Abstract
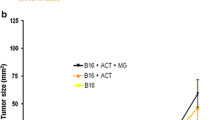
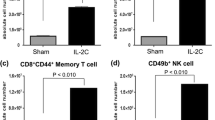
Interleukin (IL)-21 is a recently discovered cytokine in early clinical development, which has shown anti-tumor activity in various animal models. In the present study, we examine the anti-tumor activity of IL-21 protein therapy in two syngeneic tumor models and its effect on the density of tumor infiltrating T cells. We treated mice bearing established subcutaneous B16 melanomas or RenCa renal cell carcinomas with intraperitoneal (i.p.) or subcutaneous (s.c.) IL-21 protein therapy and subsequently scored the densities of tumor infiltrating CD4+ and CD8+ T cells by immunohistochemistry. Whereas both routes of IL-21 administration significantly inhibited growth of small, established RenCa and B16 tumors, only s.c. therapy significantly inhibited the growth of large, established tumors. We found a greater bioavailability and significant drainage of IL-21 to regional lymph nodes following s.c. administration, which could account for the apparent increase in anti-tumor activity. Specific depletion of CD8+ T cells with monoclonal antibodies completely abrogated the anti-tumor activity, whereas NK1.1+ cell depletion did not affect tumor growth. In accordance, both routes of IL-21 administration significantly increased the density of tumor infiltrating CD8+ T cells in both B16 and RenCa tumors; and in the RenCa model s.c. administration of IL-21 led to a significantly higher density of tumor infiltrating CD8+ T cells compared to i.p. administration. The densities of CD4+ T cells were unchanged following IL-21 treatments. Taken together, these data demonstrate that IL-21 protein has anti-tumor activity in established syngeneic tumors, and we show that IL-21 therapy markedly increases the density of tumor infiltrating CD8+ T cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IL-21:
-
Interleukin 21
- i.v.:
-
Intravenous
- i.p.:
-
Intraperitoneal
- s.c.:
-
Subcutaneous
- TILs:
-
Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes
- NK cells:
-
Natural killer cells
- CTLs:
-
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes
- AOI:
-
Area of interest
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- WT:
-
Wild type
- LN:
-
Lymph node
- IP-10:
-
Interferon-inducible protein 10
- MIG:
-
Monokine induced by interferon gamma
- I-TAC:
-
Interferon-inducible T cell alpha chemoattractant
References
Alves NL, Arosa FA, van Lier RA (2005) IL-21 sustains CD28 expression on IL-15-activated human naive CD8+ T cells. J Immunol 175:755–762
Brady J, Hayakawa Y, Smyth MJ, Nutt SL (2004) IL-21 induces the functional maturation of murine NK cells. J Immunol 172:2048–2058
Brandt K, Bulfone-Paus S, Jenckel A, Foster DC, Paus R, Ruckert R (2003) Interleukin-21 inhibits dendritic cell-mediated T cell activation and induction of contact hypersensitivity in vivo. J Invest Dermatol 121:1379–1382
Cappuccio A, Elishmereni M, Agur Z (2006) Cancer immunotherapy by interleukin-21: potential treatment strategies evaluated in a mathematical model. Cancer Res 66:7293–7300
Chang CJ, Tai KF, Roffler S, Hwang LH (2004) The immunization site of cytokine-secreting tumor cell vaccines influences the trafficking of tumor-specific T lymphocytes and antitumor efficacy against regional tumors. J Immunol 173:6025–6032
Clemente CG, Mihm MC Jr, Bufalino R, Zurrida S, Collini P, Cascinelli N (1996) Prognostic value of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in the vertical growth phase of primary cutaneous melanoma. Cancer 77:1303–1310
Comes A, Rosso O, Orengo AM, Di Carlo E, Sorrentino C, Meazza R, Piazza T, Valzasina B, Nanni P, Colombo MP, Ferrini S (2006) CD25+ regulatory T cell depletion augments immunotherapy of micrometastases by an IL-21-secreting cellular vaccine. J Immunol 176:1750–1758
Di Carlo E, Comes A, Orengo AM, Rosso O, Meazza R, Musiani P, Colombo MP, Ferrini S (2004) IL-21 induces tumor rejection by specific CTL and IFN-gamma-dependent CXC chemokines in syngeneic mice. J Immunol 172:1540–1547
