Abstract
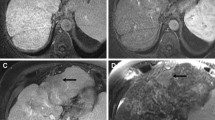
We describe ferumoxides-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging findings in a 60-year-old man with confluent hepatic fibrosis in advanced cirrhosis. The extension and internal structure of confluent fibrosis were well demonstrated with ferumoxides-enhanced proton-density spin-echo magnetic resonance images, showing a wedge-shaped area of high signal intensity corresponding to the extension of fibrosis and internal focal areas of low signal intensity, presumably corresponding to residual functioning liver parenchyma. This case suggests a potential utility of ferumoxides-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for characterizing this tumor-mimicking disorder.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 27 June 2000/Revision accepted: 18 October 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsuo, M., Kanematsu, M., Kondo, H. et al. Confluent hepatic fibrosis in cirrhosis: ferumoxides-enhanced MR imaging findings. Abdom Imaging 26, 146–148 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002610000181
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002610000181