina D, Shih JH, Green JE (2007) Identification of an integrated SV40 T/t-antigen cancer signature in aggressive human breast, prostate, and lung carcinomas with poor prognosis. Cancer Res 67(17):8065–8080. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1515
Liu Z, Guo BL, Gehrs BC, Nan L, Lopez RD (2005) Ex vivo expanded human Vgamma9Vdelta2+ gammadelta-T cells mediate innate antitumor activity against human prostate cancer cells in vitro. J Urol 173(5):1552–1556
Groh V, Rhinehart R, Secrist H, Bauer S, Grabstein KH, Spies T (1999) Broad tumor-associated expression and recognition by tumor-derived gamma delta T cells of MICA and MICB. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(12):6879–6884
Liu Z, Eltoum IE, Guo B, Beck BH, Cloud GA, Lopez RD (2008) Protective immunosurveillance and therapeutic antitumor activity of gammadelta T cells demonstrated in a mouse model of prostate cancer. J Immunol 180(9):6044–6053
Kondo M, Izumi T, Fujieda N, Kondo A, Morishita T, Matsushita H, Kakimi K (2011) Expansion of human peripheral blood γδ T cells using zoledronate. J Vis Exp (55). doi:10.3791/3182
Sakamoto M, Nakajima J, Murakawa T, Fukami T, Yoshida Y, Murayama T, Takamoto S, Matsushita H, Kakimi K (2011) Adoptive immunotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer using zoledronate-expanded gammadeltaTcells: a phase I clinical study. J Immunother 34(2):202–211. doi:10.1097/CJI.0b013e318207ecfb
Dieli F, Vermijlen D, Fulfaro F, Caccamo N, Meraviglia S, Cicero G, Roberts A, Buccheri S, D’Asaro M, Gebbia N, Salerno A, Eberl M, Hayday AC (2007) Targeting human gamma}delta T cells with zoledronate and interleukin-2 for immunotherapy of hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Res 67(15):7450–7457. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0199
Bendelac A, Savage PB, Teyton L (2007) The biology of NKT cells. Annu Rev Immunol 25:297–336. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141711
Tahir SM, Cheng O, Shaulov A, Koezuka Y, Bubley GJ, Wilson SB, Balk SP, Exley MA (2001) Loss of IFN-gamma production by invariant NK T cells in advanced cancer. J Immunol 167(7):4046–4050
Nowak M, Arredouani MS, Tun-Kyi A, Schmidt-Wolf I, Sanda MG, Balk SP, Exley MA (2010) Defective NKT cell activation by CD1d+ TRAMP prostate tumor cells is corrected by interleukin-12 with alpha-galactosylceramide. PLoS One 5(6):e11311. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011311
Bellone M, Ceccon M, Grioni M, Jachetti E, Calcinotto A, Napolitano A, Freschi M, Casorati G, Dellabona P (2010) iNKT cells control mouse spontaneous carcinoma independently of tumor-specific cytotoxic T cells. PLoS One 5(1):e8646. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008646
Cerundolo V, Silk JD, Masri SH, Salio M (2009) Harnessing invariant NKT cells in vaccination strategies. Nat Rev Immunol 9(1):28–38. doi:10.1038/nri2451
Schwemmer B, Lehmer A, Hofmann R, Braun J (1984) Natural killer cell activity in patients with prostatic carcinoma and its in vivo boosting with bacillus Calmette-Guerin. Urol Int 39(6):321–326
Wirth M, Schmitz-Drager BJ, Ackermann R (1985) Functional properties of natural killer cells in carcinoma of the prostate. J Urol 133(6):973–978
Singh SV, Warin R, Xiao D, Powolny AA, Stan SD, Arlotti JA, Zeng Y, Hahm ER, Marynowski SW, Bommareddy A, Desai D, Amin S, Parise RA, Beumer JH, Chambers WH (2009) Sulforaphane inhibits prostate carcinogenesis and pulmonary metastasis in TRAMP mice in association with increased cytotoxicity of natural killer cells. Cancer Res 69(5):2117–2125. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3502
Bronte V, Kasic T, Gri G, Gallana K, Borsellino G, Marigo I, Battistini L, Iafrate M, Prayer-Galetti T, Pagano F, Viola A (2005) Boosting antitumor responses of T lymphocytes infiltrating human prostate cancers. J Exp Med 201(8):1257–1268. doi:10.1084/jem.20042028
Kiniwa Y, Miyahara Y, Wang HY, Peng W, Peng G, Wheeler TM, Thompson TC, Old LJ, Wang RF (2007) CD8+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells mediate immunosuppression in prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13(23):6947–6958. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0842