Diederichsen AC, Hjelmborg JB, Christensen PB, Zeuthen J, Fenger C (2003) Prognostic value of the CD4+/CD8+ ratio of tumour infiltrating lymphocytes in colorectal cancer and HLA-DR expression on tumour cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother 52:423–428
Furukawa J, Hara I, Nagai H, Yao A, Oniki S, Fujisawa M (2006) Interleukin-21 gene transfection into mouse bladder cancer cells results in tumor rejection through the cytotoxic T lymphocyte response. J Urol 176:1198–1203
Geertsen PF, Gore ME, Negrier S, Tourani JM, von der MH (2004) Safety and efficacy of subcutaneous and continuous intravenous infusion rIL-2 in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 90:1156–1162
Haanen JB, Baars A, Gomez R, Weder P, Smits M, de Gruijl TD, von Blomberg BM, Bloemena E, Scheper RJ, van Ham SM, Pinedo HM, van den Eertwegh AJ (2006) Melanoma-specific tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes but not circulating melanoma-specific T cells may predict survival in resected advanced-stage melanoma patients. Cancer Immunol Immunother 55:451–458
He H, Wisner P, Yang G, Hu HM, Haley D, Miller W, O’hara A, Alvord WG, Clegg CH, Fox BA, Urba WJ, Walker EB (2006) Combined IL-21 and Low-Dose IL-2 therapy induces anti-tumor immunity and long-term curative effects in a murine melanoma tumor model. J Transl Med 4:24
Kasaian MT, Whitters MJ, Carter LL, Lowe LD, Jussif JM, Deng B, Johnson KA, Witek JS, Senices M, Konz RF, Wurster AL, Donaldson DD, Collins M, Young DA, Grusby MJ (2002) IL-21 limits NK cell responses and promotes antigen-specific T cell activation: a mediator of the transition from innate to adaptive immunity. Immunity 16:559–569
Krup OC, Kroll I, Bose G, Falkenberg FW (1999) Cytokine depot formulations as adjuvants for tumor vaccines. I. Liposome-encapsulated IL-2 as a depot formulation. J Immunother 22:525–538
Leonard WJ, Spolski R (2005) Interleukin-21: a modulator of lymphoid proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation. Nat Rev Immunol 5:688–698
Li Y, Bleakley M, Yee C (2005) IL-21 influences the frequency, phenotype, and affinity of the antigen-specific CD8 T cell response. J Immunol 175:2261–2269
Lipponen PK, Eskelinen MJ, Jauhiainen K, Harju E, Terho R (1992) Tumour infiltrating lymphocytes as an independent prognostic factor in transitional cell bladder cancer. Eur J Cancer 29A:69–75
Ma HL, Whitters MJ, Konz RF, Senices M, Young DA, Grusby MJ, Collins M, Dunussi-Joannopoulos K (2003) IL-21 activates both innate and adaptive immunity to generate potent antitumor responses that require perforin but are independent of IFN-gamma. J Immunol 171:608–615
Moroz A, Eppolito C, Li Q, Tao J, Clegg CH, Shrikant PA (2004) IL-21 enhances and sustains CD8+ T cell responses to achieve durable tumor immunity: comparative evaluation of IL-2, IL-15, and IL-21. J Immunol 173:900–999
Naito Y, Saito K, Shiiba K, Ohuchi A, Saigenji K, Nagura H, Ohtani H (1998) CD8+ T cells infiltrated within cancer cell nests as a prognostic factor in human colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 58:3491–3494
Pages F, Berger A, Camus M, Sanchez-Cabo F, Costes A, Molidor R, Mlecnik B, Kirilovsky A, Nilsson M, Damotte D, Meatchi T, Bruneval P, Cugnenc PH, Trajanoski Z, Fridman WH, Galon J (2005) Effector memory T cells, early metastasis, and survival in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 353:2654–2666
Parrish-Novak J, Dillon SR, Nelson A, Hammond A, Sprecher C, Gross JA, Johnston J, Madden K, Xu W, West J, Schrader S, Burkhead S, Heipel M, Brandt C, Kuijper JL, Kramer J, Conklin D, Presnell SR, Berry J, Shiota F, Bort S, Hambly K, Mudri S, Clegg C, Moore M, Grant FJ, Lofton-Day C, Gilbert T, Rayond F, Ching A, Yao L, Smith D, Webster P, Whitmore T, Maurer M, Kaushansky K, Holly RD, Foster D (2000) Interleukin 21 and its receptor are involved in NK cell expansion and regulation of lymphocyte function. Nature 408:57–63
Parrish-Novak J, Foster DC, Holly RD, Clegg CH (2002) Interleukin-21 and the IL-21 receptor: novel effectors of NK and T cell responses. J Leukoc Biol 72:856–863
