Abstract
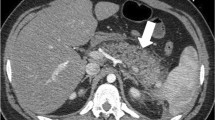
Background: Computed tomography (CT) is not always effective for demonstrating mild acute pancreatitis, and the intravenous administration of iodine contrast medium is harmful to the inflamed pancreas. The goal of this study was to evaluate the usefulness of nonenhanced magnetic resonance (MR) imaging for the depiction of mild acute pancreatitis.
Methods: We performed T1-weighted imaging with a short echo time, T2-weighted imaging, and MR cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) in 12 patients with mild acute pancreatitis. Nonenhanced CT and contrast-enhanced CT were always performed before the MR studies.
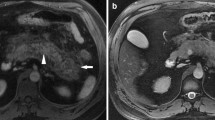
Results: T1- and T2-weighted MR images using a breath-hold or respiratory-triggered technique produced clearer images of the inflamed pancreas than did CT. Peripancreatic fat necrosis was shown by both methods. Although MRCP demonstrated no abnormalities of the pancreatic duct, it demonstrated stones in the gallbladder and common bile duct.
Conclusions: Nonenhanced MR imaging was superior to CT for depiction and confirmation of mild acute pancreatitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 8 February 2000/Revision accepted: 17 May 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amano, Y., Oishi, T., Takahashi, M. et al. Nonenhanced magnetic resonance imaging of mild acute pancreatitis. Abdom Imaging 26, 59–63 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002610000104
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002610000104