Derhovanessian E, Adams V, Hahnel K, Groeger A, Pandha H, Ward S, Pawelec G (2009) Pretreatment frequency of circulating IL-17+ CD4+ T-cells, but not Tregs, correlates with clinical response to whole-cell vaccination in prostate cancer patients. Int J Cancer 125(6):1372–1379. doi:10.1002/ijc.24497
Sfanos KS, Bruno TC, Meeker AK, De Marzo AM, Isaacs WB, Drake CG (2009) Human prostate-infiltrating CD8+ T lymphocytes are oligoclonal and PD-1+. Prostate 69(15):1694–1703. doi:10.1002/pros.21020
Higano CS, Corman JM, Smith DC, Centeno AS, Steidle CP, Gittleman M, Simons JW, Sacks N, Aimi J, Small EJ (2008) Phase 1/2 dose-escalation study of a GM-CSF-secreting, allogeneic, cellular immunotherapy for metastatic hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer 113(5):975–984. doi:10.1002/cncr.23669
Small EJ, Sacks N, Nemunaitis J, Urba WJ, Dula E, Centeno AS, Nelson WG, Ando D, Howard C, Borellini F, Nguyen M, Hege K, Simons JW (2007) Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor–secreting allogeneic cellular immunotherapy for hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13(13):3883–3891. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2937
Antonarakis ES, Drake CG (2010) Current status of immunological therapies for prostate cancer. Curr Opin Urol 20(3):241–246. doi:10.1097/MOU.0b013e3283381793
Kantoff PW, Schuetz TJ, Blumenstein BA, Glode LM, Bilhartz DL, Wyand M, Manson K, Panicali DL, Laus R, Schlom J, Dahut WL, Arlen PM, Gulley JL, Godfrey WR (2010) Overall survival analysis of a phase II randomized controlled trial of a Poxviral-based PSA-targeted immunotherapy in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol 28(7):1099–1105. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.25.0597
Karja V, Aaltomaa S, Lipponen P, Isotalo T, Talja M, Mokka R (2005) Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes: a prognostic factor of PSA-free survival in patients with local prostate carcinoma treated by radical prostatectomy. Anticancer Res 25(6C):4435–4438
Fridman WH, Mlecnik B, Bindea G, Pages F, Galon J (2011) Immunosurveillance in human non-viral cancers. Curr Opin Immunol 23(2):272–278. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2010.12.011
Wang HY, Wang RF (2007) Regulatory T cells and cancer. Curr Opin Immunol 19(2):217–223. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2007.02.004
Piersma SJ, Welters MJ, van der Burg SH (2008) Tumor-specific regulatory T cells in cancer patients. Hum Immunol 69(4–5):241–249. doi:10.1016/j.humimm.2008.02.005
Rudensky AY (2011) Regulatory T cells and Foxp3. Immunol Rev 241(1):260–268. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01018.x
Colombo MP, Piconese S (2007) Regulatory-T-cell inhibition versus depletion: the right choice in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 7(11):880–887. doi:10.1038/nrc2250
Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B, Fredriksen T, Mauger S, Bindea G, Berger A, Bruneval P, Fridman WH, Pages F, Galon J (2011) Clinical impact of different classes of infiltrating T cytotoxic and helper cells (Th1, th2, treg, th17) in patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 71(4):1263–1271. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2907
Ji Y, Zhang W (2010) Th17 cells: positive or negative role in tumor? Cancer Immunol Immunother 59(7):979–987. doi:10.1007/s00262-010-0849-6
Wada S, Yoshimura K, Hipkiss EL, Harris TJ, Yen HR, Goldberg MV, Grosso JF, Getnet D, Demarzo AM, Netto GJ, Anders R, Pardoll DM, Drake CG (2009) Cyclophosphamide augments antitumor immunity: studies in an autochthonous prostate cancer model. Cancer Res 69(10):4309–4318. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4102
Cosmi L, Liotta F, Lazzeri E, Francalanci M, Angeli R, Mazzinghi B, Santarlasci V, Manetti R, Vanini V, Romagnani P, Maggi E, Romagnani S, Annunziato F (2003) Human CD8+ CD25+ thymocytes share phenotypic and functional features with CD4+ CD25+ regulatory thymocytes. Blood 102(12):4107–4114. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-04-1320
Bienvenu B, Martin B, Auffray C, Cordier C, Becourt C, Lucas B (2005) Peripheral CD8+ CD25+ T lymphocytes from MHC class II-deficient mice exhibit regulatory activity. J Immunol 175(1):246–253