Petrulio CA, Kim-Schulze S, Kaufman HL (2006) The tumour microenvironment and implications for cancer immunotherapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther 6:671–684
Roda JM, Parihar R, Lehman A, Mani A, Tridandapani S, Carson WE III (2006) Interleukin-21 enhances NK cell activation in response to antibody-coated targets. J Immunol 177:120–129
Romagnani P, Annunziato F, Lazzeri E, Cosmi L, Beltrame C, Lasagni L, Galli G, Francalanci M, Manetti R, Marra F, Vanini V, Maggi E, Romagnani S (2001) Interferon-inducible protein 10, monokine induced by interferon gamma, and interferon-inducible T-cell alpha chemoattractant are produced by thymic epithelial cells and attract T-cell receptor (TCR) alphabeta+ CD8+ single-positive T cells, TCRgammadelta+ T cells, and natural killer-type cells in human thymus. Blood 97:601–607
Sato E, Olson SH, Ahn J, Bundy B, Nishikawa H, Qian F, Jungbluth AA, Frosina D, Gnjatic S, Ambrosone C, Kepner J, Odunsi T, Ritter G, Lele S, Chen YT, Ohtani H, Old LJ, Odunsi K (2005) Intraepithelial CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and a high CD8+/regulatory T cell ratio are associated with favorable prognosis in ovarian cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:18538–18543
Scheffer SR, Nave H, Korangy F, Schlote K, Pabst R, Jaffee EM, Manns MP, Greten TF (2003) Apoptotic, but not necrotic, tumor cell vaccines induce a potent immune response in vivo. Int J Cancer 103:205–211
Schumacher K, Haensch W, Roefzaad C, Schlag PM (2001) Prognostic significance of activated CD8(+) T cell infiltrations within esophageal carcinomas. Cancer Res 61:3932–3936
Sivori S, Cantoni C, Parolini S, Marcenaro E, Conte R, Moretta L, Moretta A (2003) IL-21 induces both rapid maturation of human CD34+ cell precursors towards NK cells and acquisition of surface killer Ig-like receptors. Eur J Immunol 33:3439–3447
Smyth MJ, Crowe NY, Godfrey DI (2001) NK cells and NKT cells collaborate in host protection from methylcholanthrene-induced fibrosarcoma. Int Immunol 13:459–463
Smyth MJ, Kelly JM, Baxter AG, Korner H, Sedgwick JD (1998) An essential role for tumor necrosis factor in natural killer cell-mediated tumor rejection in the peritoneum. J Exp Med 188:1611–1619
Smyth MJ, Wallace ME, Nutt SL, Yagita H, Godfrey DI, Hayakawa Y (2005) Sequential activation of NKT cells and NK cells provides effective innate immunotherapy of cancer. J Exp Med 201:1973–1985
Takaki R, Hayakawa Y, Nelson A, Sivakumar PV, Hughes S, Smyth MJ, Lanier LL (2005) IL-21 enhances tumor rejection through a NKG2D-dependent mechanism. J Immunol 175:2167–2173
Toomey JA, Gays F, Foster D, Brooks CG (2003) Cytokine requirements for the growth and development of mouse NK cells in vitro. J Leukoc Biol 74:233–242
Ugai S, Shimozato O, Kawamura K, Wang YQ, Yamaguchi T, Saisho H, Sakiyama S, Tagawa M (2003) Expression of the interleukin-21 gene in murine colon carcinoma cells generates systemic immunity in the inoculated hosts. Cancer Gene Ther 10:187–192
Wang G, Tschoi M, Spolski R, Lou Y, Ozaki K, Feng C, Kim G, Leonard WJ, Hwu P (2003) In vivo antitumor activity of interleukin 21 mediated by natural killer cells. Cancer Res 63:9016–9022
Zeng R, Spolski R, Finkelstein SE, Oh S, Kovanen PE, Hinrichs CS, Pise-Masison CA, Radonovich MF, Brady JN, Restifo NP, Berzofsky JA, Leonard WJ (2005) Synergy of IL-21 and IL-15 in regulating CD8+ T cell expansion and function. J Exp Med 201:139–148
Acknowledgement
We would like to thank Heidi Winther, Bodil Andreasen, Birte Jørgensen and Kirsten Meeske for technical assistance with the experiments, and Mark Smyth for valuable discussion of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Søndergaard, H., Frederiksen, K.S., Thygesen, P. et al. Interleukin 21 therapy increases the density of tumor infiltrating CD8+ T cells and inhibits the growth of syngeneic tumors. Cancer Immunol Immunother 56, 1417–1428 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-007-0285-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-007-0285-4