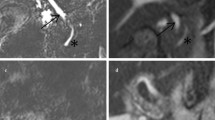
Abstract
Balanced steady state-free precession (b-SSFP) pulse sequences have a number of properties which can be useful in magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP), including short acquisition times, high signal-to-noise ratios, and T2/T1 contrast weighting. The utility and versatility of b-SSFP sequences for MRCP imaging are probably underappreciated, and this pictorial essay briefly discusses benefits and limitations of 2D and 3D b-SSFP techniques used in place of or in addition to conventional single-shot fast spin echo or 3D fast spin echo acquisitions and illustrates their appearance in several clinical cases.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wallner BK, Schumacher KA, Weidenmaier W, Friedrich JM (1991) Dilated biliary tract: evaluation with MR cholangiography with a T2-weighted contrast-enhanced fast sequence. Radiology 181:805–808
Morimoto K, Shimoi M, Shirakawa T, et al. (1992) Biliary obstruction: evaluation with three-dimensional MR cholangiography. Radiology 183:578–580
Miyazaki T, Yamashita Y, Tsuchigame T, et al. (1996) MR cholangiopancreatography using HASTE (half-Fourier acquisition single-shot turbo spin echo) sequences. AJR 166:1297–1303
Barish MA, Yucel EK, Soto JA, Chuttani R, Ferrucci JT (1995) MR cholangiopancreatography: efficacy of three-dimensional turbo spin-echo technique. AJR 165:295–300
Bilgin M, Shaikh F, Semelka RC, et al. (2009) Magnetic resonance imaging of gallbladder and biliary system. Top Magn Reson Imaging 20:31–42
Yeh BM, Liu PS, Soto JA, et al. (2009) MR imaging and CT of the biliary tract. Radiographics 29:1669–1688
Sandrasegaran K, Lin C, Akisik FM, Tann M (2010) State-of-the-art pancreatic MRI. AJR 195:42–53
Griffin N, Charles-Edwards G, Grant LA (2012) Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: the ABC of MRCP. Insights Imaging 3:11–21
Asbach P, Klessen C, Kroencke TJ, et al. (2005) Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography using a free-breathing T2-weighted turbo spin-echo sequence with navigator triggered prospective acquisition correction. Magn Reson Imaging 23:939–945
Choi JY, Lee JM, Lee JY, et al. (2008) Navigator-triggered isotropic three-dimensional magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography in the diagnosis of malignant biliary obstructions: comparison with direct cholangiography. J Magn Reson Imaging 27:94–101
Yoon LS, Catalano OA, Fritz S, et al. (2009) Another dimension in magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: comparison of 2- and 3-dimensional magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography for the evaluation of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. J Comput Assist Tomogr 33:363–368
Kinner S, Dechene A, Ladd SC, et al. (2010) Comparison of different MRCP techniques for the depiction of biliary complications after liver transplantation. Eur Radiol 20:1749–1756
Matsunaga K, Ogasawara G, Tsukano M, Iwadate Y, Inoue Y (2013) Usefulness of the navigator-echo triggering technique for free-breathing three-dimensional magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography. Magn Reson Imaging 31:396–400
Morita S, Ueno E, Suzuki K, et al. (2008) Navigator-triggered prospective acquisition correction (PACE) technique vs. conventional respiratory-triggered technique for free-breathing 3D MRCP: an initial prospective comparative study using healthy volunteers. J Magn Reson Imaging 28:673–677
Herborn CU, Vogt F, Lauenstein TC, et al. (2003) MRI of the liver: can true FISP replace HASTE? J Magn Reson Imaging 17:190–196
Morita S, Ueno E, Masukawa A, et al. (2009) Defining juxtapapillary diverticulum with 3D segmented trueFISP MRCP: comparison with conventional MRCP sequences with an oral negative contrast agent. Jpn J Radiol 27:423–429
Glockner JF, Saranathan M, Bayram E, Lee CU (2013) Breath-held MR cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) using a 3D dixon fat-water separated balanced steady state free precession sequence. Magn Reson Imaging 31(8):1263–1270
Watanabe Y, Nagayama M, Okumura A (2007) MR imaging of acute biliary disorders. Radiographics 27:477–495
Yoon JH, Cha SS, Han SS, Lee SJ, Kang MS (2006) Gallbladder adenomyomatosis: imaging findings. Abdom Imaging 31:555–563
Oikarinen H (2006) Diagnostic imaging of carcinomas of the gallbladder and the bile ducts. Acta Radiol 47:345–358
Lee CU, Glockner JF (2011) Vascular staging of renal and adrenal malignancies with a noncontrast enhanced steady state free precession technique. J Magn Reson Imaging 33:1406–1413
Elsayes KM, Oliveira EP, Narra VR, et al. (2006) MR and MRCP in the evaluation of primary sclerosing cholangitis: current applications and imaging findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr 30:398–404
Weber C, Kuhlencordt R, Grotelueschen R, et al. (2008) Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography in the diagnosis of primary sclerosing cholangitis. Endoscopy 40:739–745
Blechacz B, Komuta M, Roskams T, Gores GJ (2011) Clinical diagnosis and staging of cholangiocarcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 8:512–522
Masselli G, Gualdi G (2008) Hilar cholangiocarcinoma: MRI/MRCP in staging and treatment planning. Abdom Imaging 33:444–451
Chryssou E, Guthrie JA, Ward J, Robinson PJ (2010) Hilar cholangiocarcinoma: MR correlation with surgical and histological findings. Clin Radiol 65:781–788
Brancatelli G, Federle MP, Vilgrain V, et al. (2005) Fibropolycystic liver disease: CT and MR imaging findings. Radiographics 25:659–670
Kalb B, Sarmiento JM, Kooby DA, et al. (2009) MR imaging of cystic lesions of the pancreas. Radiographics 29:1749–1765
Vachiranubhap B, Kim YH, Balci NC, Semelka RC (2009) Magnetic resonance imaging of adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Top Magn Reson Imaging 20:3–9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glockner, J.F., Lee, C.U. Balanced steady state-free precession (b-SSFP) imaging for MRCP: techniques and applications. Abdom Imaging 39, 1309–1322 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-014-0153-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-014-0153-6