Abstract
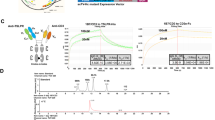
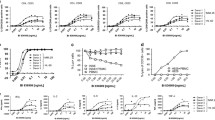
BscCD19xCD3 is a bispecific single-chain antibody construct with exceptional cytotoxic potency in vitro and in vivo. Here, we have investigated the biological activity of bscCD19xCD3 in chimpanzee, the only animal species identified in which bscCD19xCD3 showed bispecific binding, redirected B-cell lysis and cytokine production comparable to human cells. Pharmacokinetic analysis following 2-h intravenous infusion of 0.06, 0.1 or 0.12 μg/kg of bscCD19xCD3 as part of a dose escalation study in a single female chimpanzee revealed a half-life of approximately 2 h and elimination of the bispecific antibody from circulation within approximately 8 h after the end of infusion. This short exposure to bscCD19xCD3 elicited a transient increase in serum levels of IFNγ, IL-6, IL-2, soluble CD25, and transiently upregulated expression of CD69 and MHC class II on CD8-positive cells. Cytokine release and upregulation of T-cell activation markers were not observed with vehicle controls. A multiple-dose study using 5 weekly doses of 0.1 μg/kg in two animals also showed transient cytokine release and an activation of peripheral T cells with a first-dose effect, accompanied by a transient lymphopenia. While oscillations of T-cell counts were relatively even during repeated treatments, the amplitudes of peripheral B cells declined with every infusion, which was not observed in a vehicle control animal. Our data show that bscCD19xCD3 can be safely administered to chimpanzees at dose levels that cause fully reversible T-cell activation and, despite a very short exposure time, cumulative loss of peripheral B lymphocytes. A clinical trial testing prolonged administration of bscCD19xCD3 (MT103) for improving efficacy is currently ongoing.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbs IC, Clark M, Waldmann H, Chatenoud L, Koffman CG, and Sacks SH (1994) Sparing of first dose effect of monovalent anti-CD3 antibody used in allograft rejection is associated with diminished release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Ther Immunol 1:325–331
Cheng JD, Babb JS, Langer C, Aamdal S, Robert F, Engelhardt LR, Fernberg O, Schiller J, Forsberg G, Alpaugh RK, Weiner LM, Rogatko A (2004) Individualized patient dosing in phase I clinical trials: the role of escalation with overdose control in PNU-214936. J Clin Oncol 22:602–609
Chinn P, Braslawsky G, White C, Hanna N (2003) Antibody therapy of non-Hodgkin’s B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother 52:257–280
De Gast GC, Van Houten AA, Haagen IA, Klein S, De Weger RA, Van Dijk A, Phillips J, Clark M, Bast BJ (1995) Clinical experience with CD3xCD19 bispecific antibodies in patients with B cell malignancies. J Hematother 4:433–437
Dreier T, Baeuerle PA, Fichtner I, Grun M, Schlereth B, Lorenczewski G, Kufer P, Lutterbuse R, Riethmuller G, Gjorstrup P, Bargou RC (2003) T cell costimulus-independent and very efficacious inhibition of tumor growth in mice bearing subcutaneous or leukemic human B cell lymphoma xenografts by a CD19-/CD3- bispecific single-chain antibody construct. J Immunol 170:4397–4402
Dreier T, Lorenczewski G, Brandl C, Hoffmann P, Syring U, Hanakam F, Kufer P, Riethmuller G, Bargou R, Baeuerle PA (2002) Extremely potent, rapid and costimulation-independent cytotoxic T-cell response against lymphoma cells catalyzed by a single-chain bispecific antibody. Int J Cancer 100:690–697
Flynn JM, Byrd JC (2000) Campath-1H monoclonal antibody therapy. Curr Opin Oncol 12:574–581
Gidlof C, Dohlsten M, Lando P, Kalland T, Sundstrom C, Totterman TH (1997) A superantigen-antibody fusion protein for T-cell immunotherapy of human B-lineage malignancies. Blood 89:2089–2097
Grillo-Lopez AJ (2003) Rituximab (Rituxan/MabThera): the first decade (1993–2003). Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 3:767–779
