Abstract
Purpose
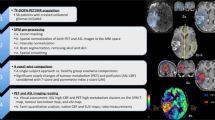
To compare the diagnostic information obtained with 6-[18F]-fluoro-l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (F-DOPA) PET and relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV) maps in recurrent or progressive glioma.
Methods
All patients with recurrent or progressive glioma referred for F-DOPA imaging at our institution between May 2010 and May 2014 were retrospectively included, provided that macroscopic disease was visible on conventional MRI images and that rCBV maps were available for comparison. The final analysis included 50 paired studies (44 patients). After image registration, automatic tumour segmentation of both sets of images was performed using the average signal in a large reference VOI including grey and white matter multiplied by 1.6. Tumour volumes identified by both modalities were compared and their spatial congruence calculated. The distances between F-DOPA uptake and rCBV hot spots, tumour-to-brain ratios (TBRs) and normalized histograms were also computed.
Results
On visual inspection, 49 of the 50 F-DOPA and 45 of the 50 rCBV studies were classified as positive. The tumour volume delineated using F-DOPA (F-DOPAvol 1.6) greatly exceeded that of rCBV maps (rCBVvol 1.6). The median F-DOPAvol 1.6 and rCBVvol 1.6 were 11.44 ml (range 0 – 220.95 ml) and 1.04 ml (range 0 – 26.30 ml), respectively (p < 0.00001). Overall, the median overlapping volume was 0.27 ml, resulting in a spatial congruence of 1.38 % (range 0 – 39.22 %). The mean hot spot distance was 27.17 mm (±16.92 mm). F-DOPA uptake TBR was significantly higher than rCBV TBR (1.76 ± 0.60 vs. 1.15 ± 0.52, respectively; p < 0.0001). The histogram analysis showed that F-DOPA provided better separation of tumour from background. In 6 of the 50 studies (12 %), however, physiological uptake in the striatum interfered with tumour delineation.
Conclusion
The information provided by F-DOPA PET and rCBV maps are substantially different. Image interpretation is easier and a larger tumour extent is identified on F-DOPA PET images than on rCBV maps. The clinical impact of such differences needs to be explored in future studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wen PY, Macdonald DR, Reardon DA, Cloughesy TF, Sorensen AG, Galanis E, et al. Updated response assessment criteria for high-grade gliomas: response assessment in neuro-oncology working group. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1963–72.
Yang I, Aghi MK. New advances that enable identification of glioblastoma recurrence. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2009;6:648–57.
Heiss WD, Raab P, Lanfermann H. Multimodality assessment of brain tumors and tumor recurrence. J Nucl Med. 2011;52:1585–600.
Langen KJ, Bröer S. Molecular transport mechanisms of radiolabeled amino acids for PET and SPECT. J Nucl Med. 2004;45:1435–6.
Arbizu J, Tejada S, Marti-Climent JM, Diez-Valle R, Prieto E, Quincoces G, et al. Quantitative volumetric analysis of gliomas with sequential MRI and 11C-methionine PET assessment: patterns of integration in therapy planning. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012;39:771–81.
Kracht LW, Miletic H, Busch S, Jacobs AH, Voges J, Hoevels M, et al. Delineation of brain tumor extent with [11C]L-methionine positron emission tomography: local comparison with stereotactic histopathology. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:7163–70.
Pauleit D, Floeth F, Hamacher K, Riemenschneider MJ, Reifenberger G, Müller HW, et al. O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine PET combined with MRI improves the diagnostic assessment of cerebral gliomas. Brain. 2005;128:678–87.
Pafundi DH, Laack NN, Youland RS, Parney IF, Lowe VJ, Giannini C, et al. Biopsy validation of 18F-DOPA PET and biodistribution in gliomas for neurosurgical planning and radiotherapy target delineation: results of a prospective pilot study. Neuro Oncol. 2013;15:1058–67.
Galldiks N, Stoffels G, Ruge MI, Rapp M, Sabel M, Reifenberger G, et al. Role of O-(2-18F-fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine PET as a diagnostic tool for detection of malignant progression in patients with low-grade glioma. J Nucl Med. 2013;54:2046–54.
Jansen NL, Suchorska B, Wenter V, Eigenbrod S, Schmid-Tannwald C, Zwergal A, et al. Dynamic 18F-FET PET in newly diagnosed astrocytic low-grade glioma identifies high-risk patients. J Nucl Med. 2014;55:198–203.
Galldiks N, Langen KJ, Holy R, Pinkawa M, Stoffels G, Nolte KW, et al. Assessment of treatment response in patients with glioblastoma using O-(2-18F-fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine PET in comparison to MRI. J Nucl Med. 2012;53:1048–57.
Harris RJ, Cloughesy TF, Pope WB, Nghiemphu PL, Lai A, Zaw T, et al. 18F-FDOPA and 18F-FLT positron emission tomography parametric response maps predict response in recurrent malignant gliomas treated with bevacizumab. Neuro Oncol. 2012;14:1079–89.
Galldiks N, Rapp M, Stoffels G, Fink GR, Shah NJ, Coenen HH, et al. Response assessment of bevacizumab in patients with recurrent malignant glioma using [18F]fluoroethyl-L-tyrosine PET in comparison to MRI. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013;40:22–33.
Pirotte BJ, Levivier M, Goldman S, Massager N, Wikler D, Dewitte O, et al. Positron emission tomography-guided volumetric resection of supratentorial high-grade gliomas: a survival analysis in 66 consecutive patients. Neurosurgery. 2009;64:471–81.
Nuutinen J, Sonninen P, Lehikoinen P, Sutinen E, Valavaara R, Eronen E, et al. Radiotherapy treatment planning and long-term follow-up with [(11)C]methionine PET in patients with low-grade astrocytoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000;48:43–52.