Joosten SA, van Meijgaarden KE, Savage ND, de Boer T, Triebel F, van der Wal A, de Heer E, Klein MR, Geluk A, Ottenhoff TH (2007) Identification of a human CD8+ regulatory T cell subset that mediates suppression through the chemokine CC chemokine ligand 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(19):8029–8034. doi:10.1073/pnas.0702257104
Grosso JF, Kelleher CC, Harris TJ, Maris CH, Hipkiss EL, De Marzo A, Anders R, Netto G, Getnet D, Bruno TC, Goldberg MV, Pardoll DM, Drake CG (2007) LAG-3 regulates CD8+ T cell accumulation and effector function in murine self- and tumor-tolerance systems. J Clin Invest 117(11):3383–3392. doi:10.1172/JCI31184
Shafer-Weaver KA, Anderson MJ, Stagliano K, Malyguine A, Greenberg NM, Hurwitz AA (2009) Cutting Edge: tumor-specific CD8+ T cells infiltrating prostatic tumors are induced to become suppressor cells. J Immunol 183(8):4848–4852. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0900848
Hochrein H, O’Keeffe M, Wagner H (2002) Human and mouse plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Hum Immunol 63(12):1103–1110
Watkins SK, Zhu Z, Riboldi E, Shafer-Weaver KA, Stagliano KE, Sklavos MM, Ambs S, Yagita H, Hurwitz AA (2011) FOXO3 programs tumor-associated DCs to become tolerogenic in human and murine prostate cancer. J Clin Invest 121(4):1361–1372. doi:10.1172/JCI44325
Gabrilovich DI, Bronte V, Chen SH, Colombo MP, Ochoa A, Ostrand-Rosenberg S, Schreiber H (2007) The terminology issue for myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Cancer Res 67(1):425; author reply 426. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3037
Sica A, Bronte V (2007) Altered macrophage differentiation and immune dysfunction in tumor development. J Clin Invest 117(5):1155–1166. doi:10.1172/JCI31422
Peranzoni E, Zilio S, Marigo I, Dolcetti L, Zanovello P, Mandruzzato S, Bronte V (2010) Myeloid-derived suppressor cell heterogeneity and subset definition. Curr Opin Immunol 22(2):238–244. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2010.01.021
Serafini P, Meckel K, Kelso M, Noonan K, Califano J, Koch W, Dolcetti L, Bronte V, Borrello I (2006) Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibition augments endogenous antitumor immunity by reducing myeloid-derived suppressor cell function. J Exp Med 203(12):2691–2702. doi:10.1084/jem.20061104
Rigamonti N, Capuano G, Ricupito A, Jachetti E, Grioni M, Generoso L, Freschi M, Bellone M (2011) Modulators of arginine metabolism do not impact on peripheral T-cell tolerance and disease progression in a model of spontaneous prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 17(5):1012–1023. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2547
Molon B, Ugel S, Del Pozzo F, Soldani C, Zilio S, Avella D, De Palma A, Mauri P, Monegal A, Rescigno M, Savino B, Colombo P, Jonjic N, Pecanic S, Lazzarato L, Fruttero R, Gasco A, Bronte V, Viola A (2011) Chemokine nitration prevents intratumoral infiltration of antigen-specific T cells. J Exp Med 208(10):1949–1962. doi:10.1084/jem.20101956
Dong H, Zhu G, Tamada K, Chen L (1999) B7–H1, a third member of the B7 family, co-stimulates T-cell proliferation and interleukin-10 secretion. Nat Med 5(12):1365–1369. doi:10.1038/70932
Latchman Y, Wood CR, Chernova T, Chaudhary D, Borde M, Chernova I, Iwai Y, Long AJ, Brown JA, Nunes R, Greenfield EA, Bourque K, Boussiotis VA, Carter LL, Carreno BM, Malenkovich N, Nishimura H, Okazaki T, Honjo T, Sharpe AH, Freeman GJ (2001) PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1 and inhibits T cell activation. Nat Immunol 2(3):261–268. doi:10.1038/85330
Nishimura H, Okazaki T, Tanaka Y, Nakatani K, Hara M, Matsumori A, Sasayama S, Mizoguchi A, Hiai H, Minato N, Honjo T (2001) Autoimmune dilated cardiomyopathy in PD-1 receptor-deficient mice. Science 291(5502):319–322. doi:10.1126/science.291.5502.319
Ebelt K, Babaryka G, Frankenberger B, Stief CG, Eisenmenger W, Kirchner T, Schendel DJ, Noessner E (2009) Prostate cancer lesions are surrounded by FOXP3+ PD-1+ and B7–H1+ lymphocyte clusters. Eur J Cancer 45(9):1664–1672. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2009.02.015
Crane CA, Panner A, Murray JC, Wilson SP, Xu H, Chen L, Simko JP, Waldman FM, Pieper RO, Parsa AT (2009) PI(3) kinase is associated with a mechanism of immunoresistance in breast and prostate cancer. Oncogene 28(2):306–312. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.384