Ishikawa H, Tsuyama N, Mahmoud MS, Fujii R, Abroun S, Liu S, Li FJ, Kawano MM (2002) CD19 expression and growth inhibition of tumours in human multiple myeloma. Leuk Lymphoma 43:613–616
Leonard JP, Link BK (2002) Immunotherapy of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma with hLL2 (epratuzumab, an anti-CD22 monoclonal antibody) and Hu1D10 (apolizumab). Semin Oncol 29:81–86
Loffler A, Gruen M, Wuchter C, Schriever F, Kufer P, Dreier T, Hanakam F, Baeuerle PA, Bommert K, Karawajew L, Dorken B, Bargou RC (2003) Efficient elimination of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia B cells by autologous T cells with a bispecific anti-CD19/anti-CD3 single-chain antibody construct. Leukemia 17:900–909
Loffler A, Kufer P, Lutterbuse R, Zettl F, Daniel PT, Schwenkenbecher JM, Riethmuller G, Dorken B, Bargou RC (2000) A recombinant bispecific single-chain antibody, CD19xCD3, induces rapid and high lymphoma-directed cytotoxicity by unstimulated T lymphocytes. Blood 95:2098–2103
Moingeon P, Chang HC, Sayre PH, Clayton LK, Alcover A, Gardner P, and Reinherz EL (1989) The structural biology of CD2. Immunol Rev 111:111–144
Olszewski AJ, Grossbard ML (2004) Empowering targeted therapy: lessons from rituximab. Sci STKE 2004:30
Pandit-Taskar N, Hamlin PA, Reyes S, Larson SM, Divgi CR (2003) New strategies in radioimmunotherapy for lymphoma. Curr Oncol Rep 5:364–371
Petrasch S, Perez-Alvarez C, Schmitz J, Kosco M, Brittinger G (1990) Antigenic phenotyping of human follicular dendritic cells isolated from nonmalignant and malignant lymphatic tissue. Eur J Immunol 20:1013–1018
Rubin LA, Nelson DL (1990) The soluble interleukin-2 receptor: biology, function, and clinical application. Ann Intern Med 113:619–627
Sapra P, Allen TM (2002) Internalizing antibodies are necessary for improved therapeutic efficacy of antibody-targeted liposomal drugs. Cancer Res 62:7190–7194
Scheuermann RH, Racila E (1995) CD19 antigen in leukemia and lymphoma diagnosis and immunotherapy. Leuk Lymphoma 18:385–397
Schriever F, Freedman AS, Freeman G, Messner E, Lee G, Daley J, Nadler LM (1989) Isolated human follicular dendritic cells display a unique antigenic phenotype. J Exp Med 169:2043–2058
Totterman TH, Gidlof C, Ragnarsson L, Hogbom E, Lindeberg M, von der Lehr N, Einarsson A, Soegaard M, Kristensson K, Kalland T, Dohlsten M (1998) Targeted superantigens for immunotherapy of haematopoietic tumours. Vox Sang 74(Suppl2):483–487
Vose JM (1999) Antibody-targeted therapy for low-grade lymphoma. Semin Hematol 36:15–20
Weiner GJ, De Gast GC (1995) Bispecific monoclonal antibody therapy of B-cell malignancy. Leuk Lymphoma 16:199–207
Wildman DE, Uddin M, Liu G, Grossman LI, Goodman M (2003) Implications of natural selection in shaping 99.4% nonsynonymous DNA identity between humans and chimpanzees: enlarging genus Homo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:7181–7188
Winkler U, Jensen M, Manzke O, Schulz H, Diehl V, Engert A (1999) Cytokine-release syndrome in patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and high lymphocyte counts after treatment with an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (rituximab, IDEC-C2B8). Blood 94:2217–2224
Witzig TE (2003) Efficacy and safety of 90Y ibritumomab tiuxetan (Zevalin) radioimmunotherapy for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Semin Oncol 30:11–16
Wolf H, Freimann U, Jung G (1994) Target cell induced T cell activation with bispecific antibodies: a new concept for tumor immunotherapy. Recent Results Cancer Res 135:185–195
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schlereth, B., Quadt, C., Dreier, T. et al. T-cell activation and B-cell depletion in chimpanzees treated with a bispecific anti-CD19/anti-CD3 single-chain antibody construct. Cancer Immunol Immunother 55, 503–514 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-005-0001-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-005-0001-1