Abstract
Purpose
The interaction of Fc fragments of antibodies with the Fcγ receptors is an essential checkpoint in antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). Specific polymorphisms at position 158 enhance FcγRIIIa affinity for IgG1 and are associated with improved clinical outcome in lymphoma patients treated with IgG1 anti-CD20 antibody. The role of ADCC in the therapeutic effects of the α-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mAb, cetuximab, in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SCCHN) is poorly defined. We employed three SCCHN cell lines to test two hypotheses: (1) SCCHN is susceptible to cetuximab-mediated ADCC, (2) efficacy of ADCC is associated with polymorphisms at position 158 of FcγRIIIa.
Experimental design
FcγRIIIa-158 polymorphisms were determined for healthy donors, and their purified NK cells were used as effector cells against three SCCHN cell lines in ADCC assays. Cytotoxicity levels were compared for each polymorphism class. Proliferation and cell cycle assays were done to examine the direct effects of cetuximab.
Results
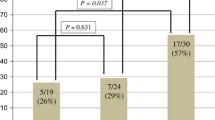
Our results indicate that SCCHN is susceptible to cetuximab-mediated ADCC in vitro. NK cytotoxic efficiency correlates with donor 158-polymorphisms in FcγRIIIa. Overall cytotoxicity was greatest for individuals having a single V allele when compared to homozygous F/F individuals; the cumulative percent cytotoxicity for each polymorphism among the cell lines was 58.2% V/V, 50.6% V/F, and 26.1% F/F (P < 0.001). Additionally, the presence of a V allele correlated with superior natural cytotoxicity against NK sensitive targets.
Conclusion
These data have both prognostic and therapeutic relevance and support the design of a prospective trial to determine the influence of FcγRIIIa polymorphisms on the clinical outcome of patients with SCCHN treated with α-EGFR mAbs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ang KK, Berkey BA, Tu X, Zhang HZ, Katz R, Hammond EH, Fu KK, Milas L (2002) Impact of epidermal growth factor receptor expression on survival and pattern of relapse in patients with advanced head and neck carcinoma. Cancer Res 62:7350–7356
Arnould L, Gelly M, Penault-Llorca F, Benoit L, Bonnetain F, Migeon C, Cabaret V, Fermeaux V, Bertheau P, Garnier J, Jeannin JF, Coudert B (2006) Trastuzumab-based treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer: an antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity mechanism? Br J Cancer 94:259–267
Biassoni R, Cantoni C, Pende D, Sivori S, Parolini S, Vitale M, Bottino C, Moretta A (2001) Human natural killer cell receptors and co-receptors. Immunol Rev 181:203–214
Bonner JA, Spencer SA (2006) Postoperative radiotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer warrants further exploration in the era of adjuvant chemotherapy and conformal radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol 24:2978–2980
Bowles JA, Weiner GJ (2005) CD16 polymorphisms and NK activation induced by monoclonal antibody-coated target cells. J Immunol Methods 304:88–99
Burtness B (2005) The role of cetuximab in the treatment of squamous cell cancer of the head and neck. Expert Opin Biol Ther 5:1085–1093
Burtness B, Goldwasser MA, Flood W, Mattar B, Forastiere AA (2005) Phase III randomized trial of cisplatin plus placebo compared with cisplatin plus cetuximab in metastatic/recurrent head and neck cancer: an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol 23:8646–8654
Cartron G, Dacheux L, Salles G, Solal-Celigny P, Bardos P, Colombat P, Watier H (2002) Therapeutic activity of humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody and polymorphism in IgG Fc receptor FcgammaRIIIa gene. Blood 99:754–758
Choong NW, Cohen EE (2006) Epidermal growth factor receptor directed therapy in head and neck cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 57:25–43
Cohen EE, Lingen MW, Vokes EE (2004) The expanding role of systemic therapy in head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol 22:1743–1752
Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, Khayat D, Bleiberg H, Santoro A, Bets D, Mueser M, Harstrick A, Verslype C, Chau I, Van Cutsem E (2004) Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 351:337–345
de Haas M, Koene HR, Kleijer M, de Vries E, Simsek S, van Tol MJ, Roos D, von dem Borne AE (1996) A triallelic Fc gamma receptor type IIIA polymorphism influences the binding of human IgG by NK cell Fc gamma RIIIa. J Immunol 156:3948–3955
Farag SS, Flinn IW, Modali R, Lehman TA, Young D, Byrd JC (2004) Fc gamma RIIIa and Fc gamma RIIa polymorphisms do not predict response to rituximab in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 103:1472–1474
Grandis JR, Sok JC (2004) Signaling through the epidermal growth factor receptor during the development of malignancy. Pharmacol Ther 102:37–46
Grandis JR, Zeng Q, Tweardy DJ (1996) Retinoic acid normalizes the increased gene transcription rate of TGF-alpha and EGFR in head and neck cancer cell lines. Nat Med 2:237–240
Hatjiharissi E, Xu L, Santos DD, Hunter ZR, Ciccarelli BT, Verselis S, Modica M, Cao Y, Manning RJ, Leleu X, Dimmock EA, Kortsaris A, Mitsiades C, Anderson KC, Fox EA, Treon SP (2007) Increased natural killer cell expression of CD16, augmented binding and ADCC activity to rituximab among individuals expressing the Fc{gamma}RIIIa-158 V/V and V/F polymorphism. Blood 110:2561–2564
Huether A, Hopfner M, Baradari V, Schuppan D, Scherubl H (2005) EGFR blockade by cetuximab alone or as combination therapy for growth control of hepatocellular cancer. Biochem Pharmacol 70:1568–1578