Piroth MD, Holy R, Pinkawa M, Stoffels G, Kaiser HJ, Galldiks N, et al. Prognostic impact of postoperative, pre-irradiation (18)F-fluoroethyl-l-tyrosine uptake in glioblastoma patients treated with radiochemotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2011;99:218–24.
Law M, Young RJ, Babb JS, Peccerelli N, Chheang S, Gruber ML, et al. Gliomas: predicting time to progression or survival with cerebral blood volume measurements at dynamic susceptibility-weighted contrast-enhanced perfusion MR imaging. Radiology. 2008;247:490–8.
Barajas Jr RF, Chang JS, Segal MR, Parsa AT, McDermott MW, Berger MS, et al. Differentiation of recurrent glioblastoma multiforme from radiation necrosis after external beam radiation therapy with dynamic susceptibility-weighted contrast-enhanced perfusion MR imaging. Radiology. 2009;253:486–96.
Hu LS, Eschbacher JM, Heiserman JE, Dueck AC, Shapiro WR, Liu S, et al. Reevaluating the imaging definition of tumor progression: perfusion MRI quantifies recurrent glioblastoma tumor fraction, pseudoprogression, and radiation necrosis to predict survival. Neuro Oncol. 2012;14:919–30.
Aronen HJ, Gazit IE, Louis DN, Buchbinder BR, Pardo FS, Weisskoff RM, et al. Cerebral blood volume maps of gliomas: comparison with tumor grade and histologic findings. Radiology. 1994;191:41–51.
Barajas Jr RF, Phillips JJ, Parvataneni R, Molinaro A, Essock-Burns E, Bourne G, et al. Regional variation in histopathologic features of tumor specimens from treatment-naive glioblastoma correlates with anatomic and physiologic MR Imaging. Neuro Oncol. 2012;14:942–54.
Sadeghi N, Salmon I, Decaestecker C, Levivier M, Metens T, Wikler D, et al. Stereotactic comparison among cerebral blood volume, methionine uptake, and histopathology in brain glioma. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28:455–61.
Dandois V, Rommel D, Renard L, Jamart J, Cosnard G. Substitution of 11C-methionine PET by perfusion MRI during the follow-up of treated high-grade gliomas: preliminary results in clinical practice. J Neuroradiol. 2010;37:89–97.
Kim YH, Oh SW, Lim YJ, Park CK, Lee SH, Kang KW, et al. Differentiating radiation necrosis from tumor recurrence in high-grade gliomas: assessing the efficacy of 18F-FDG PET, 11C-methionine PET and perfusion MRI. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2010;112:758–65.
Tietze A, Boldsen JK, Mouridsen K, Ribe L, Dyve S, Cortnum S, et al. Spatial distribution of malignant tissue in gliomas: correlations of 11C-L-methionine positron emission tomography and perfusion- and diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Acta Radiol. 2014. doi:10.1177/0284185114550020.
Filss CP, Galldiks N, Stoffels G, Sabel M, Wittsack HJ, Turowski B, et al. Comparison of 18F-FET PET and perfusion-weighted MR imaging: a PET/MR imaging hybrid study in patients with brain tumors. J Nucl Med. 2014;55:540–5.
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, et al. The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2007;114:97–109.
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–96.
Wittsack HJ, Ritzl A, Mödder U. User friendly analysis of MR investigations of the cerebral perfusion: windows(R)-based image processing. Rofo. 2002;174:742–6. Article in German.
Kratochwil C, Combs SE, Leotta K, Afshar-Oromieh A, Rieken S, Debus J, et al. Intra-individual comparison of 18F-FET and 18F-DOPA in PET imaging of recurrent brain tumors. Neuro Oncol. 2014;16:434–40.
Lapa C, Linsenmann T, Monoranu CM, Samnick S, Buck AK, Bluemel C, et al. Comparison of the amino acid tracers 18F-FET and 18F-DOPA in high-grade glioma patients. J Nucl Med. 2014;55:1611–6.
Fueger BJ, Czernin J, Cloughesy T, Silverman DH, Geist CL, Walter MA, et al. Correlation of 6-18F-fluoro-L-dopa PET uptake with proliferation and tumor grade in newly diagnosed and recurrent gliomas. J Nucl Med. 2010;51:1532–8.
Hutterer M, Nowosielski M, Putzer D, Jansen NL, Seiz M, Schocke M, et al. [18F]-fluoro-ethyl-L-tyrosine PET: a valuable diagnostic tool in neuro-oncology, but not all that glitters is glioma. Neuro Oncol. 2013;15:341–51.
Berntsson SG, Falk A, Savitcheva I, Godau A, Zetterling M, Hesselager G, et al. Perfusion and diffusion MRI combined with 11C-methionine PET in the preoperative evaluation of suspected adult low-grade gliomas. J Neurooncol. 2013;114:241–9.
Becherer A, Karanikas G, Szabó M, Zettinig G, Asenbaum S, Marosi C, et al. Brain tumour imaging with PET: a comparison between [18F]fluorodopa and [11C]methionine. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2003;30:1561–7.
Schiepers C, Chen W, Cloughesy T, Dahlbom M, Huang SC. 18F-FDOPA kinetics in brain tumors. J Nucl Med. 2007;48:1651–61.
Compliance with Ethical Standards
Conflicts of interest
None.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the study were in accordance with the standards of the institutional ethical committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Francesco Cicone and Christian P. Filss contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cicone, F., Filss, C.P., Minniti, G. et al. Volumetric assessment of recurrent or progressive gliomas: comparison between F-DOPA PET and perfusion-weighted MRI. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 42, 905–915 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-015-3018-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-015-3018-5