Francisco LM, Salinas VH, Brown KE, Vanguri VK, Freeman GJ, Kuchroo VK, Sharpe AH (2009) PD-L1 regulates the development, maintenance, and function of induced regulatory T cells. J Exp Med 206(13):3015–3029. doi:10.1084/jem.20090847
Wei S, Shreiner AB, Takeshita N, Chen L, Zou W, Chang AE (2008) Tumor-induced immune suppression of in vivo effector T-cell priming is mediated by the B7–H1/PD-1 axis and transforming growth factor beta. Cancer Res 68(13):5432–5438. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6598
Brahmer JR, Drake CG, Wollner I, Powderly JD, Picus J, Sharfman WH, Stankevich E, Pons A, Salay TM, McMiller TL, Gilson MM, Wang C, Selby M, Taube JM, Anders R, Chen L, Korman AJ, Pardoll DM, Lowy I, Topalian SL (2010) Phase I study of single-agent anti-programmed death-1 (MDX-1106) in refractory solid tumors: safety, clinical activity, pharmacodynamics, and immunologic correlates. J Clin Oncol 28(19):3167–3175. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.26.7609
Thompson CB, Allison JP (1997) The emerging role of CTLA-4 as an immune attenuator. Immunity 7(4):445–450
Leach DR, Krummel MF, Allison JP (1996) Enhancement of antitumor immunity by CTLA-4 blockade. Science 271(5256):1734–1736
Hurwitz AA, Foster BA, Kwon ED, Truong T, Choi EM, Greenberg NM, Burg MB, Allison JP (2000) Combination immunotherapy of primary prostate cancer in a transgenic mouse model using CTLA-4 blockade. Cancer Res 60(9):2444–2448
Hodi FS, O’Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW, Sosman JA, Haanen JB, Gonzalez R, Robert C, Schadendorf D, Hassel JC, Akerley W, van den Eertwegh AJ, Lutzky J, Lorigan P, Vaubel JM, Linette GP, Hogg D, Ottensmeier CH, Lebbe C, Peschel C, Quirt I, Clark JI, Wolchok JD, Weber JS, Tian J, Yellin MJ, Nichol GM, Hoos A, Urba WJ (2010) Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med 363(8):711–723. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1003466
Small EJ, Tchekmedyian NS, Rini BI, Fong L, Lowy I, Allison JP (2007) A pilot trial of CTLA-4 blockade with human anti-CTLA-4 in patients with hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13(6):1810–1815. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2318
Fong L, Kwek SS, O’Brien S, Kavanagh B, McNeel DG, Weinberg V, Lin AM, Rosenberg J, Ryan CJ, Rini BI, Small EJ (2009) Potentiating endogenous antitumor immunity to prostate cancer through combination immunotherapy with CTLA4 blockade and GM-CSF. Cancer Res 69(2):609–615. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3529
Kavanagh B, O’Brien S, Lee D, Hou Y, Weinberg V, Rini B, Allison JP, Small EJ, Fong L (2008) CTLA4 blockade expands FoxP3+ regulatory and activated effector CD4+ T cells in a dose-dependent fashion. Blood 112(4):1175–1183. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-11-125435
Munn DH, Zhou M, Attwood JT, Bondarev I, Conway SJ, Marshall B, Brown C, Mellor AL (1998) Prevention of allogeneic fetal rejection by tryptophan catabolism. Science 281(5380):1191–1193
Baban B, Chandler PR, Johnson BA III, Huang L, Li M, Sharpe ML, Francisco LM, Sharpe AH, Blazar BR, Munn DH, Mellor AL (2011) Physiologic control of IDO competence in splenic dendritic cells. J Immunol 187(5):2329–2335. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1100276
Uyttenhove C, Pilotte L, Theate I, Stroobant V, Colau D, Parmentier N, Boon T, Van den Eynde BJ (2003) Evidence for a tumoral immune resistance mechanism based on tryptophan degradation by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Nat Med 9(10):1269–1274. doi:10.1038/nm934
Kallberg E, Wikstrom P, Bergh A, Ivars F, Leanderson T (2010) Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) activity influence tumor growth in the TRAMP prostate cancer model. Prostate 70(13):1461–1470. doi:10.1002/pros.21181
Chung KT, Gadupudi GS (2011) Possible roles of excess tryptophan metabolites in cancer. Environ Mol Mutagen 52(2):81–104. doi:10.1002/em.20588
Silk JD, Lakhal S, Laynes R, Vallius L, Karydis I, Marcea C, Boyd CA, Cerundolo V (2011) IDO induces expression of a novel tryptophan transporter in mouse and human tumor cells. J Immunol 187(4):1617–1625. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1000815