Jemal A, Murray T, Ward E, Samuels A, Tiwari RC, Ghafoor A, Feuer EJ, Thun MJ (2005) Cancer statistics, 2005. CA Cancer J Clin 55:10–30
Koene HR, Kleijer M, Algra J, Roos D, von dem Borne AE, de Haas M (1997) Fc gammaRIIIa-158V/F polymorphism influences the binding of IgG by natural killer cell Fc gammaRIIIa, independently of the Fc gammaRIIIa-48L/R/H phenotype. Blood 90:1109–1114
Kurai J, Chikumi H, Hashimoto K, Yamaguchi K, Yamasaki A, Sako T, Touge H, Makino H, Takata M, Miyata M, Nakamoto M, Burioka N, Shimizu E (2007) Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity mediated by cetuximab against lung cancer cell lines. Clin Cancer Res 13:1552–1561
Li S, Schmitz KR, Jeffrey PD, Wiltzius JJ, Kussie P, Ferguson KM (2005) Structural basis for inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor by cetuximab. Cancer Cell 7:301–311
Lin TS, Flinn IW, Modali R, Lehman TA, Webb J, Waymer S, Moran ME, Lucas MS, Farag SS, Byrd JC (2005) FCGR3A and FCGR2A polymorphisms may not correlate with response to alemtuzumab in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 105:289–291
Moretta L, Moretta A (2004) Unravelling natural killer cell function: triggering and inhibitory human NK receptors. EMBO J 23:255–259
Moretta A, Bottino C, Vitale M, Pende D, Cantoni C, Mingari MC, Biassoni R, Moretta L (2001) Activating receptors and coreceptors involved in human natural killer cell-mediated cytolysis. Annu Rev Immunol 19:197–223
Naramura M, Gillies SD, Mendelsohn J, Reisfeld RA, Mueller BM (1993) Therapeutic potential of chimeric and murine anti-(epidermal growth factor receptor) antibodies in a metastasis model for human melanoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother 37:343–349
Nieto A, Caliz R, Pascual M, Mataran L, Garcia S, Martin J (2000) Involvement of Fcgamma receptor IIIA genotypes in susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43:735–739
Peruzzi B, Bottaro DP (2006) Targeting the c-Met signaling pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12:3657–3660
Raben D, Helfrich B, Chan DC, Ciardiello F, Zhao L, Franklin W, Baron AE, Zeng C, Johnson TK, Bunn PA Jr (2005) The effects of cetuximab alone and in combination with radiation and/or chemotherapy in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11:795–805
Shields RL, Namenuk AK, Hong K, Meng YG, Rae J, Briggs J, Xie D, Lai J, Stadlen A, Li B, Fox JA, Presta LG (2001) High resolution mapping of the binding site on human IgG1 for Fc gamma RI, Fc gamma RII, Fc gamma RIII, and FcRn and design of IgG1 variants with improved binding to the Fc gamma R. J Biol Chem 276:6591–6604
Sivori S, Pende D, Bottino C, Marcenaro E, Pessino A, Biassoni R, Moretta L, Moretta A (1999) NKp46 is the major triggering receptor involved in the natural cytotoxicity of fresh or cultured human NK cells. Correlation between surface density of NKp46 and natural cytotoxicity against autologous, allogeneic or xenogeneic target cells. Eur J Immunol 29:1656–1666
Vance BA, Huizinga TW, Wardwell K, Guyre PM (1993) Binding of monomeric human IgG defines an expression polymorphism of Fc gamma RIII on large granular lymphocyte/natural killer cells. J Immunol 151:6429–6439
Weng WK, Levy R (2003) Two immunoglobulin G fragment C receptor polymorphisms independently predict response to rituximab in patients with follicular lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 21:3940–3947
Weng WK, Czerwinski D, Timmerman J, Hsu FJ, Levy R (2004) Clinical outcome of lymphoma patients after idiotype vaccination is correlated with humoral immune response and immunoglobulin G Fc receptor genotype. J Clin Oncol 22:4717–4724
Wheeler DL, Huang S, Kruser TJ, Nechrebecki MM, Armstrong EA, Benavente S, Gondi V, Hsu KT, Harari PM (2008) Mechanisms of acquired resistance to cetuximab: role of HER (ErbB) family members. Oncogene 27(28):3944–3956
Zhang W, Gordon M, Schultheis AM, Yang DY, Nagashima F, Azuma M, Chang HM, Borucka E, Lurje G, Sherrod AE, Iqbal S, Groshen S, Lenz HJ (2007) FCGR2A and FCGR3A polymorphisms associated with clinical outcome of epidermal growth factor receptor expressing metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with single-agent cetuximab. J Clin Oncol 25:3712–3718
Acknowledgments
Scott E. Strome receives royalties through the Mayo Clinic College of Medicine through licensure of intellectual property related to specific co stimulatory molecules to various third parties. This work was supported in part by American Cancer Society Institutional Research Pilot grant IRG-97-153-04.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Contribution: S. Chan performed experiments and analyzed data; S.E. Strome, S. Chan, C.J. Voskens, L. Wei, D. Schulze, and R.J. Taylor designed and analyzed data; R.J. Taylor, S. Chan, D.H. Schulze, and S.E. Strome authored the manuscript. G. Tian and R.J. Taylor provided statistical consultation. Other important contributions were made by A. Wood, J. Wolf, and A. Chapoval. Cetuximab was obtained from University of Maryland School of Medicine, Marlene and Stewart Greenebaum Cancer Center Pharmacy (Baltimore, MD, USA). S.E. Strome is a co-founder and major stock holder of Gliknik Inc., a Biotechnology Company.
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00262-009-0720-9
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taylor, R.J., Chan, SL., Wood, A. et al. FcγRIIIa polymorphisms and cetuximab induced cytotoxicity in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer Immunol Immunother 58, 997–1006 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-008-0613-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-008-0613-3