Liu X, Newton RC, Friedman SM, Scherle PA (2009) Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, an emerging target for anti-cancer therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 9(8):938–952
Opitz CA, Litzenburger UM, Sahm F, Ott M, Tritschler I, Trump S, Schumacher T, Jestaedt L, Schrenk D, Weller M, Jugold M, Guillemin GJ, Miller CL, Lutz C, Radlwimmer B, Lehmann I, von Deimling A, Wick W, Platten M (2011) An endogenous tumour-promoting ligand of the human aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Nature 478(7368):197–203. doi:10.1038/nature10491
Chung AS, Lee J, Ferrara N (2010) Targeting the tumour vasculature: insights from physiological angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 10(7):505–514. doi:10.1038/nrc2868
Piali L, Fichtel A, Terpe HJ, Imhof BA, Gisler RH (1995) Endothelial vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 expression is suppressed by melanoma and carcinoma. J Exp Med 181(2):811–816
Bellone M, Mondino A, Corti A (2008) Vascular targeting, chemotherapy and active immunotherapy: teaming up to attack cancer. Trends Immunol 29(5):235–241. doi:10.1016/j.it.2008.02.003
Corti A, Curnis F, Arap W, Pasqualini R (2008) The neovasculature homing motif NGR: more than meets the eye. Blood 112(7):2628–2635. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-04-150862
Bertilaccio MT, Grioni M, Sutherland BW, Degl’Innocenti E, Freschi M, Jachetti E, Greenberg NM, Corti A, Bellone M (2008) Vasculature-targeted tumor necrosis factor-alpha increases the therapeutic index of doxorubicin against prostate cancer. Prostate 68(10):1105–1115. doi:10.1002/pros.20775
Calcinotto A, Grioni M, Jachetti E, Curnis F, Mondino A, Parmiani G, Corti A, Bellone M (2012) Targeting tumor necrosis factor-alpha to neoangiogenic vessels enhances lymphocyte infiltration in tumors and increases the therapeutic potential of immunotherapy. J Immunol (in press)
Grinshtein N, Bridle B, Wan Y, Bramson JL (2009) Neoadjuvant vaccination provides superior protection against tumor relapse following surgery compared with adjuvant vaccination. Cancer Res 69(9):3979–3985. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3385
Noguchi M, Yao A, Harada M, Nakashima O, Komohara Y, Yamada S, Itoh K, Matsuoka K (2007) Immunological evaluation of neoadjuvant peptide vaccination before radical prostatectomy for patients with localized prostate cancer. Prostate 67(9):933–942. doi:10.1002/pros.20572
Zitvogel L, Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F, Kroemer G (2008) Immunological aspects of cancer chemotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol 8(1):59–73. doi:10.1038/nri2216
Jones CU, Hunt D, McGowan DG, Amin MB, Chetner MP, Bruner DW, Leibenhaut MH, Husain SM, Rotman M, Souhami L, Sandler HM, Shipley WU (2011) Radiotherapy and short-term androgen deprivation for localized prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 365(2):107–118. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1012348
Carthon BC, Wolchok JD, Yuan J, Kamat A, Ng Tang DS, Sun J, Ku G, Troncoso P, Logothetis CJ, Allison JP, Sharma P (2010) Preoperative CTLA-4 blockade: tolerability and immune monitoring in the setting of a presurgical clinical trial. Clin Cancer Res 16(10):2861–2871. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0569
Hess Michelini R, Freschi M, Manzo T, Jachetti E, Degl’Innocenti E, Grioni M, Basso V, Bonini C, Simpson E, Mondino A, Bellone M (2010) Concomitant tumor and minor histocompatibility antigen-specific immunity initiate rejection and maintain remission from established spontaneous solid tumors. Cancer Res 70(9):3505–3514. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4253
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants of the Italian Association for Cancer Research (AIRC, Milan), the Ministry of Health (Rome), the Ministry of University and Research (FIRB; Rome) and Alleanza Contro il Cancro, Programma Straordinario di Ricerca Oncologica 2006, Programma 3 to M.B.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rigamonti, N., Bellone, M. Prostate cancer, tumor immunity and a renewed sense of optimism in immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother 61, 453–468 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-012-1216-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-012-1216-6